Abstract
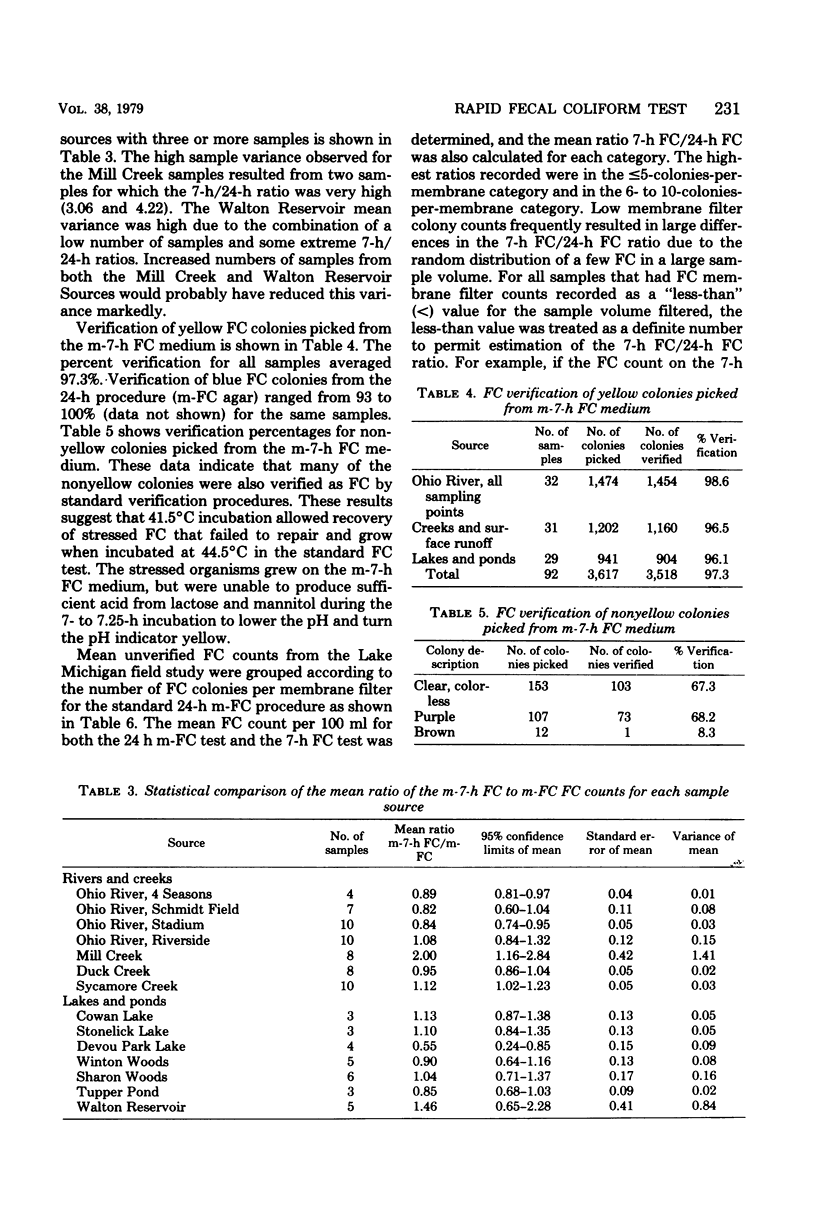
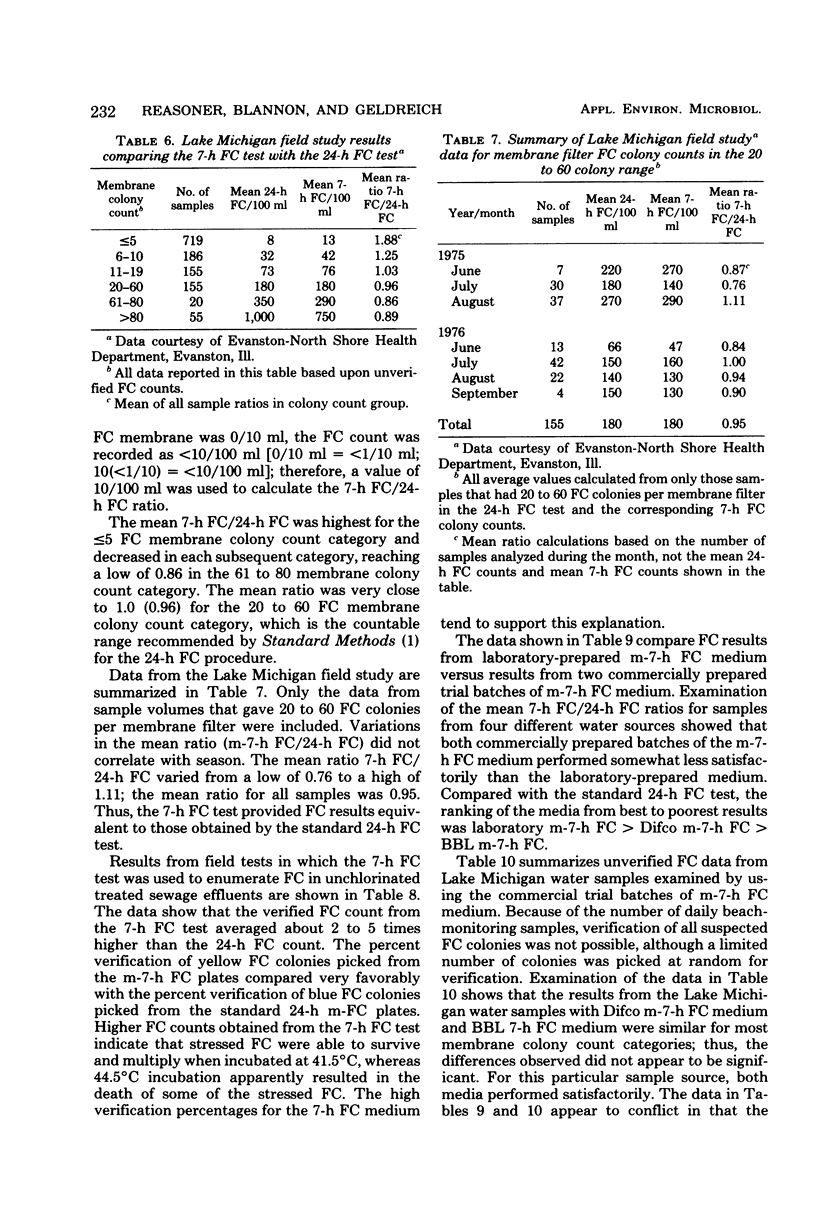
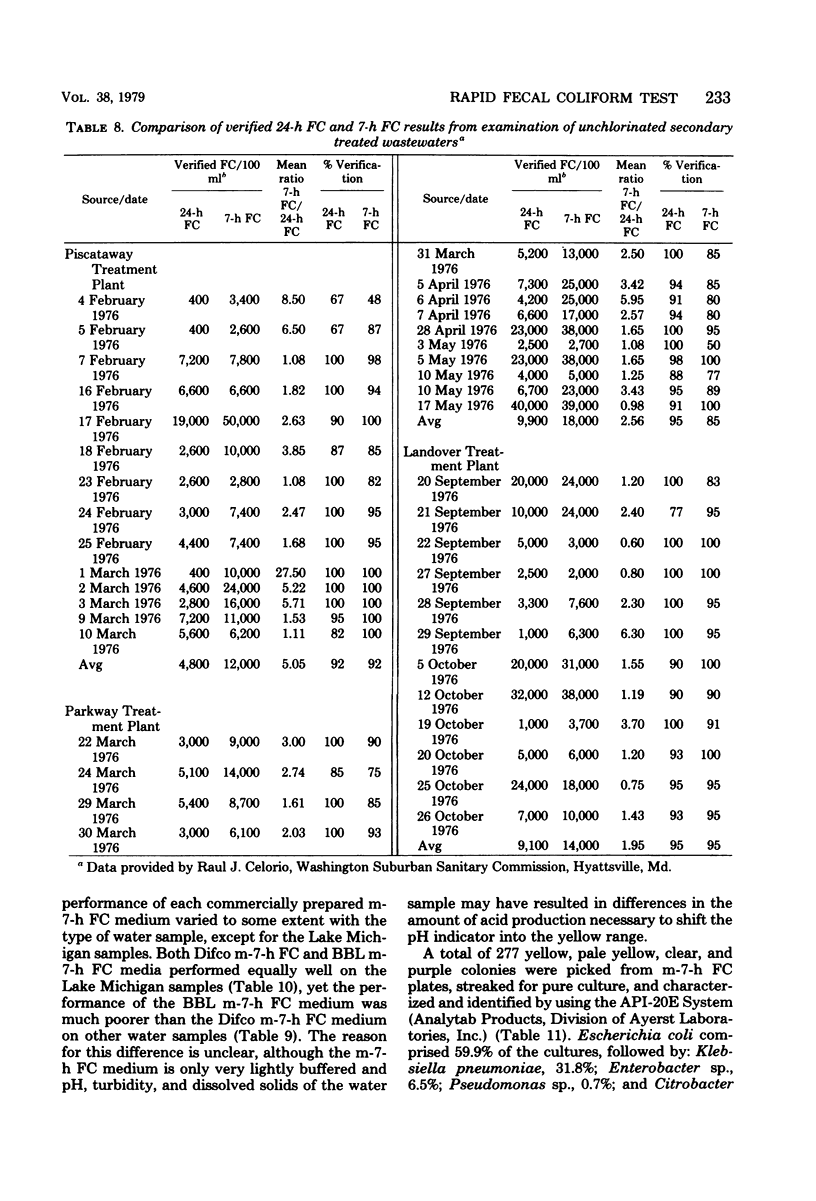
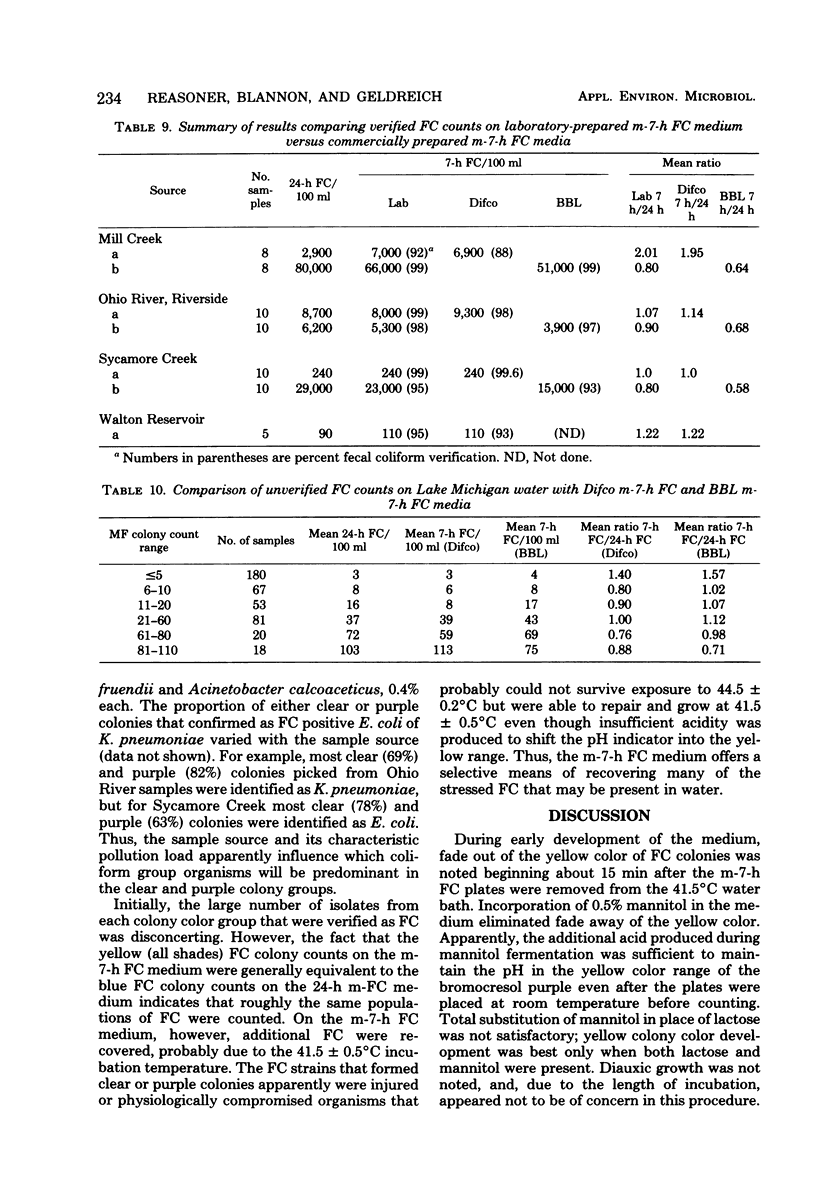
A rapid 7-h fecal coliform (FC) test for the detection of FC in water has been developed. This membrane filter test utilizes a lightly buffered lactose-based medium (m-7-h FC medium) combined with a sensitive pH indicator system. FC colonies appeared yellow against a light purple background after incubation at 41.5 degrees C for 7 to 7.25 h. Comparison of FC test results showed that the mean verified FC count ratio (7-h FC count/24-h FC count) for surface water samples was 1.08. The mean FC count ratio (7-h FC count/24-h FC count) for unchlorinater wastewater ranged from 1.95 to 5.05. Verification of yellow FC colonies from m-7-h FC medium averaged 97%. Data from field tests on Lake Michigan bathing beach water samples showed that unverified 7-h FC counts averaged 96% of the 24-h FC counts. The 7-h FC test was found to be suitable for the examination of surface waters and unchlorinated sewage and could serve as an emergency test for detection of sewage or fecal contamination of potable water.