Abstract
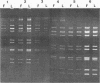
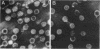
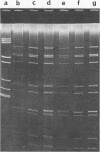
A procedure has been developed for the isolation of rotavirus from human fecal specimens based on the resistance of the virus to treatment with cold 1% lithium dodecyl sulfate at neutral pH. A single detergent treatment of fecal material followed by low- and high-speed centrifugations yielded a virus suspension of sufficient purity for viral ribonucleic acid to be analyzed directly by electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Detection of a new virus by electron microscopy of faecal extracts from children with acute gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):149–151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boatman S., Kaper J. M. Molecular organization and stabilizing forces of simple RNA viruses. IV. Selective interference with protein-RNA interactions by use of sodium dodecyl sulfate. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Graham A. F. Reovirus: RNA polymerase activity in purified virions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croxson M. C., Bellamy A. R. Two strains of human rotavirus in Auckland. N Z Med J. 1979 Sep 26;90(644):235–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H. Viral gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1979;25:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Sereno M. M., Wyatt R. G., Mebus C. A., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Comparison of human and animal rotavirus strains by gel electrophoresis of viral RNA. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. THE EXTRACTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM POLIOVIRUS BY TREATMENT WITH SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:360–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapoles J. E., Anderegg J. W., Rueckert R. R. Properties of poliovirus propagated in medium containing cesium chloride: implications for picornaviral structure. Virology. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr In vitro assembly of poliovirus-related particles. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Biochemical and biophysical characteristics of diarrhea viruses of human and calf origin. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1229–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1229-1235.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseto A., Escaig J., Delain E., Cohen J., Scherrer R. Structure of rotaviruses as studied by the freeze-drying technique. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):471–475. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90571-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Characteristics of the genome of human infantile enteritis virus (Rotavirus). J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):267–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.267-270.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the in vitro transcription of reovirus RNA catalyzed by reovirus cores. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):822–831. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen A. M., Cummings J. H. The microbial contribution to human faecal mass. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):45–56. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H. Serotypes of human rotavirus. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):39–39. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissis G., Lambert J. P. Different serotypes of human rotaviruses. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):38–39. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]