Abstract
Quantitative mineralization studies on radiolabeled compounds having high vapor pressures need to cope with several technical difficulties. An incubation and trapping system is described that was successfully used in mineralization studies on highly volatile trichlorobenzenes and other xenobiotic pollutants.
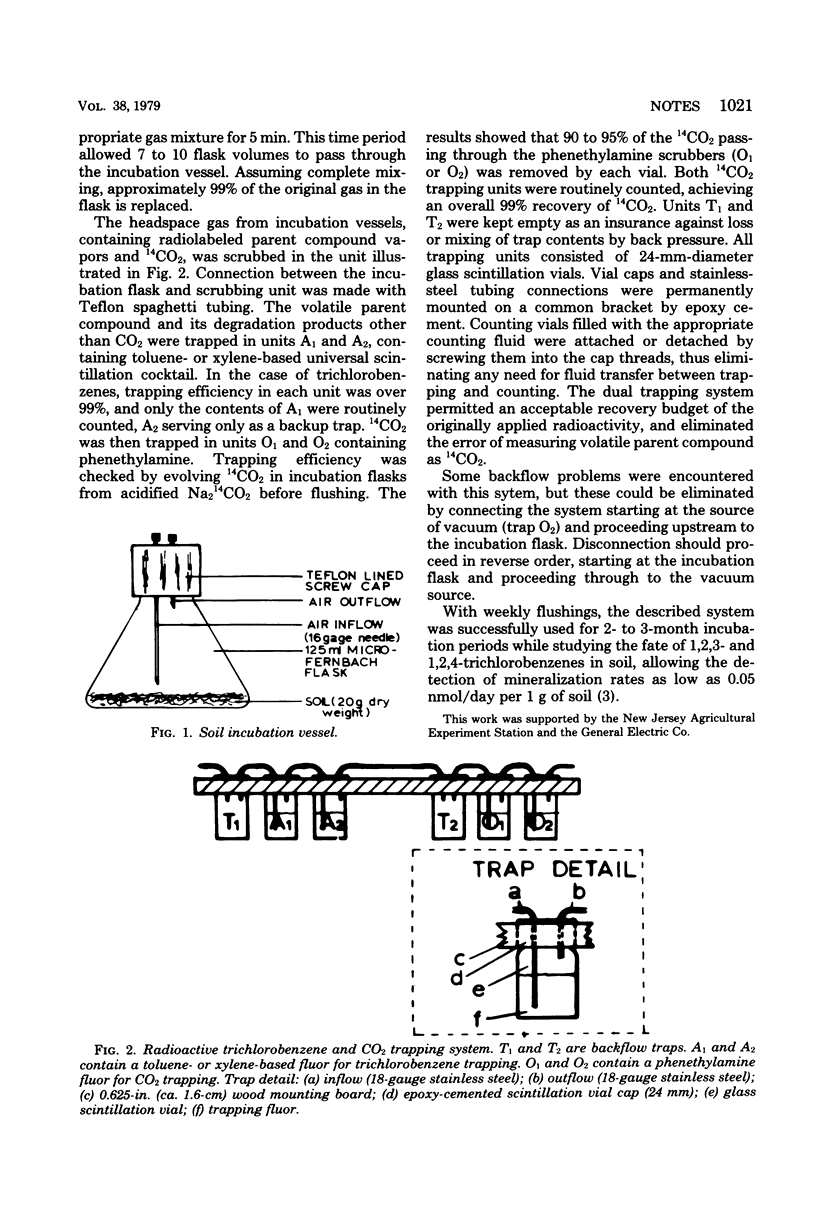
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hsu T. S., Bartha R. Accelerated mineralization of two organophosphate insecticides in the rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.36-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinucci A. C., Bartha R. Biodegradation of 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene in soil and in liquid enrichment culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):811–817. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.811-817.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zeikus J. G. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous end products of anaerobic metabolism. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.258-261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


