Abstract
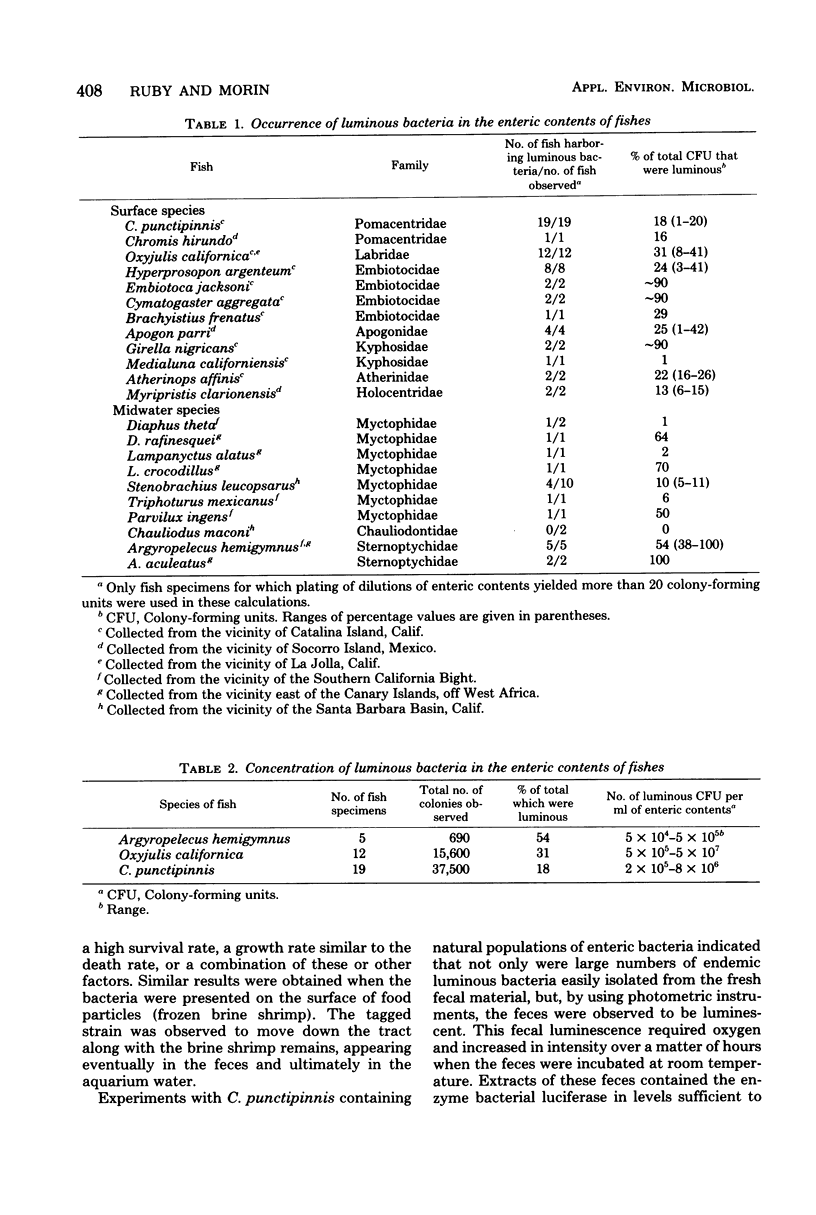
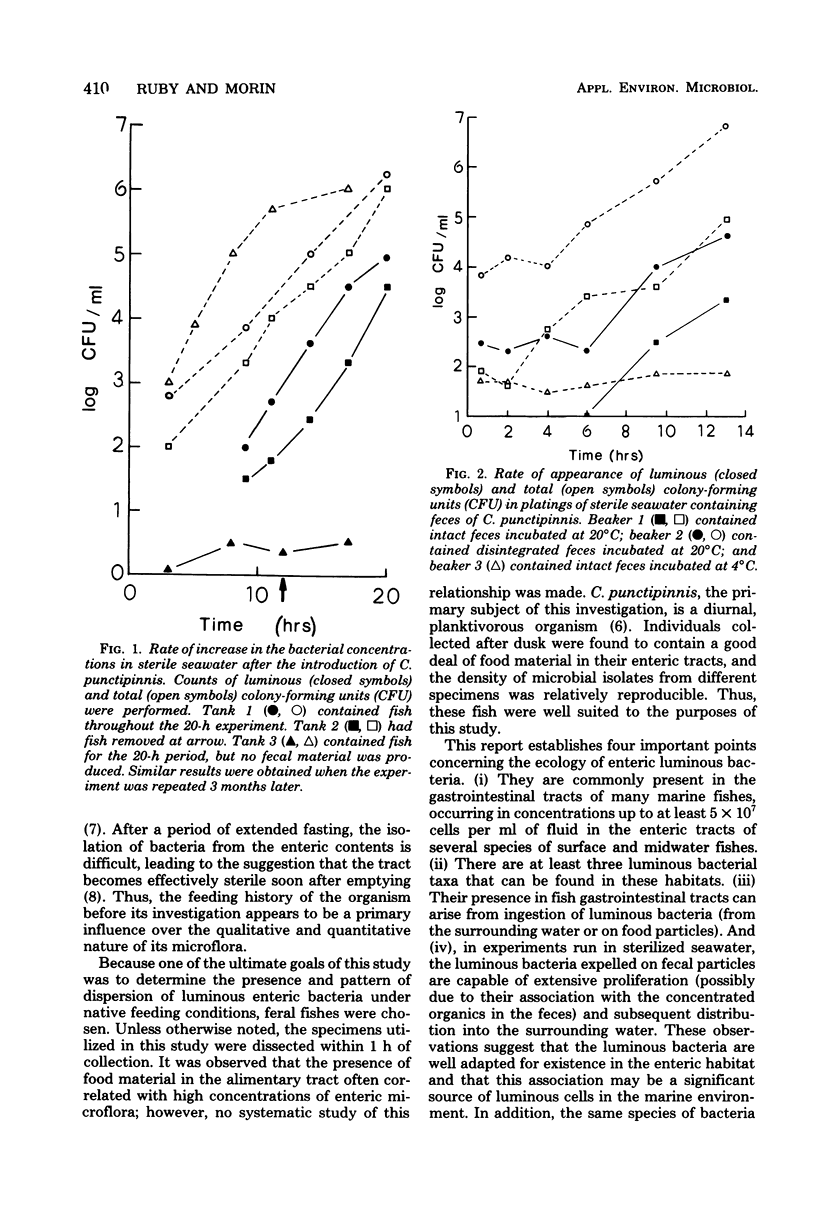
Three taxa of luminous bacteria (Photobacterium fischeri, P. phosphoreum, and Beneckea spp.) were found in the enteric microbial populations of 22 species of surface- and midwater-dwelling fishes. These bacteria often occurred in concentrations ranging between 105 and 107 colony-forming units per ml of enteric contents. By using a genetically marked strain, it was determined that luminous cells entering the fish during ingestion of seawater or contaminated particles traversed the alimentary tract and survived the digestive processes. After excretion, luminous bacteria proliferated extensively on the fecal material and became distributed into the surrounding seawater. Thus, this enteric habitat may serve as an enrichment of viable cells entering the planktonic luminous population.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann P., Baumann L. Biology of the marine enterobacteria: genera Beneckea and Photobacterium. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:39–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. W., Nealson K. H. Bacterial bioluminescence. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:549–595. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nealson K. H., Platt T., Hastings J. W. Cellular control of the synthesis and activity of the bacterial luminescent system. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):313–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.313-322.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichelt J. L., Baumann P., Baumann L. Study of genetic relationships among marine species of the genera Beneckea and Photobacterium by means of in vitro DNA/DNA hybridization. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Oct 11;110(1):101–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00416975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers P., McElroy W. D. BIOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF ALDEHYDE AND LUCIFERASE MUTANTS OF LUMINOUS BACTERIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Feb 15;41(2):67–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.2.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Nealson K. H. Symbiotic association of Photobacterium fischeri with the marine luminous fish Monocentris japonica; a model of symbiosis based on bacterial studies. Biol Bull. 1976 Dec;151(3):574–586. doi: 10.2307/1540507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


