Abstract
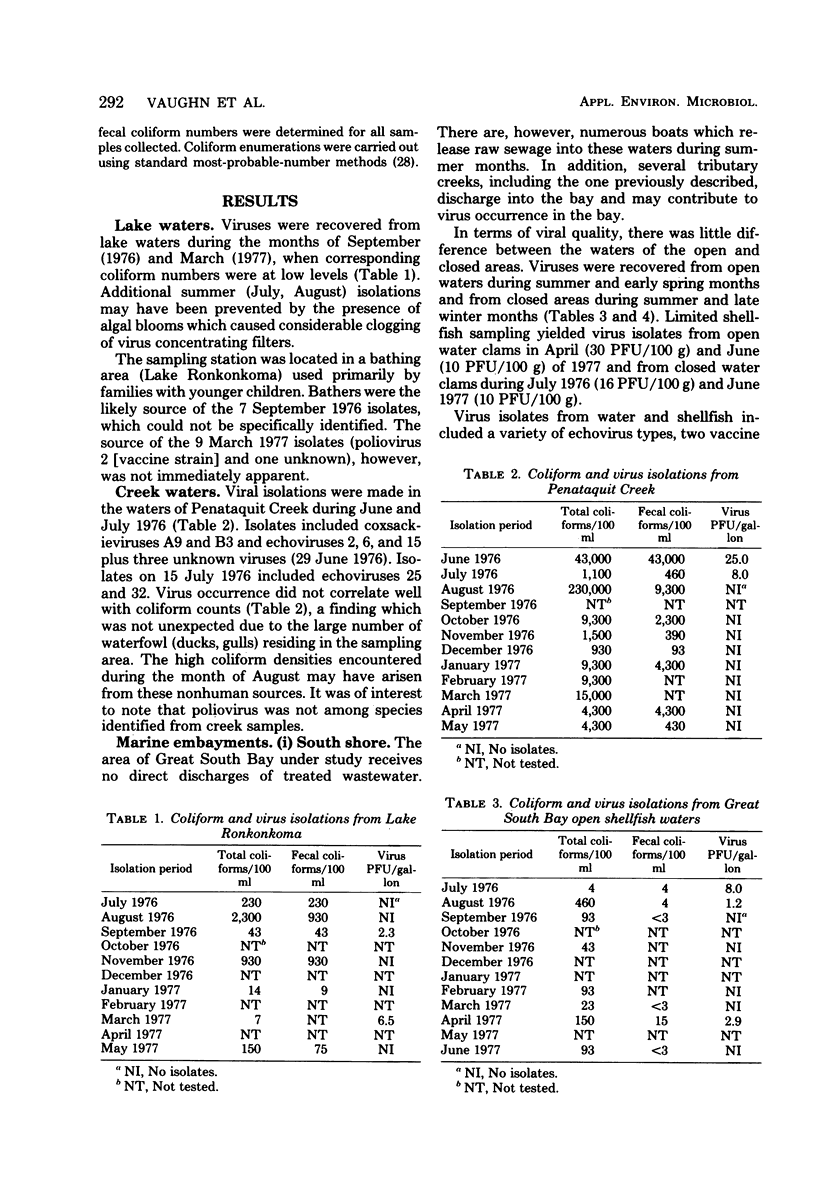
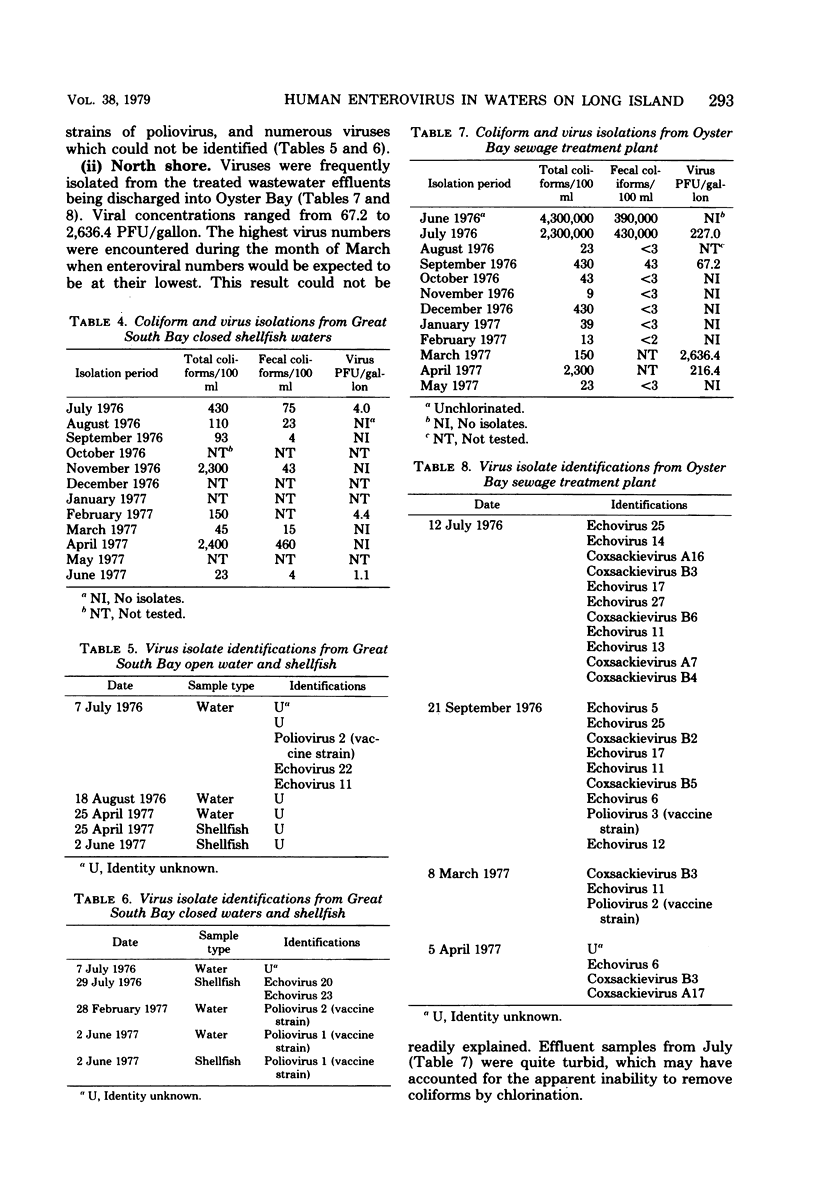
A variety of surface water systems, including a lake, a creek, and two marine embayments, were analyzed on a monthly basis for indigenous human enteroviruses and coliform bacteria. Findings are discussed in terms of the probable pollution sources to each system and their relationship to data from previous studies.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Flora S., De Renzi G. P., Badolati G. Detection of animal viruses in coastal seawater and sediments. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):472–475. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.472-475.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis F. A. Coxsackie group A in oysters and mussels. Lancet. 1973 Jun 2;1(7814):1262–1262. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of viruses from large volumes of tap water using pleated membrane filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):221–226. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.221-226.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Schaiberger G. E. Effect of particulates on virus survival in seawater. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1975 Jan;47(1):93–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Smith E. M., Melnick J. L. Development of a quantitative method for detecting enteroviruses in estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):158–163. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.158-163.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., Kostenbader K. D., Jr, CLIVER D. O. Persistence of enteroviruses in lake water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):895–896. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.895-896.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. F., Jr, Jakubowski W., Akin E. W., Clarke N. A. Detection of virus in water: sensitivity of the tentative standard method for drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):254–261. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.254-261.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S., Gilbert J., Hetrick F. Stability of human enteroviruses in estuarine and marine waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Aug;32(2):245–249. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.2.245-249.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Magnusson S., Lund E. Studies on the nature of the virus inactivating capacity of sea water. