Abstract
A method for the quantitative analysis of Penicillium roqueforti toxin using a high-performance liquid chromatography system is proposed.
Full text
PDF
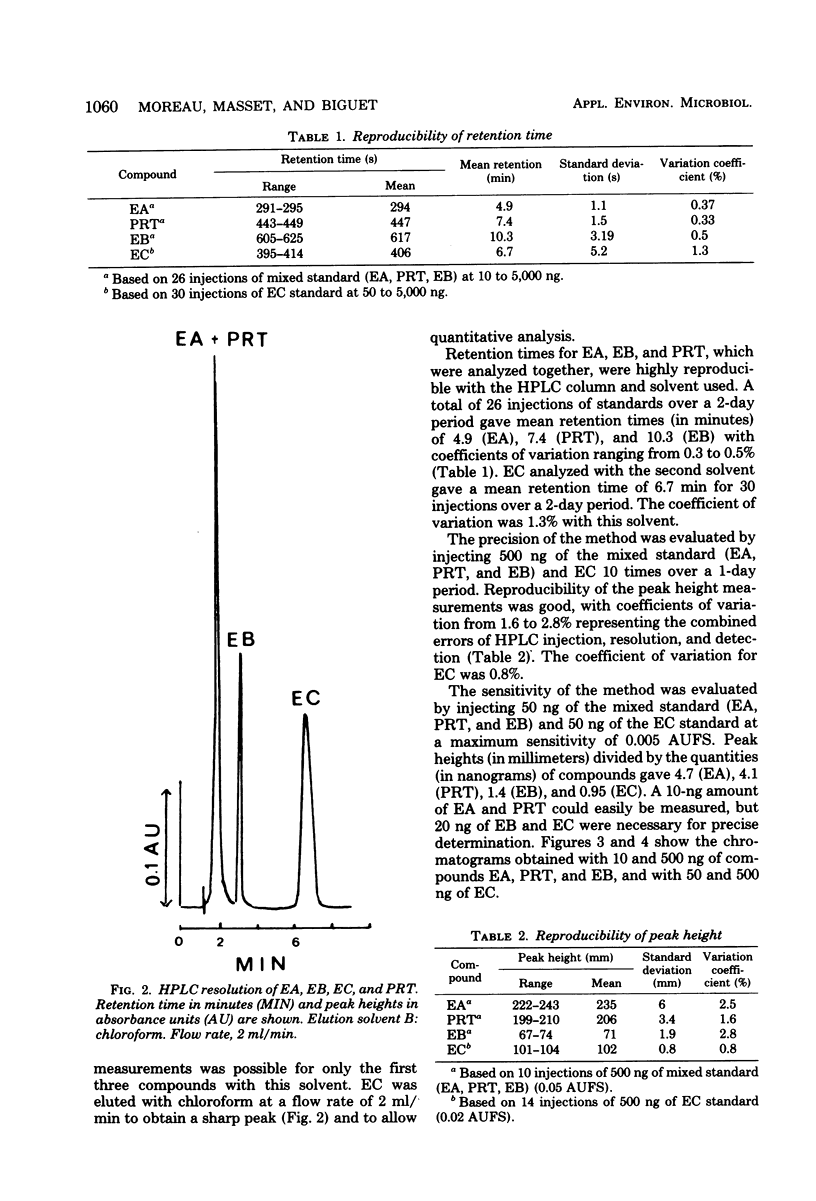
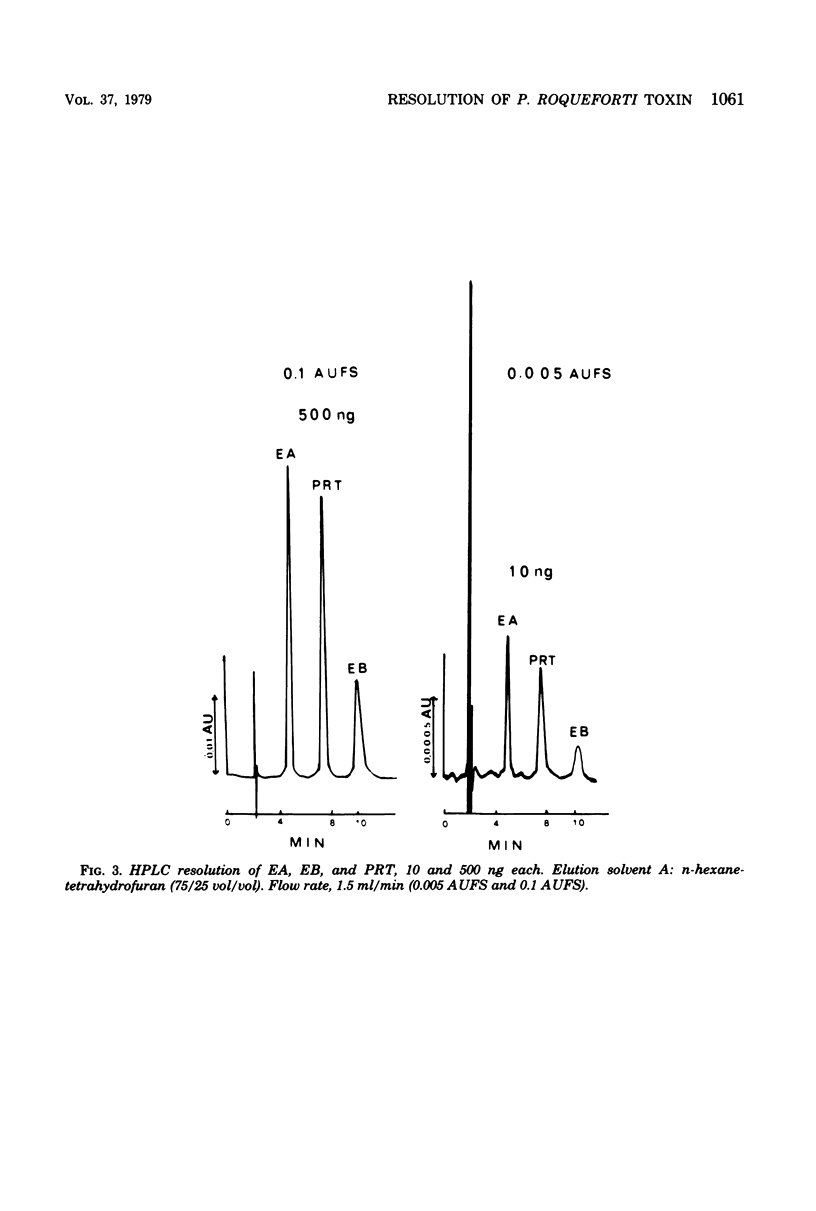
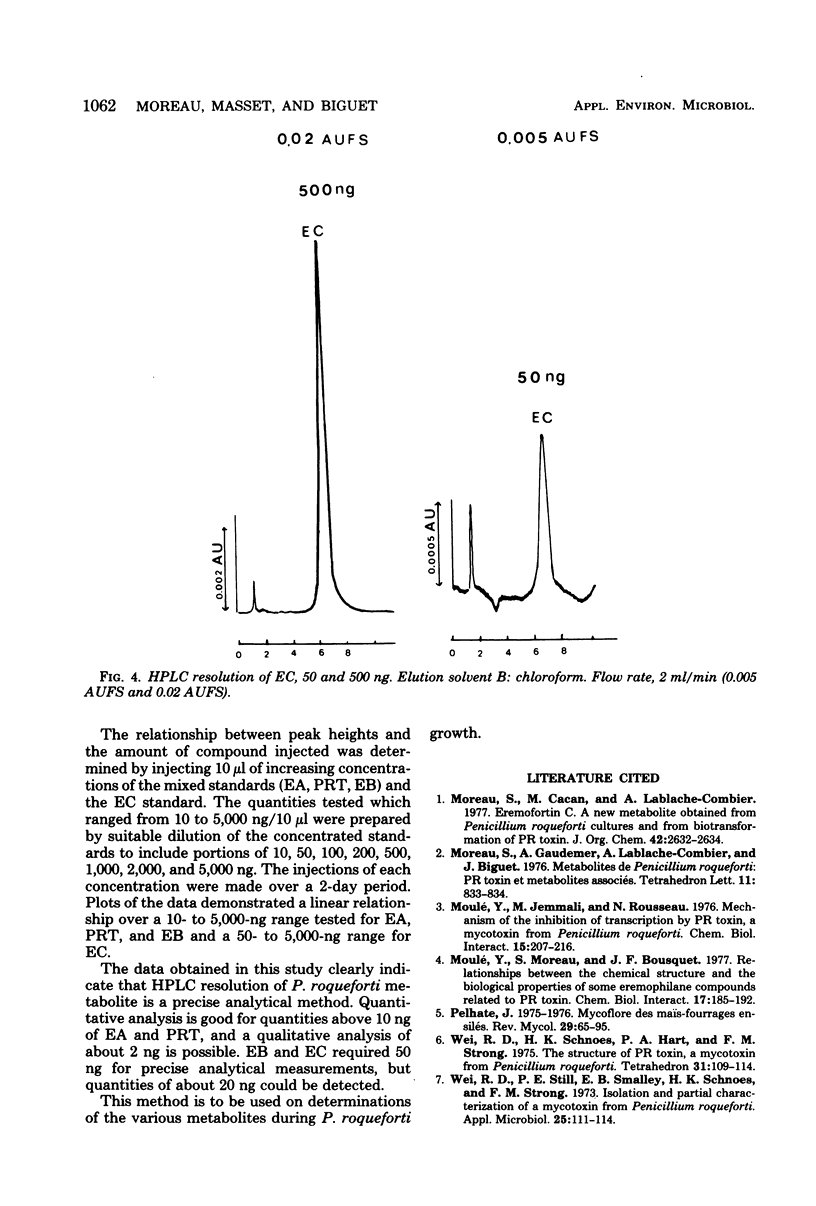
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Moreau S., Cacan M. Eremofortin C.A new metabolite obtained from penicillium roqueforti cultures and from biotransformation of PR toxin. J Org Chem. 1977 Jul 22;42(15):2632–2634. doi: 10.1021/jo00435a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulé Y., Jemmali M., Rousseau N. Mechanism of the inhibition of transcription by PR toxin, a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti. Chem Biol Interact. 1976 Aug;14(3-4):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(76)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulé Y., Moreau S., Bousquet J. F. Relationships between the chemical structure and the biological properties of some eremophilane compounds related to PR toxin. Chem Biol Interact. 1977 May;17(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(77)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei R. D., Still P. E., Smalley E. B., Schnoes H. K., Strong F. M. Isolation and partial characterization of a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):111–114. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.111-114.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


