Abstract
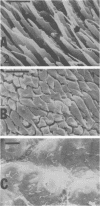
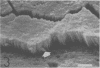
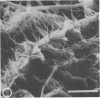
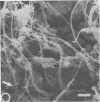
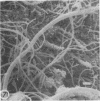
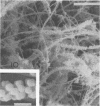
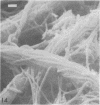
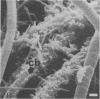
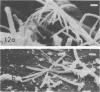
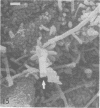
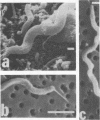
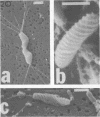
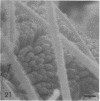
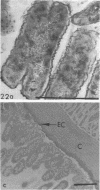
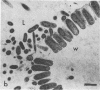
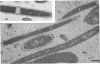
A morphological study employing scanning and transmission electron microscopy was made by the alimentary tract of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana L. A. complex microbiota of diverse morphology, which could not be readily dislodged, was observed and found to be restricted to the hindgut, particularly the colon. Numerous filamentous forms were noted, and some are described, including the morphologically distinct Methanospirillum. Flora was noted attached to the cuticular lining and cuticular filaments of the colon, and several spiral forms were observed in the luminal contents from the colon.
Full text
PDF





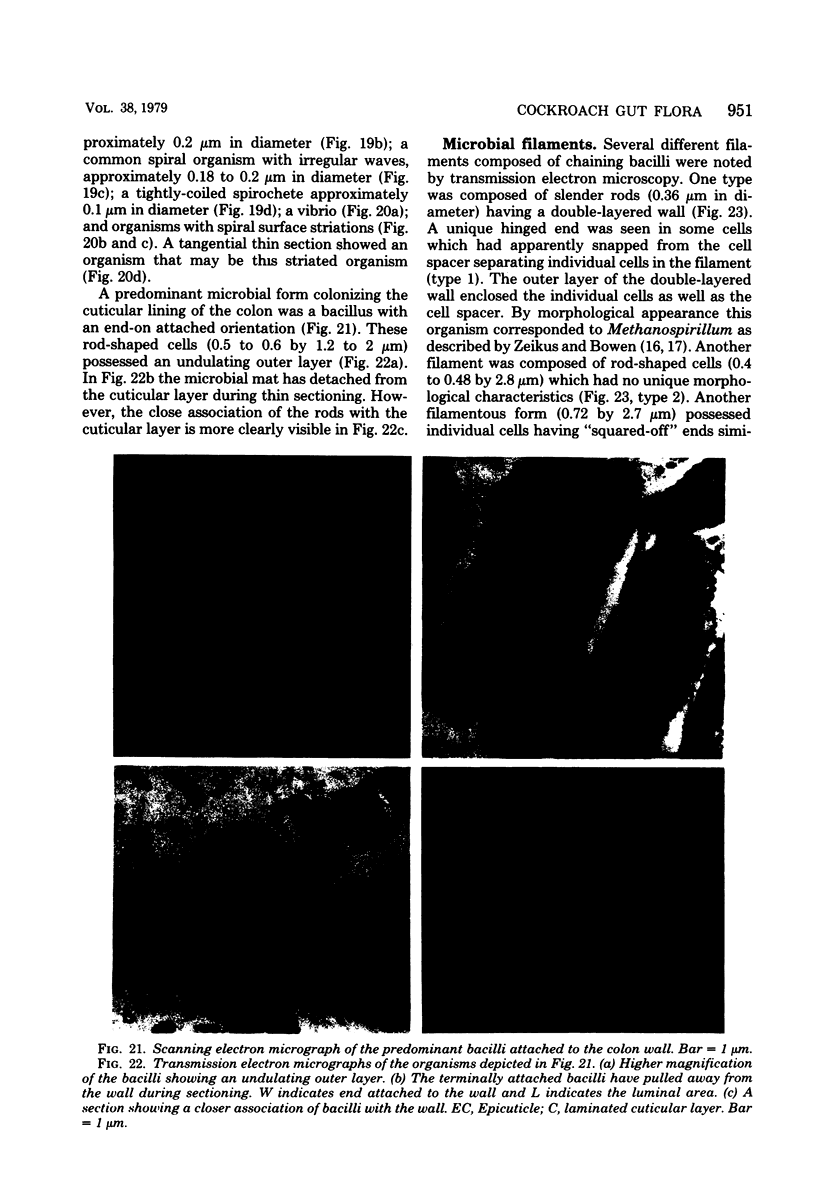

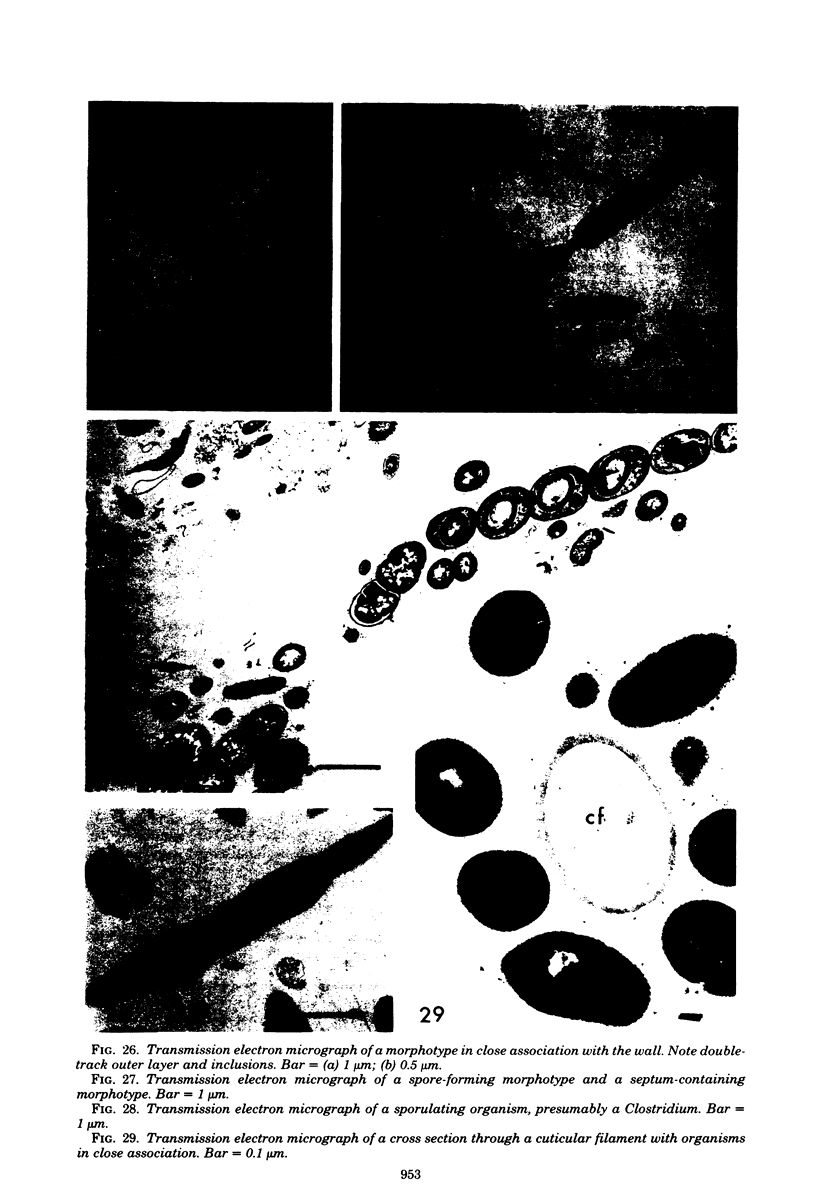


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bignell D. E., Oskarsson H., Anderson J. M. Association of actinomycete-like bacteria with soil-feeding termites (termitidae, termitinae). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):339–342. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.339-342.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracke J. W., Cruden D. L., Markovetz A. J. Effect of metronidazole on the intestinal microflora of the american cockroach, Periplaneta americana l. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):115–120. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A., Pankratz H. S. In situ morphology of the gut microbiota of wood-eating termites [Reticulitermes flavipes (Kollar) and Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki]. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):406–426. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.406-426.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase D. G., Erlandsen S. L. Evidence for a complex life cycle and endospore formation in the attached, filamentous, segmented bacterium from murine ileum. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):572–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.572-583.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruden D. L., Markovetz A. J. Carboxymethyl cellulose decomposition by intestinal bacteria of cockroaches. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Sep;38(3):369–372. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.3.369-372.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Savage D. C. Habitat, succession, attachment, and morphology of segmented, filamentous microbes indigenous to the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):948–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.948-956.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglesong M. A., Walker D. H., Jr, Puffer J. S., Markovetz A. J. Ultrastructal morphology of some prokaryotic microorganisms associated with the hindgut of cockroaches. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):336–345. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.336-345.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Bowen V. G. Comparative ultrastructure of methanogenic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Feb;21(2):121–129. doi: 10.1139/m75-019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Bowen V. G. Fine structure of Methanospirillum hungatii. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):373–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.373-380.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]