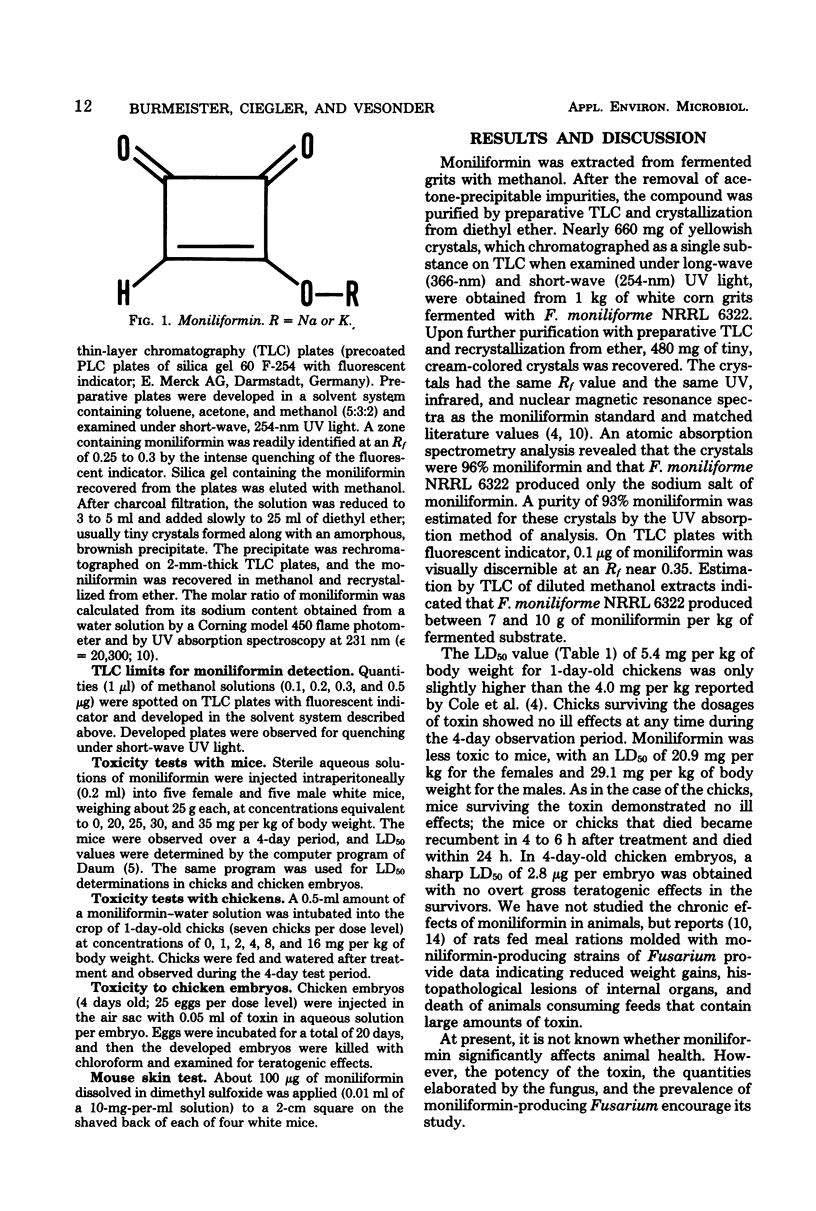
Abstract
Fusarium moniliforme NRRL 6322 produced about 600 mg of recoverable moniliformin, a mycotoxic metabolite, per kg of corn grit medium. The moniliformin was extracted from the grits with methanol, purified by preparative thin-layer chromatography, and crystallized from ether. The 50% lethal dose for chicken embryos was 2.8 microgram per egg. For 1-day-old chicks dosed with moniliformin by crop intubation and for female and male mice injected intraperitoneally, the 50% lethal doses were 5.4, 20.9, and 29.1 mg per kg of body weight, respectively. The toxin did not cause a reaction on mouse skin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole R. J., Kirksey J. W., Cutler H. G., Doupnik B. L., Peckham J. C. Toxin from Fusarium moniliforme: Effects on Plants and Animals. Science. 1973 Mar 30;179(4080):1324–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4080.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joffe A. Z., Palti J., Arbel-Sherman R. Fusarium moniliforme Sheld. in Israel (Gibberella fujikuroi (Saw.) Wollenw.). Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1973 Jul 5;50(2):85–107. doi: 10.1007/BF02049949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellerman T. S., Marasas W. F., Pienaar J. G., Naudé T. W. A mycotoxicosis of equidae caused by Fusarium moniliforme sheldon. A preliminary communication. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1972 Dec;39(4):205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriek N. P., Marasas W. F., Steyn P. S., van Rensburg S. J., Steyn M. Toxicity of a moniliformin-producing strain of Fusarium moniliforme var. subglutinans isolated from maize. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1977 Dec;15(6):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0015-6264(77)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabie C. J., Lübben A., Louw A. I., Rathbone E. B., Steyn P. S., Vleggaar R. Moniliformin, a mycotoxin from Fusarium fusarioides. J Agric Food Chem. 1978 Mar-Apr;26(2):375–379. doi: 10.1021/jf60216a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharby T. F., Templeton G. E., Beasley J. N., Stephenson E. L. Toxicity resulting from feeding experimentally molded corn to broiler chicks. Poult Sci. 1973 May;52(3):1007–1014. doi: 10.3382/ps.0521007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer J. P., Clardy J., Cole R. J., Kirksey J. W., Hill R. K., Carlson M. R., Isidor J. L. Structure and synthesis of moniliformin, a novel cyclobutane microbial toxin. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Apr 3;96(7):2267–2268. doi: 10.1021/ja00814a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Ishikawa Y., Nakajima M., Sakai K., Ishii K. Toxicological approaches to the metabolites of Fusaria. I. Screening of toxic strains. Jpn J Exp Med. 1971 Aug;41(4):257–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Sato N., Ishii K., Sakai K., Tsunoda H. Biological and chemical detection of trichothecene mycotoxins of Fusarium species. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):699–704. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.699-704.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. J., Maronpot R. R. Causative fungus agent of leucoencephalomalacia in equine animals. Vet Rec. 1971 May 8;88(19):484–486. doi: 10.1136/vr.88.19.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



