Abstract
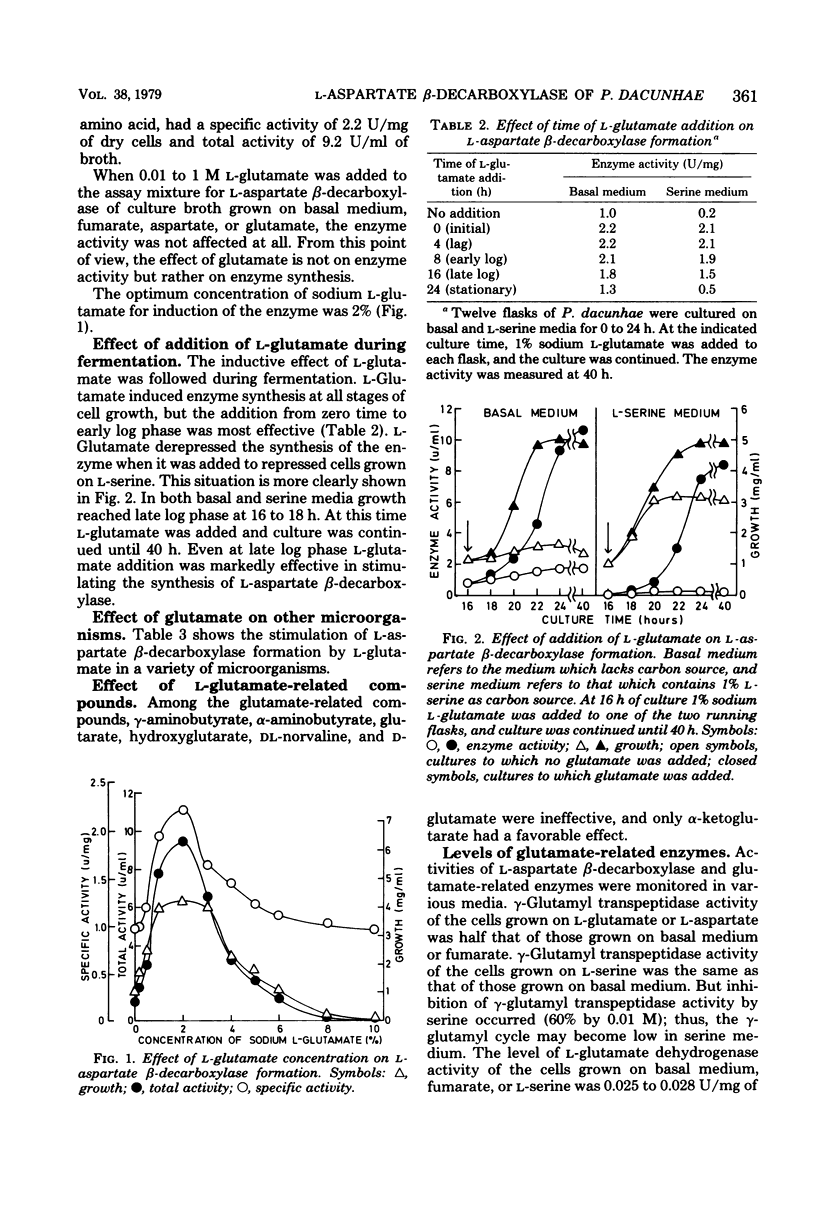
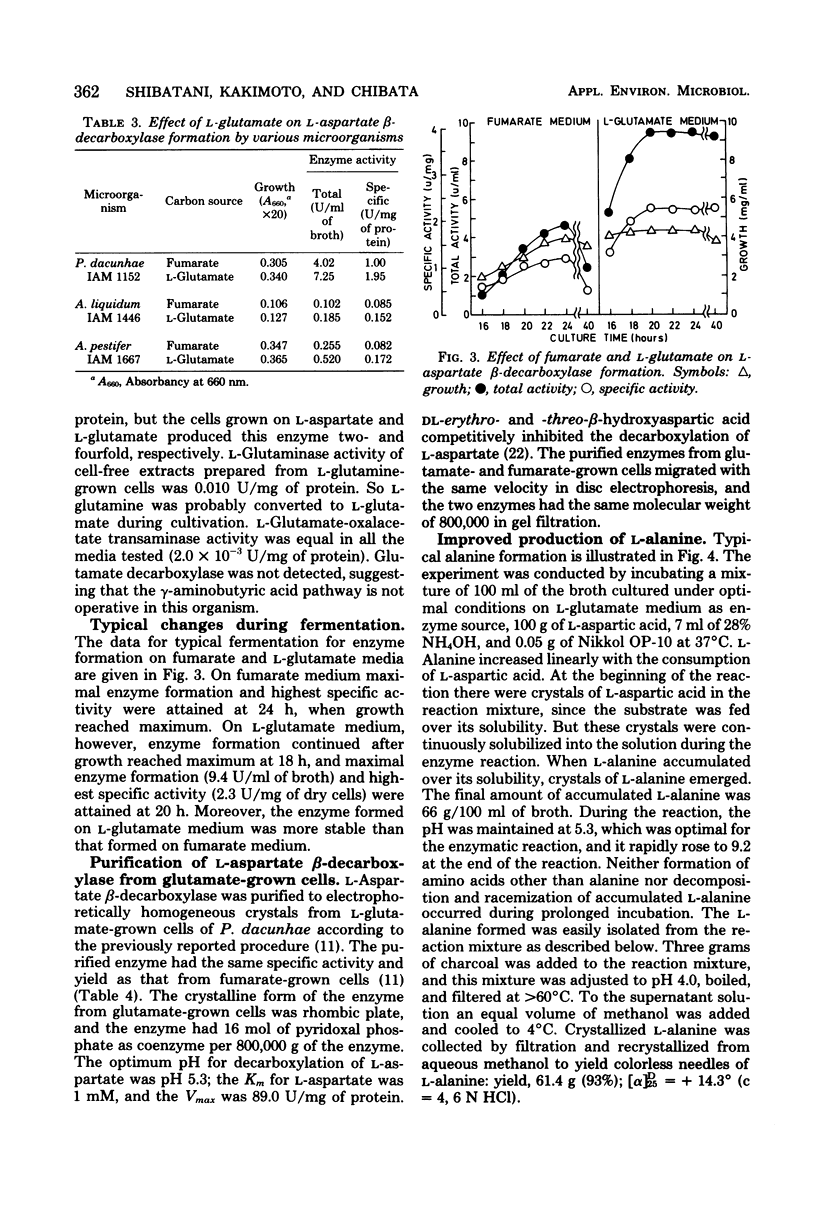
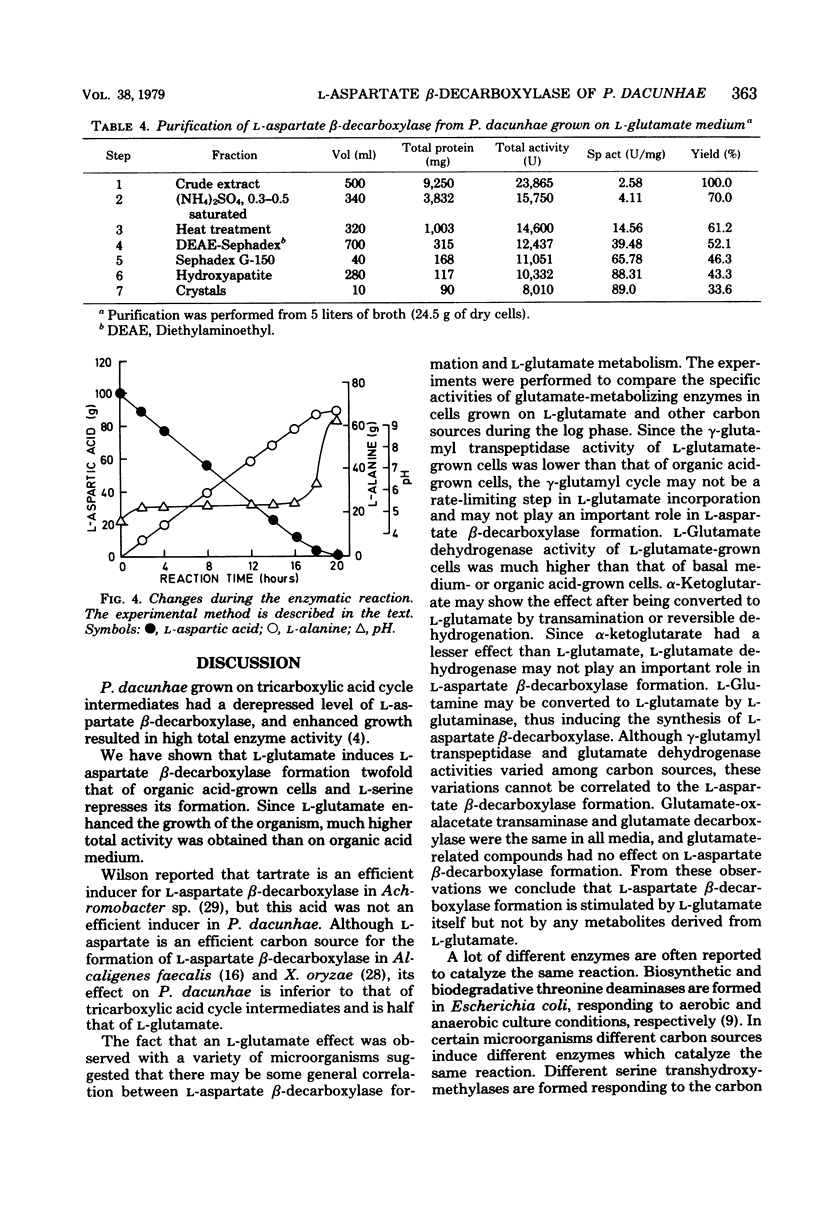
The formation of L-asparate beta-decarboxylase by Pseudomonas dacunhae was compared on media containing a variety of organic acids and amino acids as a carbon source. Although the enzyme was formed constitutively when the organism was grown on basal medium or on that containing tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates, it was induced twofold by L-glutamate and repressed one-tenth by L-serine. L-Glutamine, L-proline, L-leucine, glycine, and L-threonine also showed induction effects lower than that of L-glutamate. L-Glutamate derepressed the serine effect. This glutamate effect was observed effect was observed with other microoganisms, e.g., Achromobacter pestifer and Achromobacter liquidum. Since the intermediates from L-glutamate metabolism had no effect, this induction effect was specific to L-glutamate. The formation of some glutamate-related enzymes was measured and is discussed in relation to the formation of L-asparate beta-decarboxylase. L-Asparate beta-decarboxylase was purified to an electrophoretically homogenous state from L-glutamate-grown cells of P. dacunhae, and some properties were compared with those of the enzyme from fumarate-grown cells. The two enzymes were identical in disc electrophoresis, molecular weight, and some enzymatic properties. The industrial production of L-alanine from L-aspartic acid acid was improved by using the culture broth with highly induced L-asparate beta-decarboxylase (9.4 U/ml of broth).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BHEEMESWAR B. Studies on transaminase and decarboxylase catalysed by extracts of the silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Nature. 1955 Sep 17;176(4481):555–556. doi: 10.1038/176555b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATTANEO-LACOMBE J., SENEZ J. C., BEAUMONT P. Sur la purification de la 4-aspartique décarboxylase de Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Dec;30(3):458–465. