Abstract
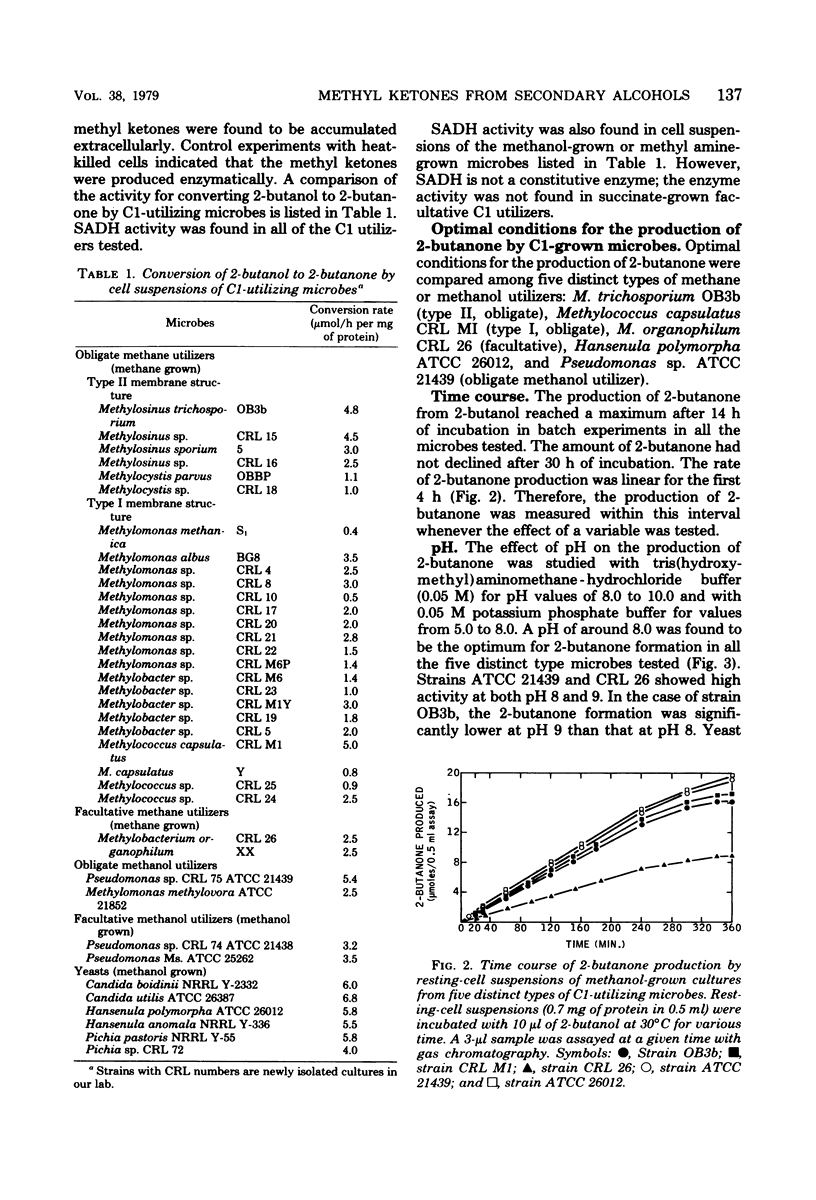
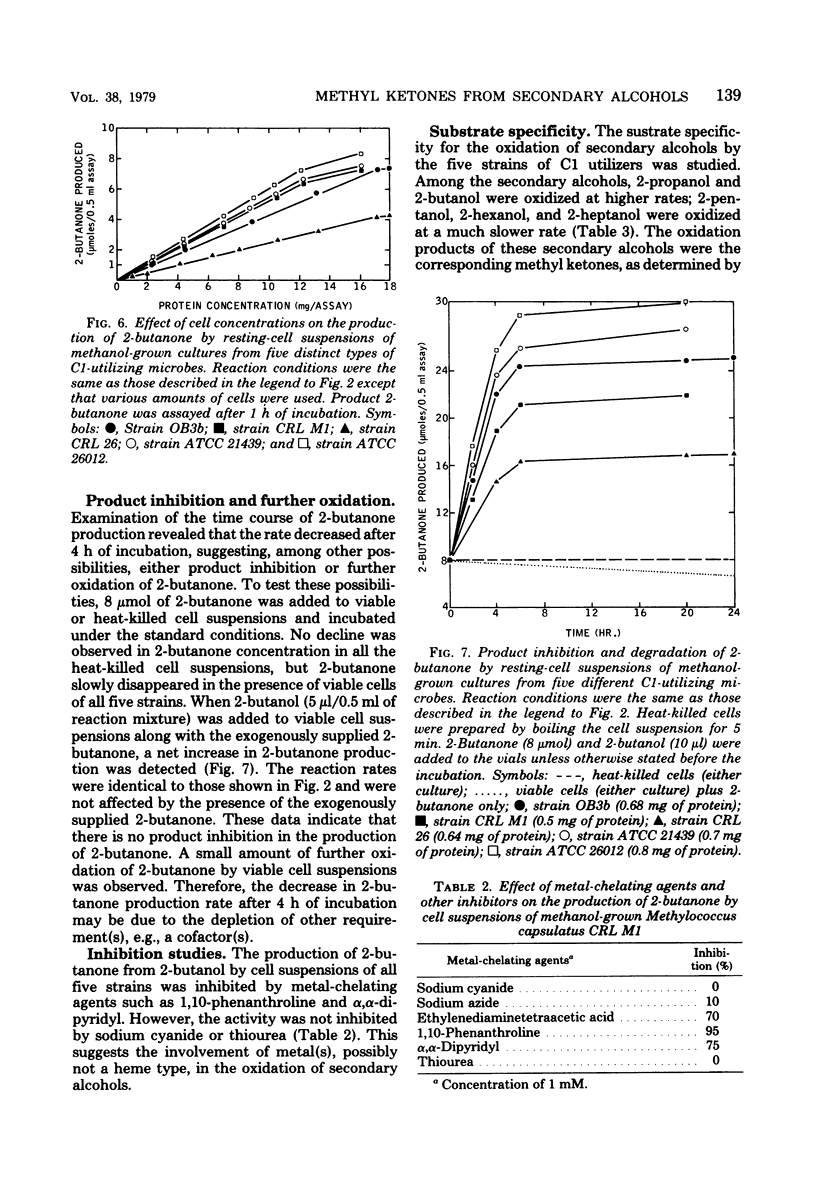
Cultures of methane- or methanol-utilizing microbes, including obligate (both types I and II) and facultative methylotrophic bacteria, obligate methanol utilizers, and methanol-grown yeasts were isolated from lake water of Warinanco Park, Linden, N.J., and lake and soil samples of Bayway Refinery, Linden, N.J. Resting-cell suspensions of these, and of other known C1-utilizing microbes, oxidized secondary alcohols to their corresponding methyl ketones. The product methyl ketones accumulated extracellularly. Succinate-grown cells of facultative methylotrophs did not oxidize secondary alcohols. Among the secondary alcohols, 2-butanol was oxidized at the highest rate. The optimal conditions for in vivo methyl ketone formation were compared among five different types of C1-utilizing microbes. Some enzymatic degradation of 2-butanone was observed. The product, 2-butanone, did not inhibit the oxidation of 2-butanol. The rate of the 2-butanone production was linear for the first 4 h of incubation for all five cultures tested. A yeast culture had the highest production rate. The optimum temperature for the production of 2-butanone was 35°C for all the bacteria tested. The yeast culture had a higher temperature optimum (40°C), and there was a reasonably high 2-butanone production rate even at 45°C. Metal-chelating agents inhibit the production of 2-butanone, suggesting the involvement of metal(s) in the oxidation of secondary alcohols. Secondary alcohol dehydrogenase activity was found in the cell-free soluble extract of sonically disrupted cells. The cell-free system requires a cofactor, specifically nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, for its activity. This is the first report of a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent, secondary alcohol-specific enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony C., Zatman L. J. The microbial oxidation of methanol. Purification and properties of the alcohol dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas sp. M27. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):953–959. doi: 10.1042/bj1040953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellion E., Wu G. T. Alcohol dehydrogenases from a facultative methylotrophic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):251–258. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.251-258.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Stirling D. I., Dalton H. The soluble methane mono-oxygenase of Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath). Its ability to oxygenate n-alkanes, n-alkenes, ethers, and alicyclic, aromatic and heterocyclic compounds. