Abstract
Extreme halophilic bacteria were isolated from the ocean off the coast of Spain. All were gram-negative cocci. One isolate was compared to Halococcus sp. NCMB 757 and was found to have similar characteristics.
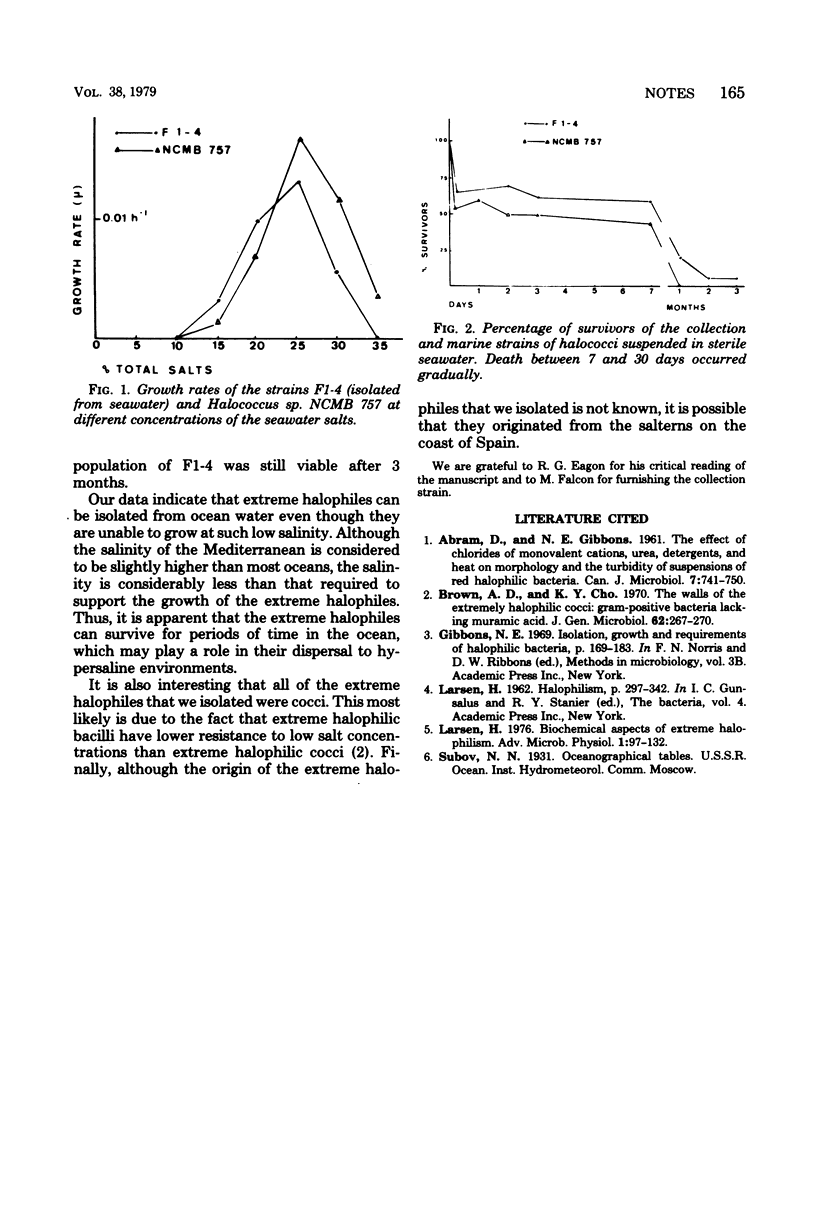
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAM D., GIBBONS N. E. The effect of chlorides of monovalent cations, urea, detergents, and heat on morphology and the turbidity of suspensions of red halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Oct;7:741–750. doi: 10.1139/m61-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D., Cho K. Y. The walls of the extremely halophilic cocci: gram-positive bacteria lacking muramic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Aug;62(2):267–270. doi: 10.1099/00221287-62-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


