Abstract
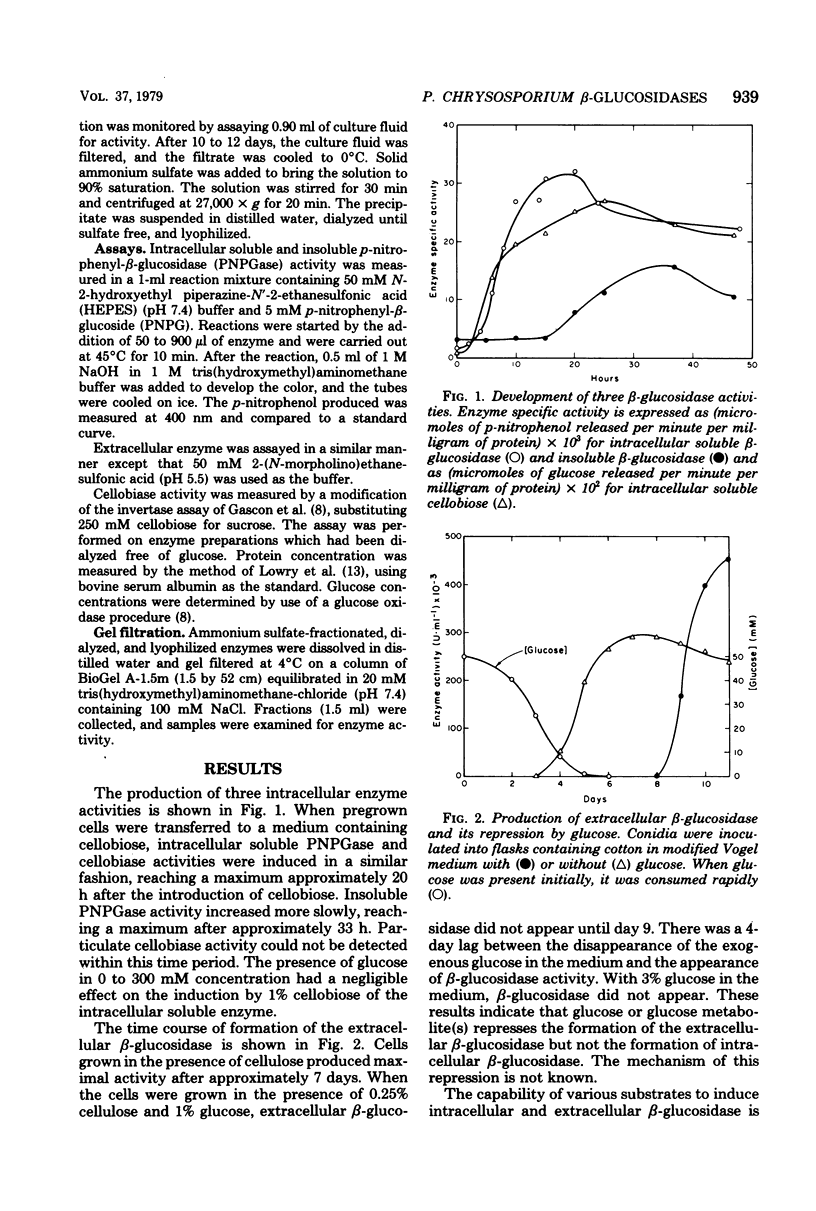
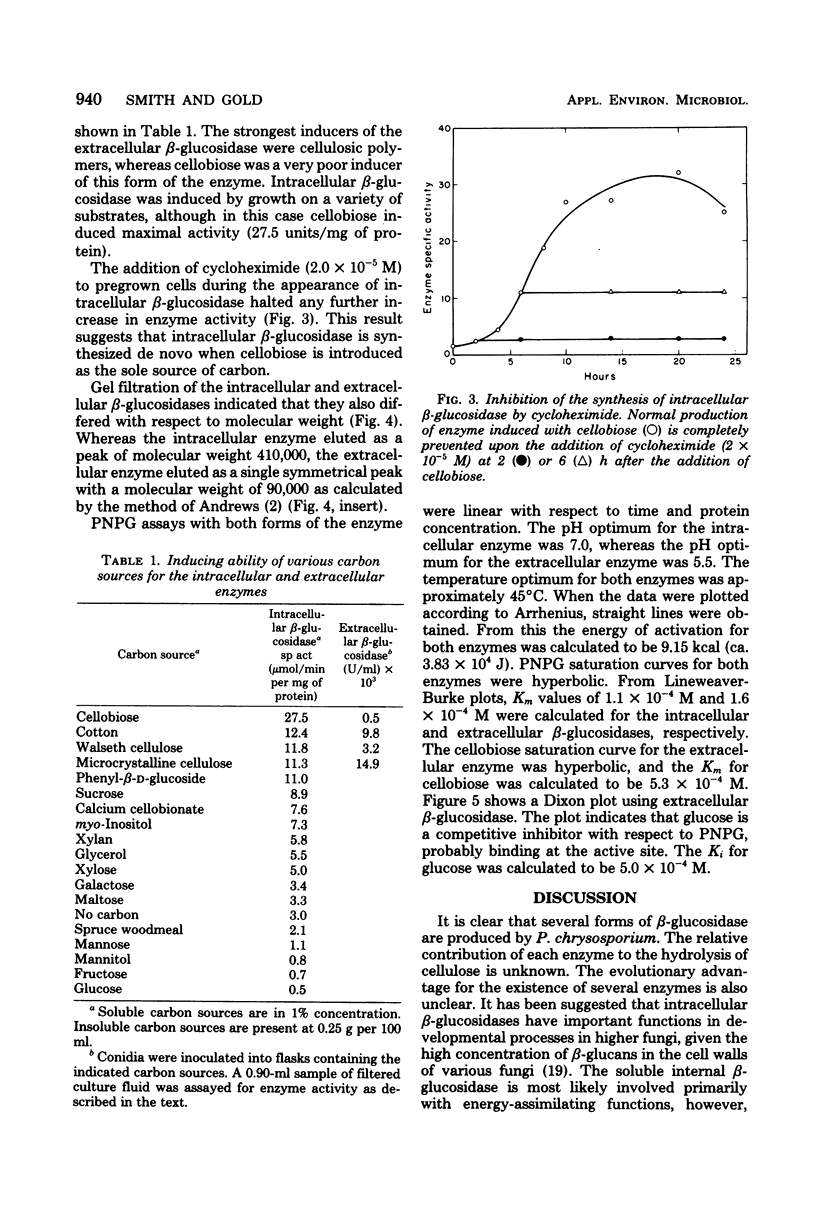
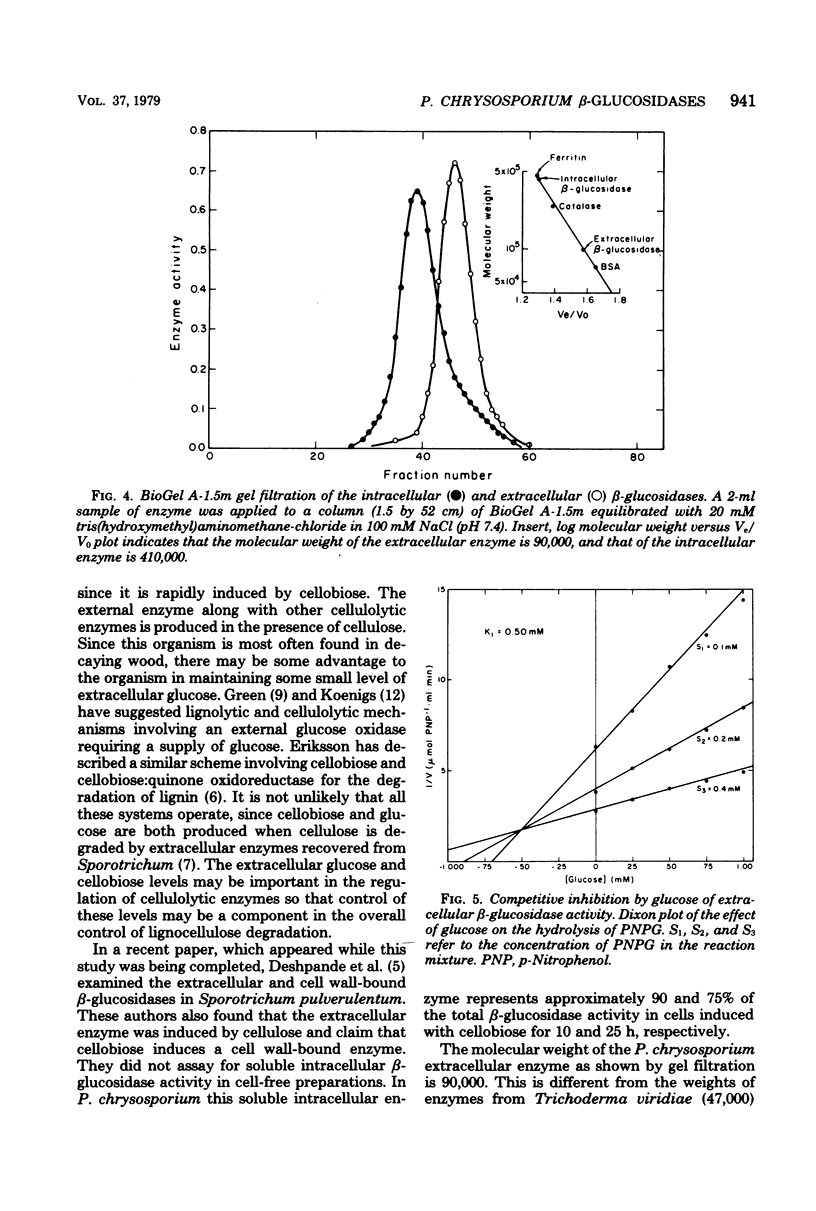
Phanerochaete chrysosporium produces intracellular soluble and particulate β-glucosidases and an extracellular β-glucosidase. The extracellular enzyme is induced by cellulose but repressed in the presence of glucose. The molecular weight of this enzyme is 90,000. The Km for p-nitrophenyl-β-glucoside is 1.6 × 10−4 M; the Ki for glucose, a competitive inhibitor, is 5.0 × 10−4 M. The Km for cellobiose is 5.3 × 10−4 M. The intracellular soluble enzyme is induced by cellobiose; this induction is prevented by cycloheximide. The presence of 300 mM glucose in the medium, however, had no effect on induction. The Km for p-nitrophenyl-β-glucoside is 1.1 × 10−4 M. The molecular weight of this enzyme is ∼410,000. Both enzymes have an optimal temperature of 45°C and an Eact of 9.15 kcal (ca. 3.83 × 104 J). The pH optima, however, were ∼7.0 and 5.5 for the intracellular and extracellular enzymes, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berghem L. E., Pettersson L. G. The mechanism of enzymatic cellulose degradation. Isolation and some properties of a beta-glucosidase from Trichoderma viride. