Abstract
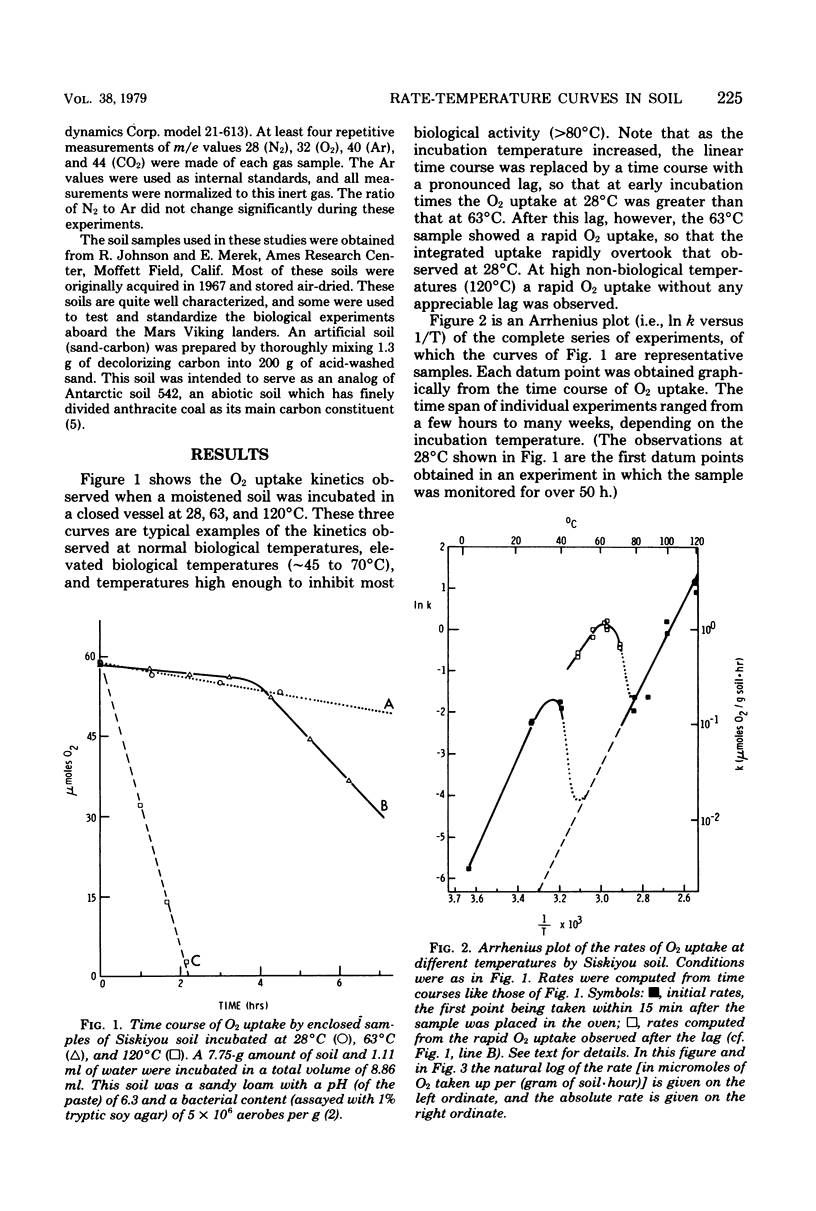
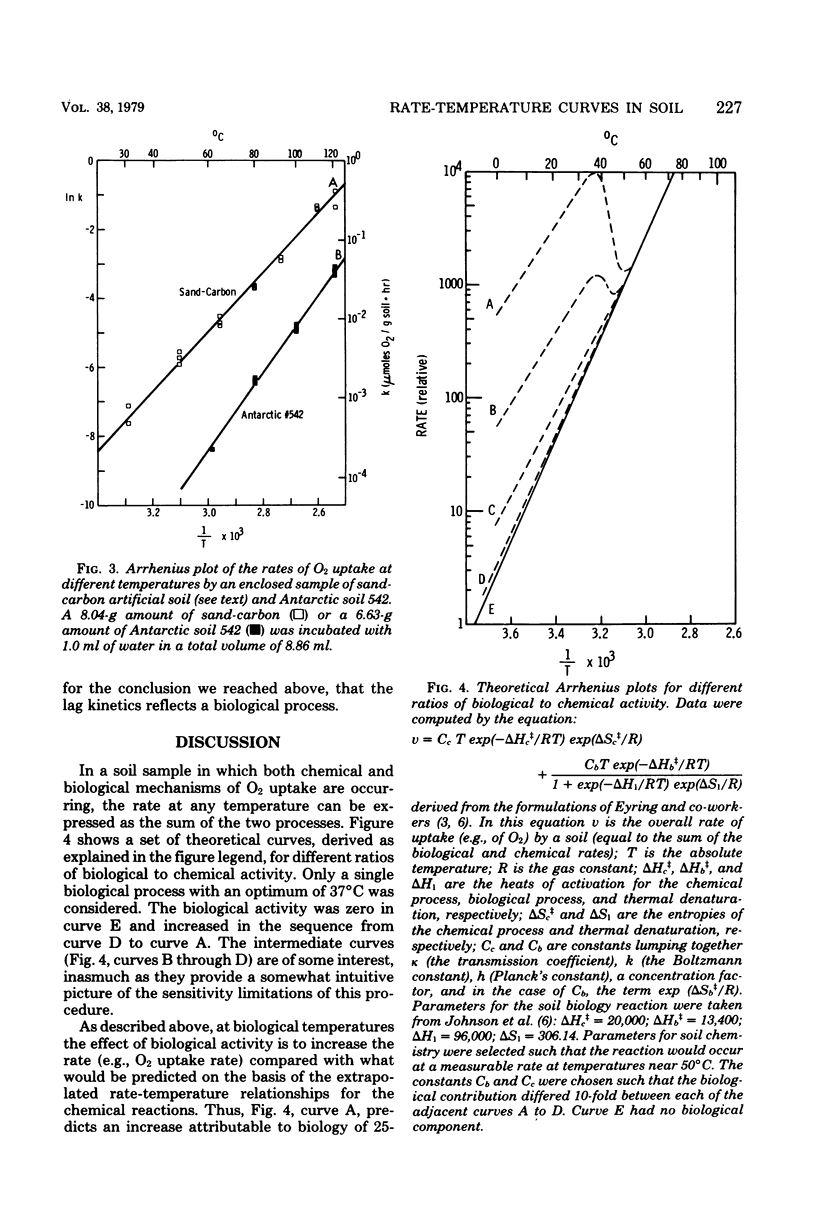
Experiments are described in which we used a mass spectrometer to monitor O2 uptake of enclosed soil samples as a function of temperature. We found that an Arrhenius plot of the rate of O2 uptake showed pronounced local maxima attributable to biological activity, whereas similar plots of rates obtained with abiotic soils yielded straight lines. This procedure thus provides a basis for distinguishing biological from chemical activity for reactions, such as O2 uptake, that can occur via either biological or chemical pathways.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Horowitz N. H., Bauman A. J., Cameron R. E., Geiger P. J., Hubbard J. S., Shulman G. P., Simmonds P. G., Westberg K. Sterile soil from Antarctica: organic analysis. Science. 1969 May 30;164(3883):1054–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3883.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmer R., Kok B. A unified procedure for the detection of life on Mars. Science. 1971 Oct 15;174(4006):233–239. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4006.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmer R., Kok B. An integrated multi-purpose biology instrument utilizing a single detector, the mass spectrometer. Life Sci Space Res. 1972;10:211–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


