Abstract
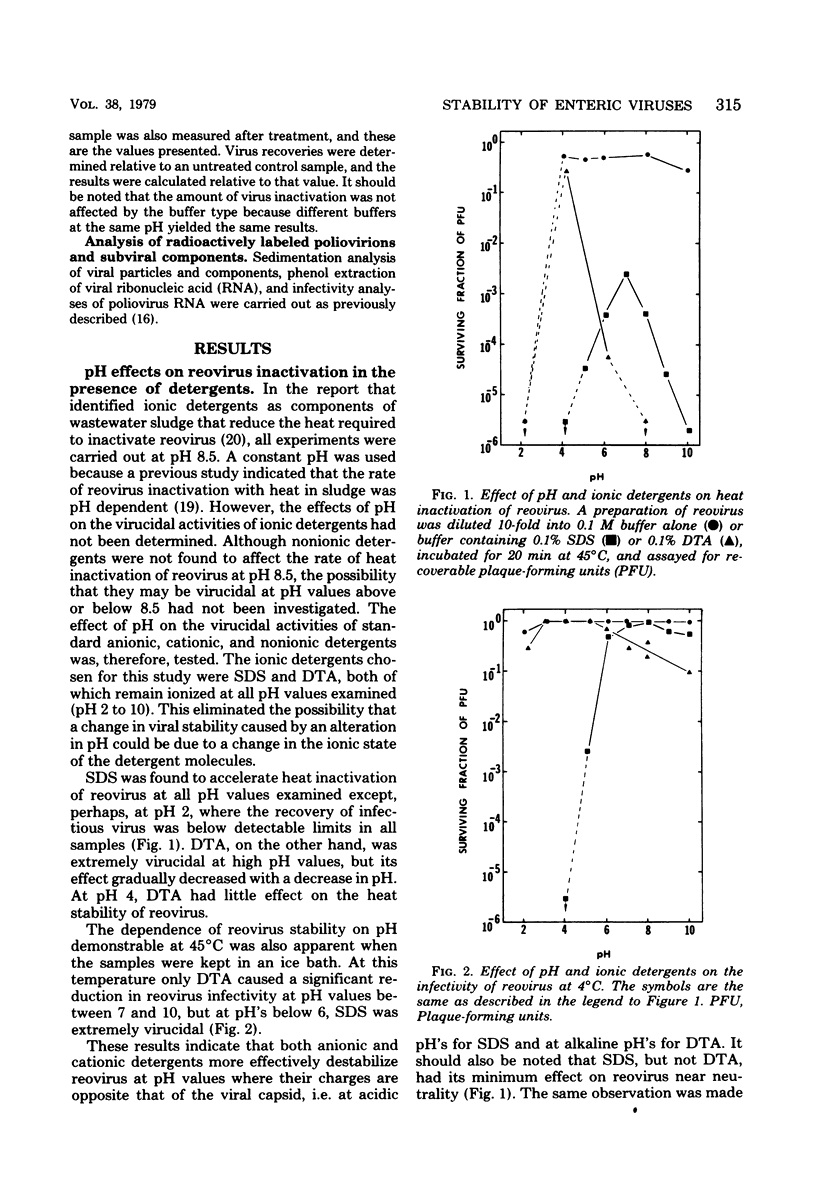
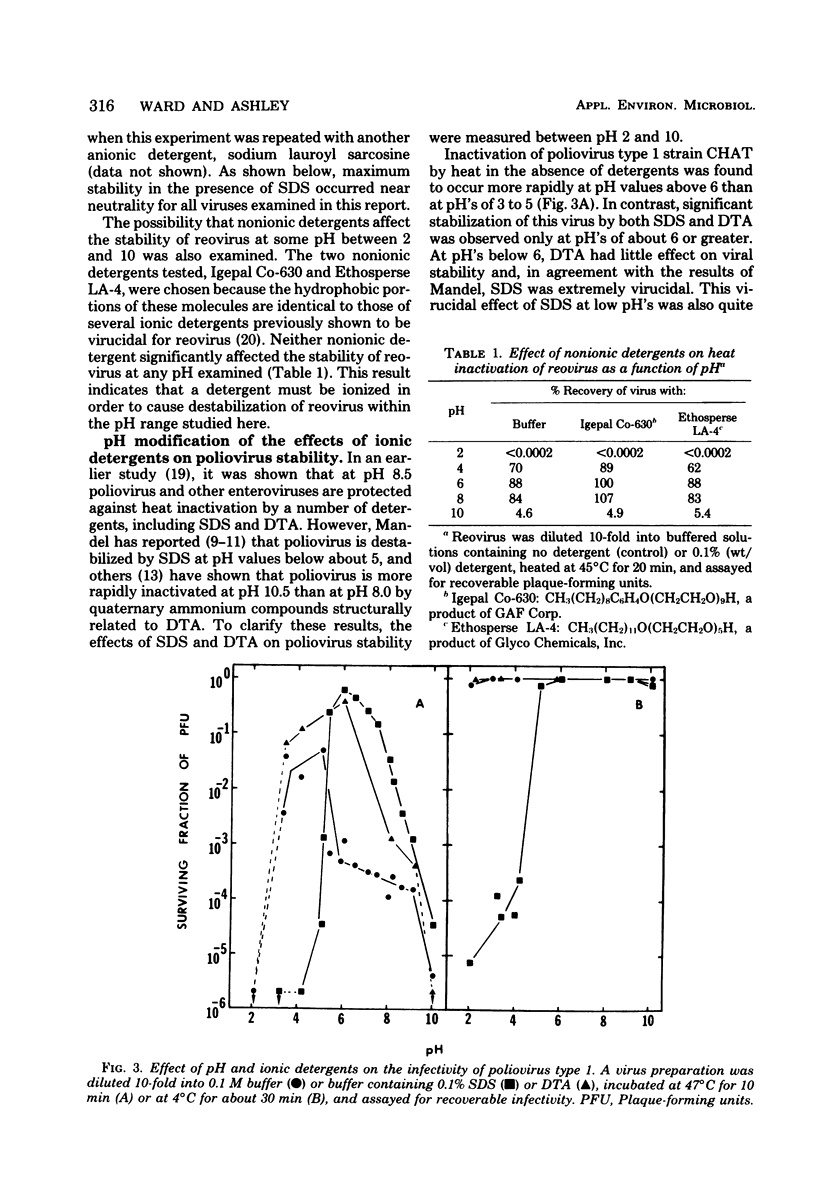
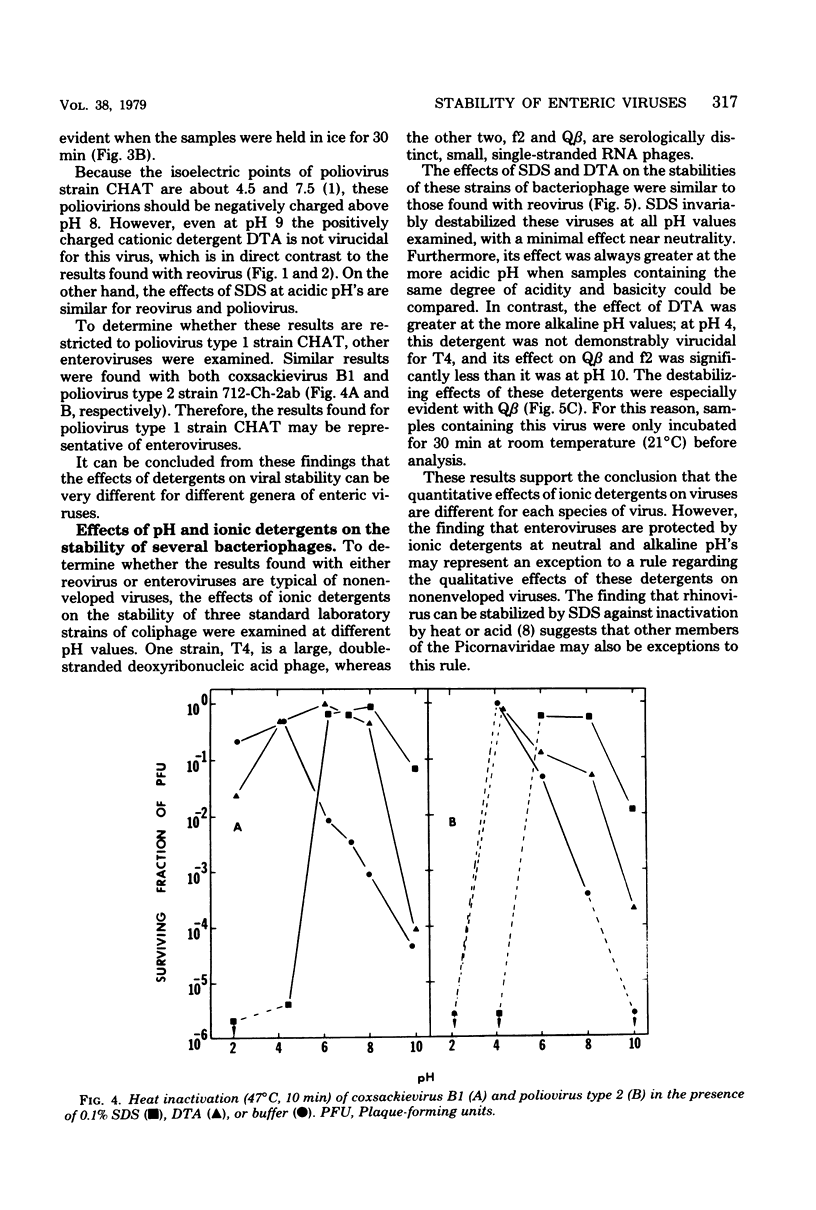
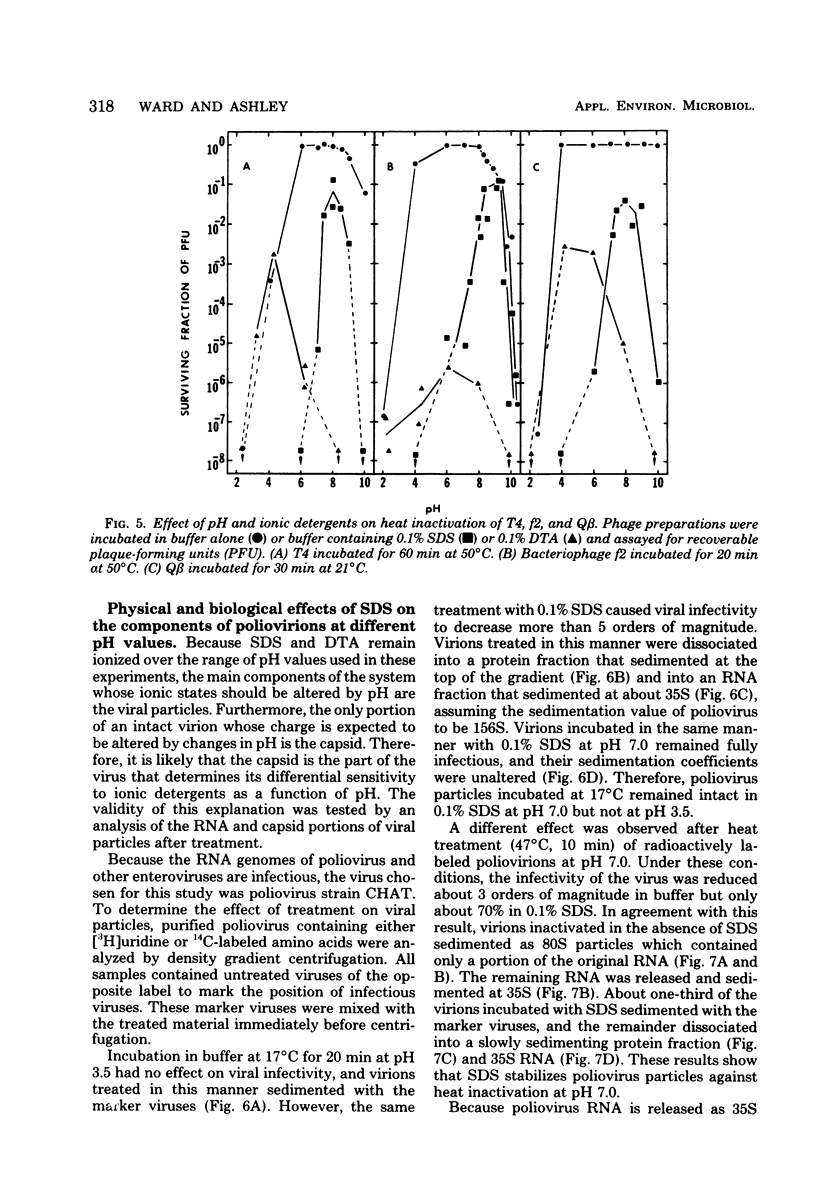
The effect of detergents on the stability of enteric viruses was found to be highly dependent on pH. This was demonstrated primarily with two ionic detergents, sodium dodecyl sulfate (an anionic detergent) and dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride (a cationic detergent). Both detergents were shown to be potent virucidal agents for reovirus, but the effects of sodium dodecyl sulfate were minimal near neutrality and much more pronounced at low than at high pH values. Dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride was extremely virucidal at high pH's but had little observable effect on reovirus stability at low pH values. In contrast, both detergents protected enteroviruses against heat at neutral and alkaline pH's. However, as was found with reovirus, sodium dodecyl sulfate was extremely virucidal at pH values below 5, even when the virus samples were incubated in ice. At different pH's the effects of