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 15;46(2):295–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande V., Eriksson K. E., Pettersson B. Production , purification and partial characterization of 1,4-beta-glucosidase enzymes from Sporotrichum pulverulentum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 15;90(1):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson K. E., Rzedowski W. Extracellualr enzyme system utilized by the fungus Chrysosporium lignorum for the breakdown of cellulose. I. Studies on the enzyme production. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):683–688. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascón S., Lampen J. O. Purification of the internal invertase of yeast. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1567–1572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. R. Significance of glucose oxidase in lignin degradation. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):78–80. doi: 10.1038/268078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Connors W. J., Bleam R. D., Hackett W. F., Zeikus J. G. Preparation and microbial decomposition of synthetic [14C]ligins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2515–2519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenigs J. W. Hydrogen peroxide and iron: a microbial cellulolytic system? Biotechnol Bioeng Symp. 1975;(5):151–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHADEVAN P. R., EBERHART B. THE BETA-GLUCOSIDASE SYSTEM OF NEUROSPORA CRASSA. II. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF ARYL BETA-GLUCOSIDASE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Oct;108:22–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingle M., Halvorson H. O. Biochemical and genetic characterization of -glucosidase mutants in Saccharomyces lactis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):196–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.196-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. W., Niederpruem D. J. Control of beta-glucosidases in schizophyllum commune. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Aug;13(8):1009–1020. doi: 10.1139/m67-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



