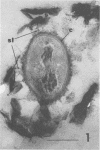
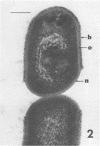
Abstract
Pure cultures of Arthrobacter globiformis and four fresh soil isolates were incubated individually in autoclaved soil, in both the presence and absence of glucose. These bacteria grew in the soil and, except for A. globiformis, eventually attached firmly to the soil solids. Firmly attached cells were defined as those which could not be separated from the soil solids by blending combined with a series of low-speed centrifugal washings. The attachment attained by the soil isolates appeared to duplicate that of the overall bacterial population that resides naturally in unaltered, unamended soil. Cell attachment in the autoclaved-soil system was accelerated slightly by glucose, but, except for one soil isolate, several months of incubation were still required before firm attachment was complete. Electron microscopy indicated that all attached cells produced extracellular polysaccharide slimes in the autoclaved soil and that these materials appeared to connect the cells to surrounding pieces of soil debris. The actual role of polysaccharides in attachment was not clear, however, because at least one of these organisms possessed extracellular slime during the long period in which it had not yet attached to the soil.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. E. Ultrastructure of rumen bacterial attachment to forage cell walls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):562–568. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.562-568.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae H. C., Casida L. E., Jr Responses of indigenous microorganisms to soil incubation as viewed by transmission electron microscopy of cell thin sections. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1462–1473. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1462-1473.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae H. C., Cota-Robles E. H., Casida L. E. Microflora of soil as viewed by transmission electron microscopy. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):637–648. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.637-648.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill D. L., Casida L. E., Jr Microflora of soil as viewed by freeze-etching. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1319–1327. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1319-1327.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill D. L., Labeda D. P., Casida L. E., Jr Simplified procedures for releasing and concentrating microorganisms from soil for transmission electron microscopy viewing as thin-sectioned and frozen-etched preparations. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):252–262. doi: 10.1139/m75-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill D. L., Rucinsky T. E., Casida L. E., Jr Release of microorganisms from soil with respect to transmission electron microscopy viewing and plate counts. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1977;43(1):73–87. doi: 10.1007/BF02316212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagle G. D., Pfister R. M., Vela G. R. Improved staining of extracellular polymer for electron microscopy: examination of Azotobacter, Zoogloea, Leuconostoc, and Bacillus. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):477–487. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.477-487.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Hironaka R., Jones G. A., Nicas T., Costerton J. W. Frothy feedlot bloat in cattle: production of extracellular polysaccharides and development of viscosity in cultures of Streptococcus bovis. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Apr;22(4):450–459. doi: 10.1139/m76-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. J., Dimmick I. Soil Bacteria Similar in Morphology to Mycobacterium and Corynebacterium. J Bacteriol. 1947 Sep;54(3):291–303. doi: 10.1128/jb.54.3.291-303.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglesong M. A., Walker D. H., Jr, Puffer J. S., Markovetz A. J. Ultrastructal morphology of some prokaryotic microorganisms associated with the hindgut of cockroaches. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):336–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.336-345.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim B. Extracellular polysaccharides and microbial plaque. Int Dent J. 1970 Dec;20(4):657–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. W., Sieburth J. M. In situ morphology of nitrifying-like bacteria in aquaculture systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):423–432. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.423-432.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C., Cruickshank R. H., Bushby H. V. The orientation of certain root-nodule bacteria at interfaces, including legume root-hair surfaces. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Nov;91(1):198–200. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-1-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C. Interaction between colloidal montmorillonite and cells of Rhizobium species with different inogenic surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 1;156(1):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C., Stout R., Mitchell R. Selective sorption of bacteria from seawater. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):1413–1416. doi: 10.1139/m71-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubentschik L., Roisin M. B., Bieljansky F. M. Adsorption of Bacteria in Salt Lakes. J Bacteriol. 1936 Jul;32(1):11–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.1.11-31.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro T., Stotzky G. Sorption between microorganisms and clay minerals as determined by the electrical sensing zone particle analyser. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):299–307. doi: 10.1139/m68-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobell C. E. The Effect of Solid Surfaces upon Bacterial Activity. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):39–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.39-56.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]