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Evaluation of recovery methods to detect coliforms in water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):590–595. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.590-595.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Influence of environmental stress on enumeration of indicator bacteria from natural waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):186–194. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.186-194.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Aoust J. Y. Recovery of sublethally heat-injured Salmonella typhimurium on supplemented plating media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):483–486. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.483-486.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawe L. L., Penrose W. R. "Bactericidal" property of seawater: death or debilitation? Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):829–833. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.829-833.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. L., Clausen E. M., Litsky W. Two-temperature membrane filter method for enumerating fecal coliform bacteria from chlorinated effluents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jun;33(6):1259–1264. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.6.1259-1264.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoadley A. W., Cheng C. M. The recovery of indicator bacteria on selective media. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;37(1):45–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein D. A., Wu S. Stress: a factor to be considered in heterotrophic microorganism enumeration from aquatic environments. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):429–431. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.429-431.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. D. Membrane filter method for recovery of fecal coliforms in chlorinated sewage effluents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):547–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.547-552.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B., Speck M. L. Plating procedure for the enumeration of coliforms from dairy products. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Apr;35(4):820–822. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.4.820-822.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. G., McFeters G. A., Schillinger J. E. Membrane filter technique for the quantification of stressed fecal coliforms in the aquatic environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jul;34(1):42–46. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.1.42-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Klein D. A. Starvation effects on Escherichia coli and aquatic bacterial responses to nutrient addition and secondary warming stresses. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):216–220. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.216-220.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