detergents on the stabilities of coliphages T4, f1, and Q beta were qualitatively similar to those found with reovirus. Differences in viral stability in these experiments appeared to be due to the effects of pH on the ionic states of the viral capsid proteins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bawden F. C. The effects of alkali and some simple organic substances on three plant viruses. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1278–1292. doi: 10.1042/bj0341278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
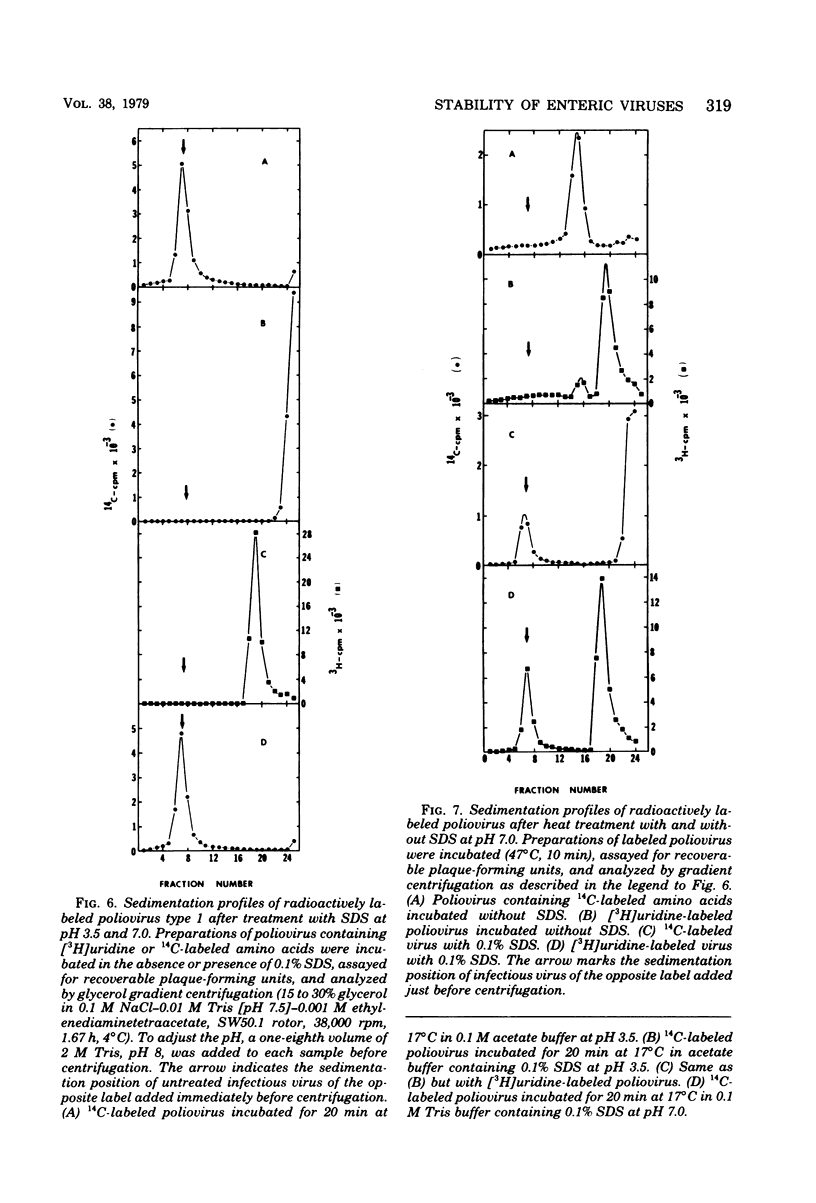
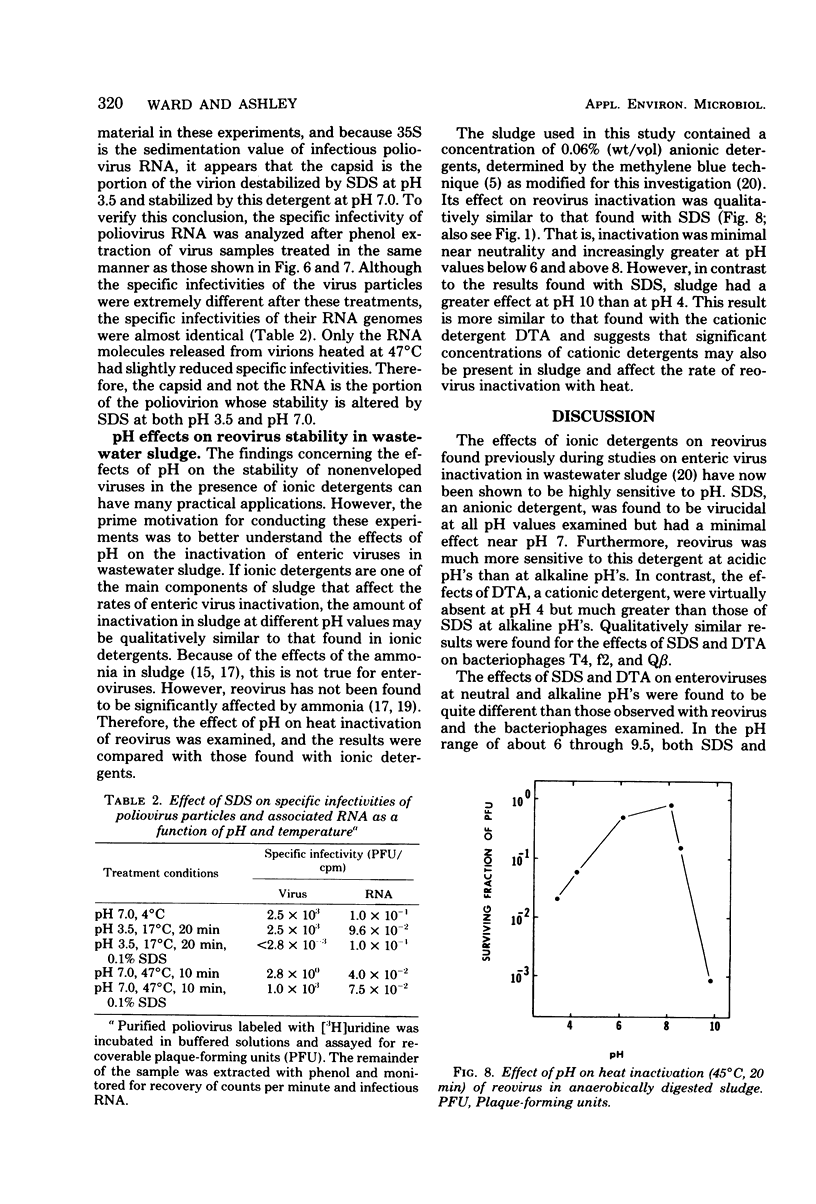
- Breindl M. The structure of heated poliovirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1971 Jun;11(3):147–156. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-11-3-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SINGER B., WILLIAMS R. C. Infectivity of viral nucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jul;25(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90422-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R., Sharp D. G. Viral aggregation: effects of salts on the aggregation of poliovirus and reovirus at low pH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1084–1094. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1084-1094.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Noble-Harvey J. Comparison of in vitro and cell-mediated alteration of a human Rhinovirus and its inhibition by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):819–826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.819-826.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. THE EXTRACTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM POLIOVIRUS BY TREATMENT WITH SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:360–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. The use of sodium dodecyl sulfate in studies on the interaction of poliovirus and HeLa cells. Virology. 1962 Jun;17:288–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Chemical disinfection of holding-tank sewage. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):861–866. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.861-866.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreenivasaya M., Pirie N. W. The disintegration of tobacco mosaic virus preparations with sodium dodecyl sulphate. Biochem J. 1938 Oct;32(10):1707–1710. doi: 10.1042/bj0321707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Discovery of an agent in wastewater sludge that reduces the heat required to inactivate reovirus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):681–688. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.681-688.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Heat inactivation of enteric viruses in dewatered wastewater sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):898–905. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.898-905.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Identification of detergents as components of wastewater sludge that modify the thermal stability of reovirus and enteroviruses. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):889–897. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.889-897.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Identification of the virucidal agent in wastewater sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):860–864. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.860-864.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Inactivation of enteric viruses in wastewater sludge through dewatering by evaporation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):564–570. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.564-570.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Inactivation of poliovirus in digested sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):921–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.921-930.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S., Moseley R. H. Heat inactivation of poliovirus in wastewater sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):339–346. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.339-346.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L. Mechanism of poliovirus inactivation by ammonia. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):299–305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.299-305.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