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;17(3):409–413. doi: 10.1007/BF01241195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSLEY J. W. Epidemiologic aspects of viral agents in relation to waterborne diseases. Public Health Rep. 1963 Apr;78:328–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Hedström C. E., Lycke E. The virus inactivating capacity of sea water. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(4):551–559. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L., Rennick V., Hampil B., Schmidt N. J., Ho H. H. Lyophilized combination pools of enterovirus equine antisera: preparation and test procedures for the identification of field strains of 42 enteroviruses. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;48(3):263–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestor I., Costin L. Presence of certain enteroviruses (Coxsackie) in sewage effluents and in river waters of Roumania. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1976;20(2):137–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. T., Newman J. S. Inactivation of polioviruses and coxsackieviruses in surface water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):334–340. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.334-340.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RHODES A. J., CLARK E. M., KNOWLES D. S., GOODFELLOW A. M., DONOHUE W. L. Prolonged survival of human poliomyelitis virus in experimentally infected river water. Can J Public Health. 1950 Apr;41(4):146–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simková A., Wallnerová Z. Isolations of coxsackie viruses from Danube river water. Acta Virol. 1973 Jul;17(4):363–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simková A., Wallnerová Z. Survival of small amounts of Coxsackie A4 virus in Danube river water under laboratory conditions. Acta Virol. 1973 Nov;17(6):505–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Development of a simple method for concentrating enteroviruses from oysters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jan;29(1):21–26. doi: 10.1128/am.29.1.21-26.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Lewis A. L., Mountain C. W., Pierce L. V. Demonstration of virus in groundwater after effluent discharge onto soil. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):751–757. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.751-757.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



