Abstract
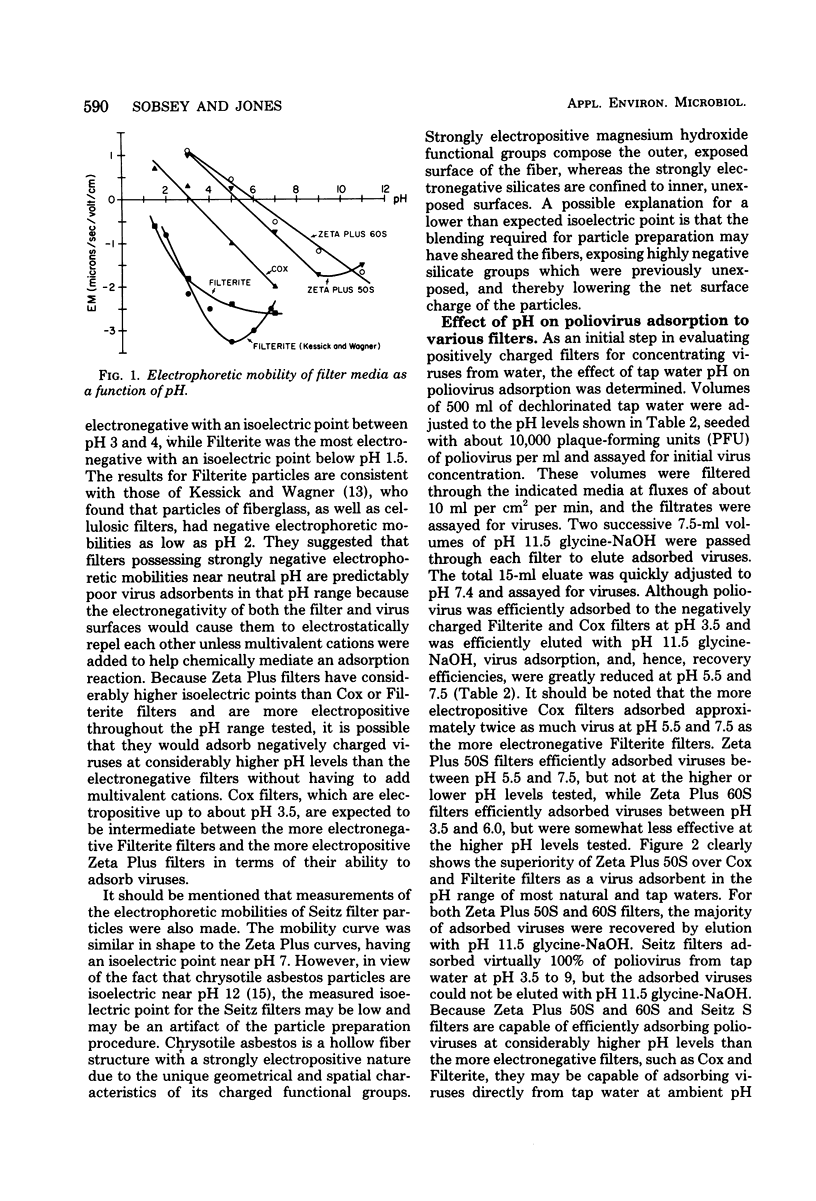
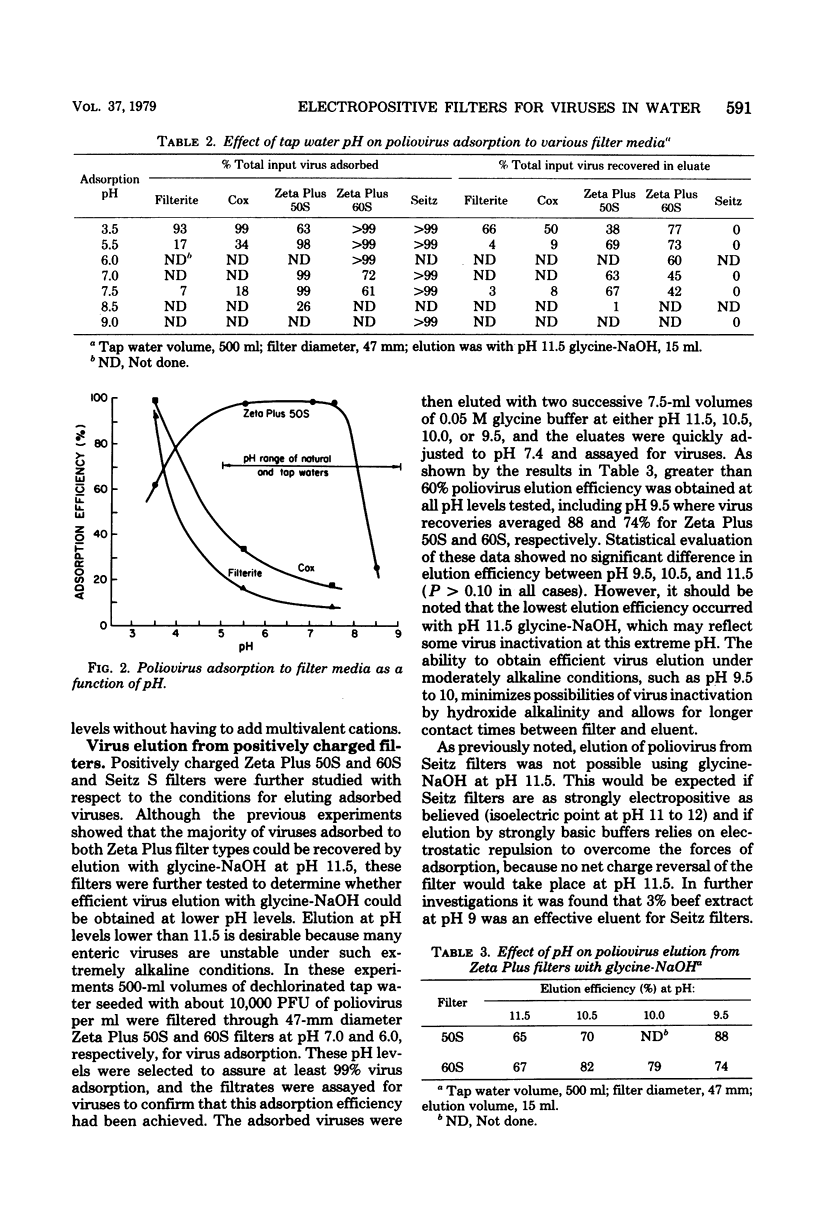
Microporous filters that are more electropositive than the negatively charged filters currently used for virus concentrations from water by filter adsorption-elution methods were evaluated for poliovirus recovery from tap water. Zeta Plus filters composed of diatomaceous earth-cellulose-"charge-modified" resin mixtures and having a net positive charge of up to pH 5 to 6 efficiently adsorbed poliovirus from tap water at ambient pH levels 7.0 to 7.5 without added multivalent cation salts. The adsorbed virus were eluted with glycine-NaOH, pH 9.5 to 11.5. Electropositive asbestos-cellulose filters efficiently adsorbed poliovirus from tap water without added multivalent cation salts between pH 3.5 and 9.0, and the absorbed viruses could be eluted with 3% beef extract, pH 9, but not with pH 9.5 to 11.5 glycine-NaOH. Under water quality conditions in which poliovirus recoveries from large volumes of water were less than 5% with conventional negatively charged filters and standard methods, recoveries with Zeta Plus filters averaged 64 and 22.5% for one- and two-stage concentration procedures, respectively. Electropositive filters appear to offer distinct advantages over conventional negatively charged filters for concentrating enteric viruses from water, and their behavior tends to confirm the importance of electrostatic forces in virus recovery from water by microporous filter adsorption-elution methods.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farrah S. R., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of viruses from large volumes of tap water using pleated membrane filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):221–226. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.221-226.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R., Sharp D. G. Aggregation of poliovirus and reovirus by dilution in water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.159-167.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Farrah S. R., Goyal S. M., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses from large volumes of tap water, treated sewage, and seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):540–548. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.540-548.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. F., Jr, Jakubowski W., Akin E. W., Clarke N. A. Detection of virus in water: sensitivity of the tentative standard method for drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):254–261. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.254-261.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski W., Hill W. F., Jr, Clarke N. A. Comparative study of four microporous filters for concentrating viruses from drinking water. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jul;30(1):58–65. doi: 10.1128/am.30.1.58-65.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenelson E., Fattal B., Hostovesky T. Organic flocculation: an efficient second-step concentration method for the detection of viruses in tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):638–639. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.638-639.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Carrick R. J., Jensen H. R. Improved methods for detecting enteric viruses in oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):121–128. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.121-128.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Wallis C., Henderson M., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses from large volumes of water. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):529–534. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.529-534.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



