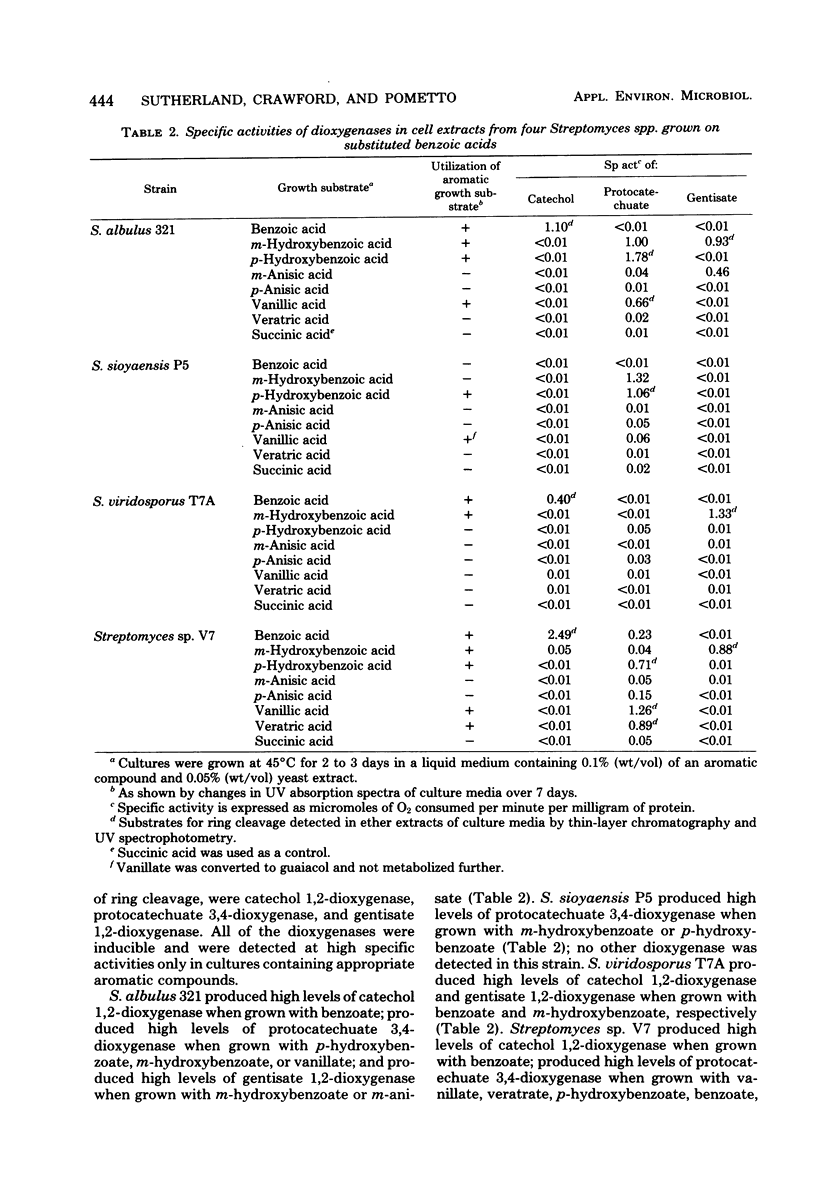
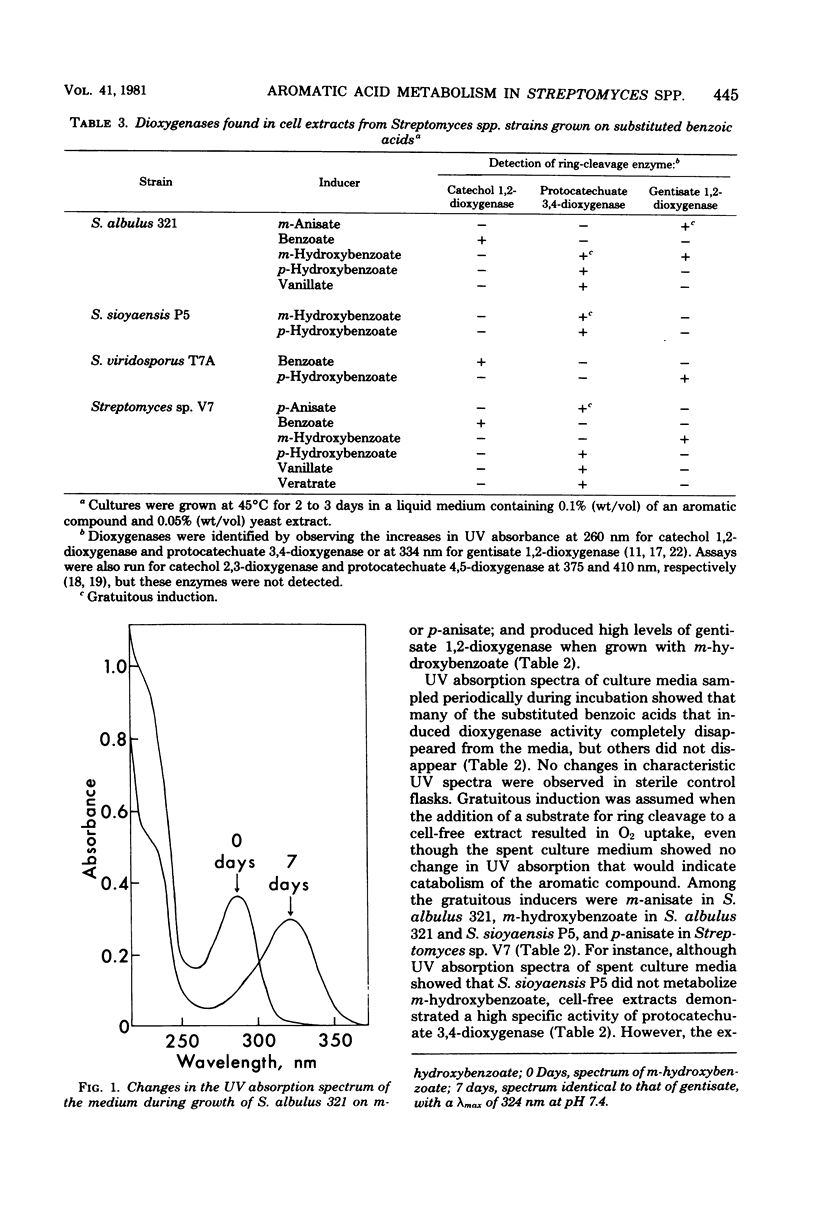
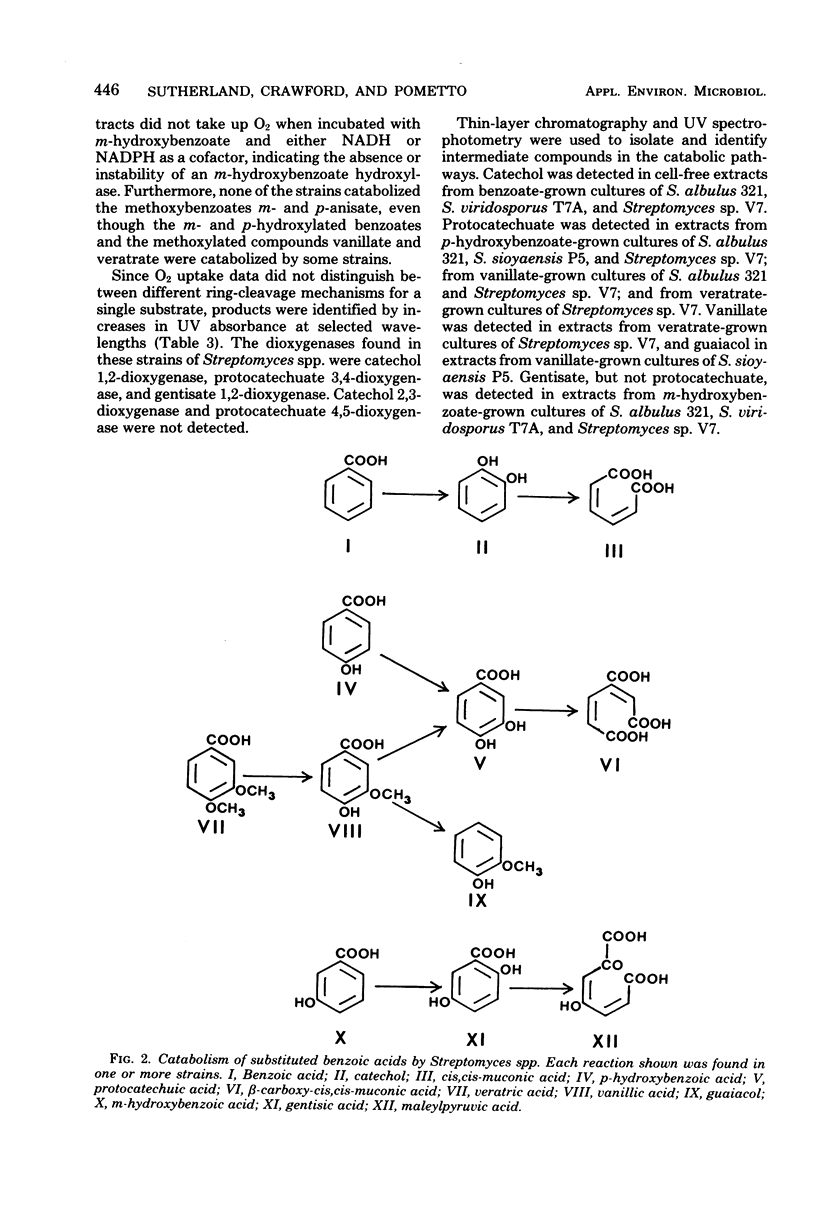
Abstract
Four thermotolerant actinomycetes from soil, identified as Streptomyces albulus 321, Streptomyces sioyaensis P5, Streptomyces viridosporus T7A, and Streptomyces sp. V7, were grown at 45°C in media containing either benzoic acid or hydroxyl- and methoxyl-substituted benzoic acids as the principal carbon sources. Benzoic acid was converted to catechol; p-hydroxybenzoic, vanillic, and veratric acids were converted to protocatechuic acid; and m-hydroxybenzoic acid was converted to gentisic acid. Catechol, protocatechuic acid, and gentisic acid were cleaved by catechol 1,2-dioxygenase, protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase, and gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase, respectively. Dioxygenases appeared only in induced cultures. m-Hydroxybenzoic, m-anisic, and p-anisic acids were gratuitous inducers of dioxygenases in some strains. One strain converted vanillic acid to guaiacol.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAIN R. B., CARTWRIGHT N. J. On the properties of some aromatic ring-opening enzymes of species of the genus Nocardia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jan 15;37:197–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90225-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTWRIGHT N. J., CAIN R. B. Bacterial degradation of the nitrobenzoic acids. Biochem J. 1959 Feb;71(2):248–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0710248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B., Bilton R. F., Darrah J. A. The metabolism of aromatic acids by micro-organisms. Metabolic pathways in the fungi. