Abstract
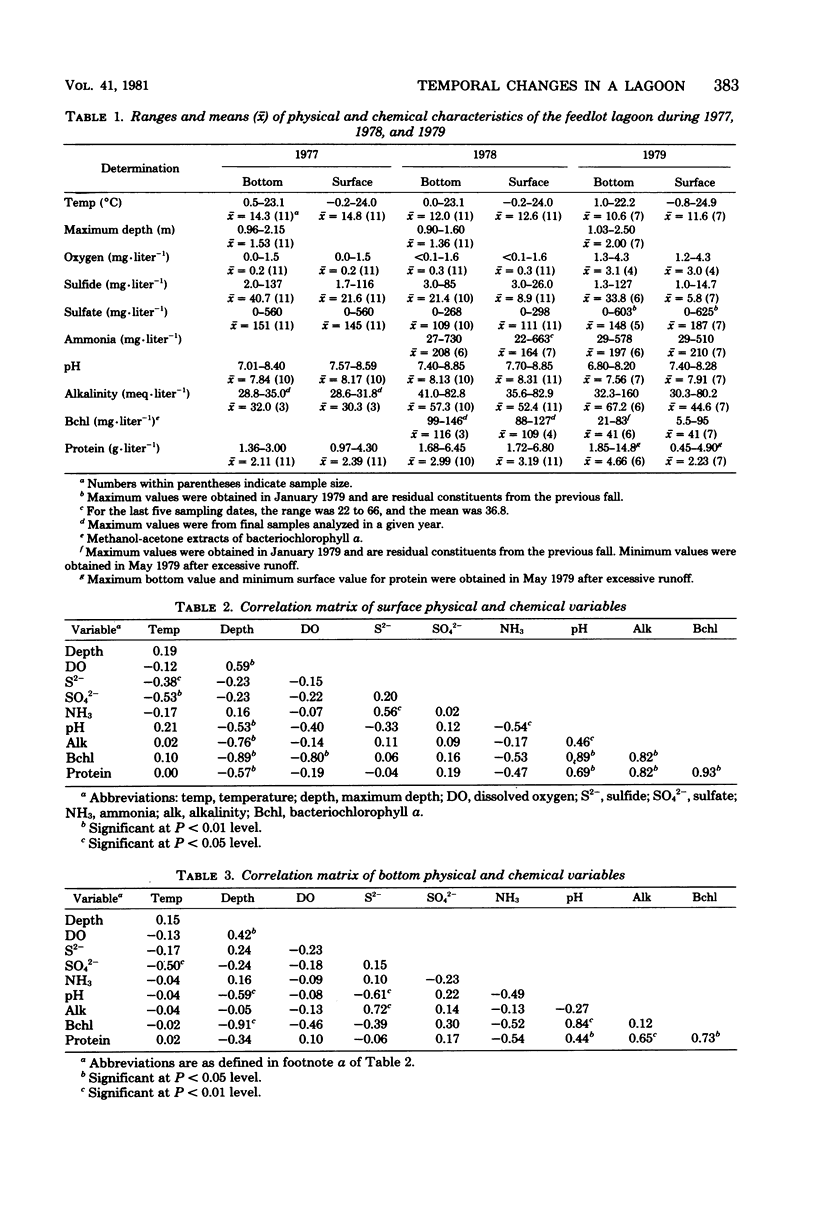
Temporal changes in a feedlot drainage lagoon with a predominance of the phototrophic purple sulfur bacterium, Thiopedia rosea, were investigated during a 3-year period. The surface protein and bacteriochlorophyll concentrations, which indirectly measure T. rosea abundance, peaked annually during the fall months and coincided with the intensity of pink coloration. Surface bacteriochlorophyll concentration correlated with pH, alkalinity, and protein. The pH range was optimal for the survival of T. rosea. Surface sulfide concentration, which increased over the winter and early spring, reached low levels during the fall months. The most striking pattern to emerge was the marked increase in sulfate concentration that occurred each fall and winter. The protein peaks, which preceded the sulfate peaks, were indicative of the sulfate concentrations that would follow. During 1977 and 1978, the lagoon was essentially anaerobic and provided adequate growth conditions for T. rosea. Above-average precipitation during early 1979 raised the water level and altered the chemistry of the lagoon. Dissolved oxygen was higher during the final year, and, concurrently, concentrations of bacteriochlorophyll declined. Aeration of the lagoon resulted in a decrease in T. rosea.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell D. E., Tiedje J. M. A morphological study of anaerobic bacteria from the hypolimnia of two Michigan lakes. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):362–376. doi: 10.1139/m75-051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell D. E., Tiedje J. M. The structure of anaerobic bacterial communities in the hypolimnia of several Michigan lakes. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):377–385. doi: 10.1139/m75-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart S. A., Turner M. E. Lagoons for livestock manure. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1965 Nov;37(11):1578–1596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm H. W., Vennes J. W. Occurrence of purple sulfur bacteria in a sewage treatment lagoon. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):988–996. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.988-996.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OYAMA V. I., EAGLE H. Measurement of cell growth in tissue culture with a phenol reagent (folin-ciocalteau). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):305–307. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siefert E., Irgens R. L., Pfennig N. Phototrophic purple and green bacteria in a sewage treatment plant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.38-44.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUEPER H. G., SCHLEGEL H. G. SULPHUR METABOLISM IN THIORHODACEAE. I. QUANTITATIVE MEASUREMENTS ON GROWING CELLS OF CHROMATIUM OKENII. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1964;30:225–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02046728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gemerden H. Growth measurements of Chromatium cultures. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;64(2):103–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00406968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