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKSEY K. E., RAINBOW C. Metabolic patterns in acetic acid bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jan;27:135–142. doi: 10.1099/00221287-27-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V. Studies on the aspartic decarboxylase of Nocardia globerula. Biochem J. 1958 Feb;68(2):221–225. doi: 10.1042/bj0680221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chibata I., Kakimoto T., Kato J. Enzymatic production of L-alanine by Pseudomonas dacunhae. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Sep;13(5):638–645. doi: 10.1128/am.13.5.638-645.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chibata I., Kakimoto T., Kato J., Shibatani T., Nishimura N. On the activation mechanism of L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase from Pseudomonas dacunhae by alpha-ketoglutarate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Aug 13;32(3):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90670-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles R., Schoffeniels E. Décarboxylation des acides aspartique et oxaloacétique chez le homard et l'écrevisse. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1966;48(3):397–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakimoto T., Kato J., Shibatani T., Nishimura N., Chibata I. Crystalline L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase of Pseudomonas dacunhae. I. Crystallization and some physiocochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):353–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEISTER A., SOBER H. A., TICE S. V. Enzymatic decarboxylation of aspartic acid to alpha-alanine. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):577–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHIMURA J. S., MANNING J. M., MEISTER A. Studies on the mechanism of activation acid beta-decarboxylase by alpha-keto acids and pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1962 May 25;1:442–447. doi: 10.1021/bi00909a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVOGRODSKY A., MEISTER A. CONTROL OF ASPARTATE BETA-DECARBOXYLASE ACTIVITY BY TRANSAMINATION. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:879–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M. L., Hanson R. S. Serine transhydroxymethylase isoenzymes from a facultative methylotroph. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):985–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.985-996.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN G. R. Amino acid decarboxylases in a pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1960 Dec;80:830–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.6.830-836.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENEZ J. C., CATTANEO-LACOMBE J. Transformation de l'acide L-aspartique en alpha-alanine par des extraits de Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1956 Feb 13;242(7):941–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUKUYA R., SCHWERT G. W. Glutamic acid decarboxylase. I. Isolation procedures and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1649–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Interaction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase with amino acids, dipeptides, and derivatives and analogs of glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7593–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Regulation of the activity of L-aspartate beta-decarboxylase by a novel allosteric mechanism. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1660–1668. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese F. M., Boccu E., Conventi L. Glutamate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli: induction, purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 19;377(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN H. W., HORN M. J., BLUM A. E. Microbiological determination of alanine in proteins and foods. Anal Biochem. 1963 Jan;5:70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON E. M. Crystalline L-aspartate 4-carboxy-lyase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:345–348. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91840-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON E. M., KORNBERG H. L. PROPERTIES OF CRYSTALLINE L-ASPARTATE 4-CARBOXY-LYASE FROM ACHROMOBACTER SP. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:578–587. doi: 10.1042/bj0880578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