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):797–828. doi: 10.1042/bj1080797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright N. J., Smith A. R. Bacterial attack on phenolic ethers: An enzyme system demethylating vanillic acid. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):826–841. doi: 10.1042/bj1020826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catroux G., Fournier J. C., Riviere J. Mise en évidence rapide de lútilisation des acides-phénols par des souches bactériennes isolées de sol. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1969 Jan;116(1):99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinsworth W. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Stereospecific enzymes in the degradation of aromatic compounds by pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):922–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.922-931.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L., Hutton S. W., Chapman P. J. Purification and properties of gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase from Moraxella osloensis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):794–799. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.794-799.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L., McCoy E., Harkin J. M., Kirk T. K., Obst J. R. Degradation of methoxylated benzoic acids by a Nocardia from a lignin-rich environment: significance to lignin degradation and effect of chloro substituents. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Aug;26(2):176–184. doi: 10.1128/am.26.2.176-184.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L. Novel pathway for degradation of protocatechuic acid in Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):531–536. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.531-536.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L., Olson P. P. Microbial catabolism of vanillate: decarboxylation to guaiacol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):539–543. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.4.539-543.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Alderson G. The actinomycete-genus Rhodococcus: a home for the "rhodochrous" complex. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 May;100(1):99–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-100-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOJIMA Y., ITADA N., HAYAISHI O. Metapyrocatachase: a new catechol-cleaving enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1961 Aug;236:2223–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK L. The enzymic oxidation of gentisic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:117–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD D. L., STANIER R. Y., INGRAHAM J. L. The enzymatic formation of beta-carboxymuconic acid. J Biol Chem. 1954 Oct;210(2):809–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Stanier R. Y. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3776–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treccani V., Galli E., Catelani D., Sorlini C. Induction of 1,2- and 2,3-diphenol oxygenases in Pseudomonas desmolyticum. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1968;8(1):65–69. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630080108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



