Abstract
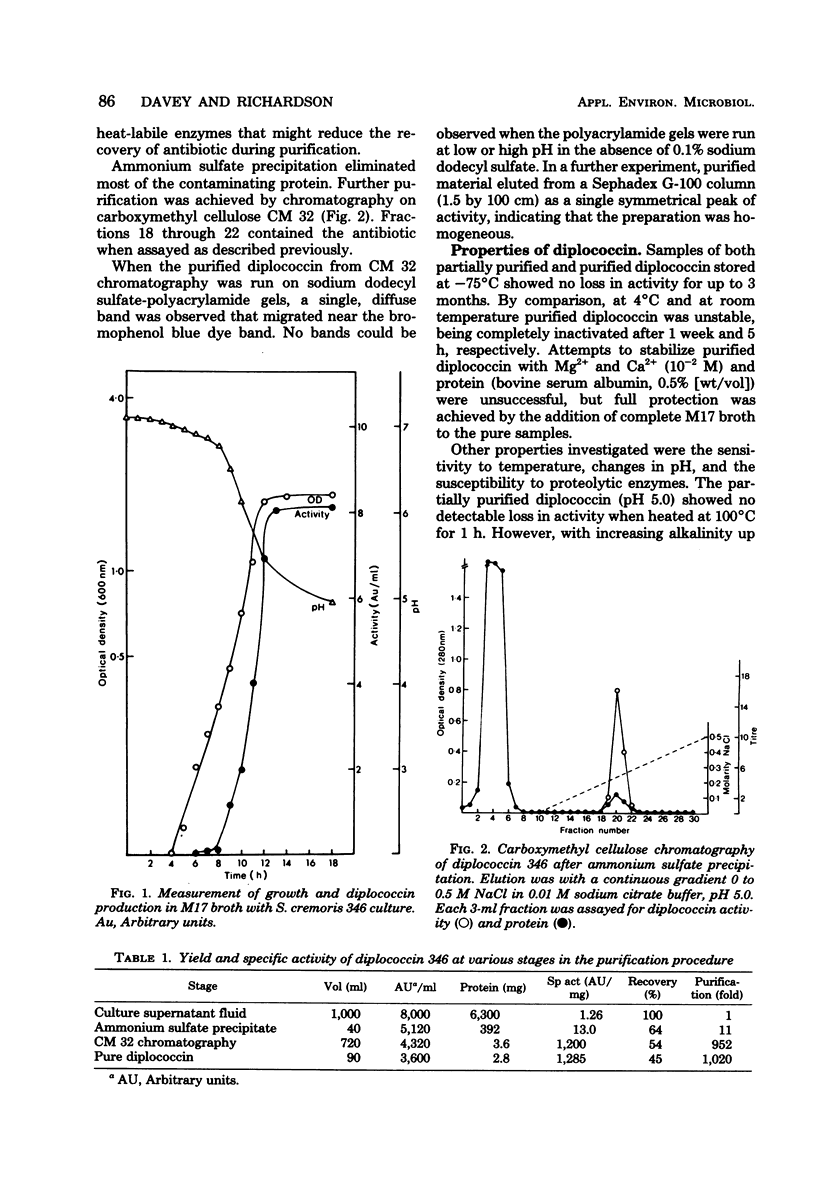
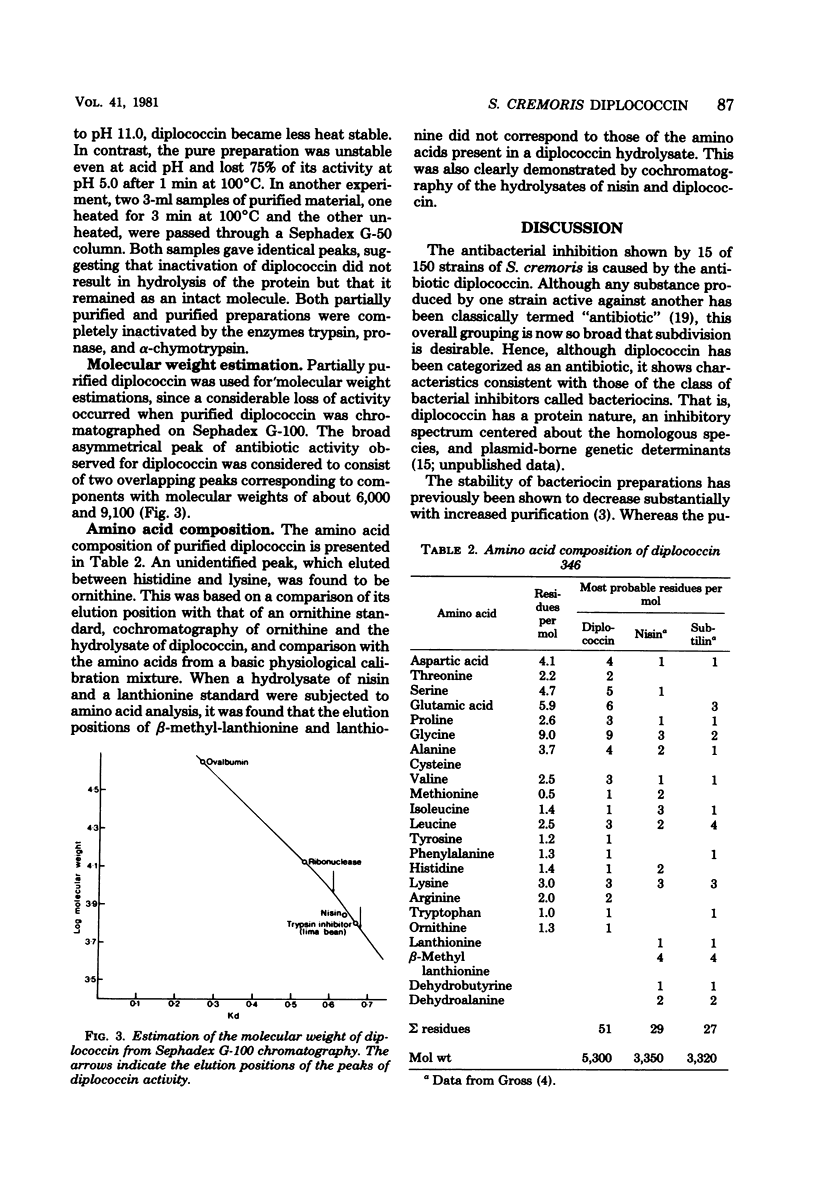
Eleven of 150 Streptococcus cremoris strains examined produced the bacteriocin diplococcin. The diplococcin activity spectrum was restricted to S. cremoris and Streptococcus lactis strains, and none of a wide range of other gram-positive or gram-negative strains were inhibited. The diplococcin produced by S. cremoris 346 was purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation and column chromatography. Purified diplococcin was very unstable at room temperature and lost 75% of its activity after heating at 100°C for 1 min. The proteolytic enzymes trypsin, pronase, and α-chymotrypsin completely inactivated diplococcin. The amino acid composition showed a high content of acidic and neutral acids and a correspondingly low content of basic amino acids, including one residue of ornithine per mole. From the amino acid analysis a molecular weight of 5,300 was estimated. Diplococcin was readily distinguished from the S. lactis bacteriocin nisin by its restricted activity spectrum, its biological properties, and by cross-reaction experiments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of molecular size and molecular weights of biological compounds by gel filtration. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J. S., Kautter J. A. Purification and some properties of two boticins. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):19–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.19-26.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A. Nisin: its preservative effect and function in the growth cycle of the producer organism. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1978;7:297–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L., Tombs M. P., Hurst A. Mobility-molecular weight relationships of small proteins and peptides in acrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):24–29. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90260-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis B., Mahoney R. R. Inactivation of nisin by alpha-chymotrypsin. J Dairy Sci. 1969 Sep;52(9):1448–1449. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(69)86771-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford A. E. Diplococcin, an anti-bacterial protein elaborated by certain milk streptococci. Biochem J. 1944;38(2):178–182. doi: 10.1042/bj0380178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocin of a group B streptococcus: partial purification and characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):764–772. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Read R. S., McGiven A. R. Bacteriocin of a group A streptococcus: partial purification and properties. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):214–221. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead H. R. A substance inhibiting bacterial growth, produced by certain strains of lactic streptococci. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):1793–1800. doi: 10.1042/bj0271793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