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):395–402. doi: 10.1042/bj1650395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Davis R. H. A methane-dependent coccus, with notes on classification and nomenclature of obligate, methane-utilizing bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1924–1931. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1924-1931.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou C. T., Patel R. N., Laskin A. I., Barnabe N., Marczak I. Identification and purification of a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent secondary alcohol dehydrogenase from C1-utilizing microbes. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEADBETTER E. R., FOSTER J. W. Bacterial oxidation of gaseous alkanes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1960;35:92–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00425597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUKINS H. B., FOSTER J. W. METHYL KETONE METABOLISM IN HYDROCARBON-UTILIZING MYCOBACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1074–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1074-1087.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta R. J. Pyridine nucleotide-linked oxidation of methanol in methanol-assimilating yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1165–1167. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1165-1167.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehaus W. G., Jr, Frielle T., Kingsley E. A., Jr Purification and characterization of a secondary alcohol dehydrogenase from a pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.177-183.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. N., Felix A. Microbial oxidation of methane and methanol: crystallization and properties of methanol dehydrogenase from Methylosinus sporium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):413–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.413-424.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. N., Hou C. T., Felix A. Microbial oxidation of methane and methanol: crystallization of methanol dehydrogenase and properties of holo- and apomethanol dehydrogenase from Methylomonas methanica. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):641–649. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.641-649.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittenbury R., Phillips K. C., Wilkinson J. F. Enrichment, isolation and some properties of methane-utilizing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 May;61(2):205–218. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



