Abstract
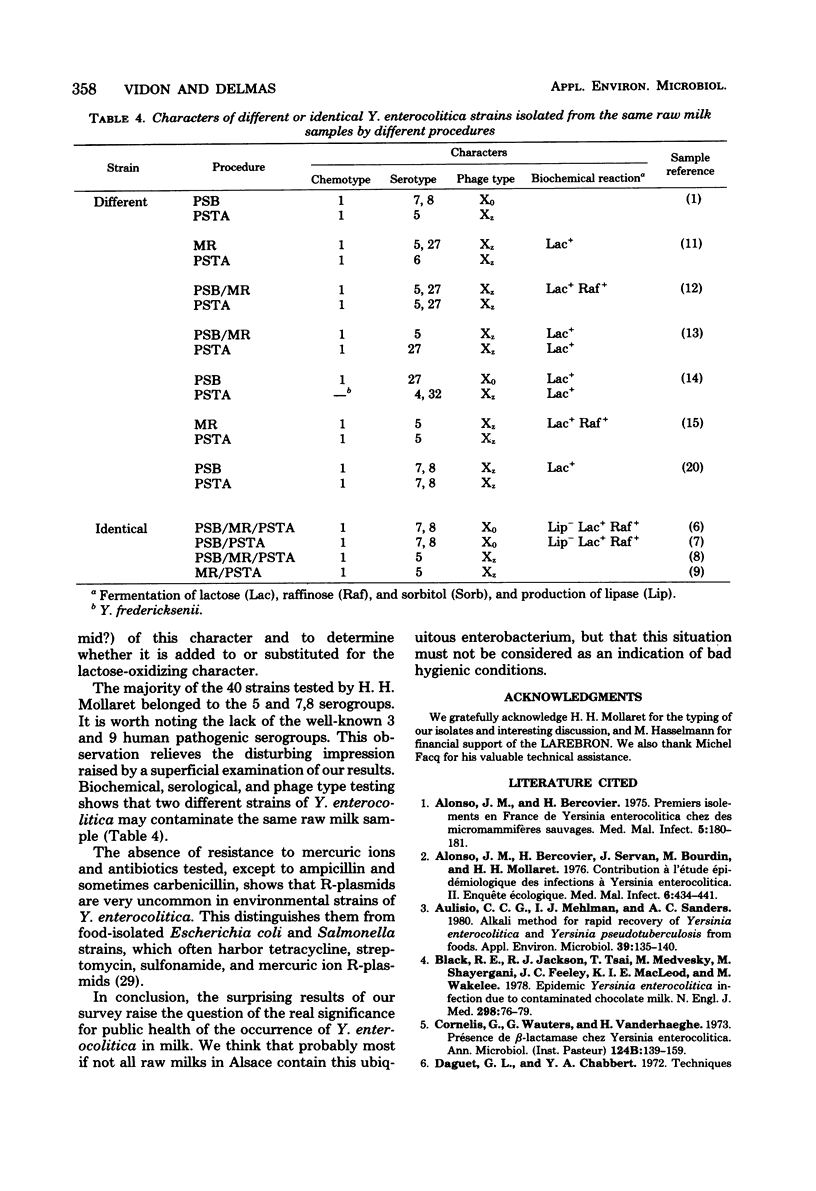
A total of 75 raw milk samples collected from a central dairy or from retailers in Alsace, France, were analyzed for the presence of Yersinia enterocolitica. Three procedures were used: enrichment at 4 degrees C for 1 month; enrichment in modified Rappaport medium at room temperature for 72 h after a preenrichment at 4 degrees C for 1 month; and enrichment in a new medium containing sucrose, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, sodium azide, and ampicillin (PSTA) at 28 degrees C for 48 h after a preenrichment at 4 degrees C for 1 month. Isolation of Y. enterocolitica was made on Hektoen medium plus ampicillin. Sixty-one samples were positive (81.4%), but the PSTA medium produced the greatest number of isolates. Biochemical, serological, and phage typing of 40 isolates showed that chemotype 1 and serogroup O:5 were predominant. In seven cases, two different strains were obtained from the same samples. Most of the 66 isolates tested for their antimicrobial susceptibility were resistant to ampicillin and carbenicillin, and all were sensitive to tetracycline, chloramphenicol, streptomycin, sulfonamides, and mercuric ions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aulisio C. C., Mehlman I. J., Sanders A. C. Alkali method for rapid recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis from foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.135-140.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Jackson R. J., Tsai T., Medvesky M., Shayegani M., Feeley J. C., MacLeod K. I., Wakelee A. M. Epidemic Yersinia enterocolitica infection due to contaminated chocolate milk. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 12;298(2):76–79. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801122980204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., Ito Y., Saito K., Tsubokura M., Otsuki K. Role of the fly in the transport of Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):1009–1010. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.1009-1010.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S., Greenwood J. R., Pickett M. J., Mah R. A. Recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica from streams and lakes of California. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):352–354. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.352-354.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith A. K., Feeley J. C., Skaliy P., Wells J. G., Wood B. T. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from well water and growth in distilled water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):745–750. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.745-750.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from milk and a dairy farm in Australia. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;46(1):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb02589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kurose M. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from cow's intestinal contents and beef meat. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1975 Feb;37(1):91–93. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.37.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko K. I., Hamada S., Kasai Y., Kato E. Occurrence of Yersinia enterocolitica in house rats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):314–318. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.314-318.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G. Yersinia enterocolitica in small rodents from Norway, Sweden and Finland. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen J. Yersinia enterocolitica in drinking-water. Scand J Infect Dis. 1972;4(2):125–127. doi: 10.3109/inf.1972.4.issue-2.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Harris M. E., McClain D., Smith R. E., Johnston R. W. Two modified selenite media for the recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica from meats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):205–209. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.205-209.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H. Two plating media modified with Tween 80 for isolating Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):215–216. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.215-216.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from Danish swine and dogs. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Oct;84B(5):317–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Toma S. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from raw milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):54–58. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.54-58.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadaro M., Infortuna M. Isolamento di Yersinia enterocolitica in Mitilus galloprovincialis Lamk. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1968 Nov 30;44(22):1896–1897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma S., Deidrick V. R. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from swine. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Dec;2(6):478–481. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.6.478-481.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma S. Survey on the incidence of Yersinia enterocolitica in the province of Ontario. Can J Public Health. 1973 Sep-Oct;64(5):477–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubokura M., Otsuki K., Itagaki K. Studies on Yersinia enterocolitica. I. Isolation of Y. enterocolitica from swine. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1973 Oct;35(5):419–424. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.35.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidon D. J., Jacob S., Ganzenmuller M. Incidences of simple and transferable drug resistance in Escherichia coli and Salmonella isolated from various foods: identification of a R plasmid in S. saint-paul. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Feb-Mar;129(2):155–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zen-Yoji H., Sakai S., Maruyama T., Yanagawa Y. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis from swine, cattle and rats at an abattoir. Jpn J Microbiol. 1974 Jan;18(1):103–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1974.tb00753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


