Abstract
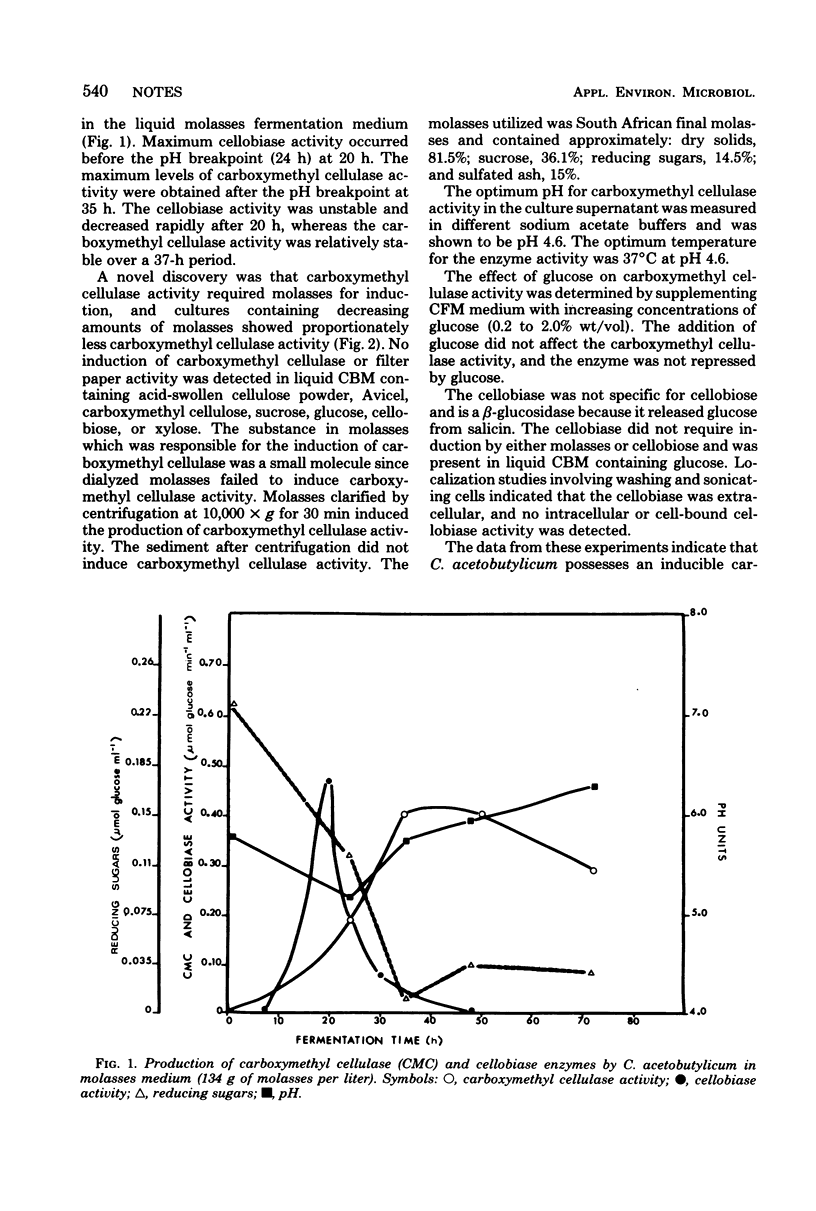
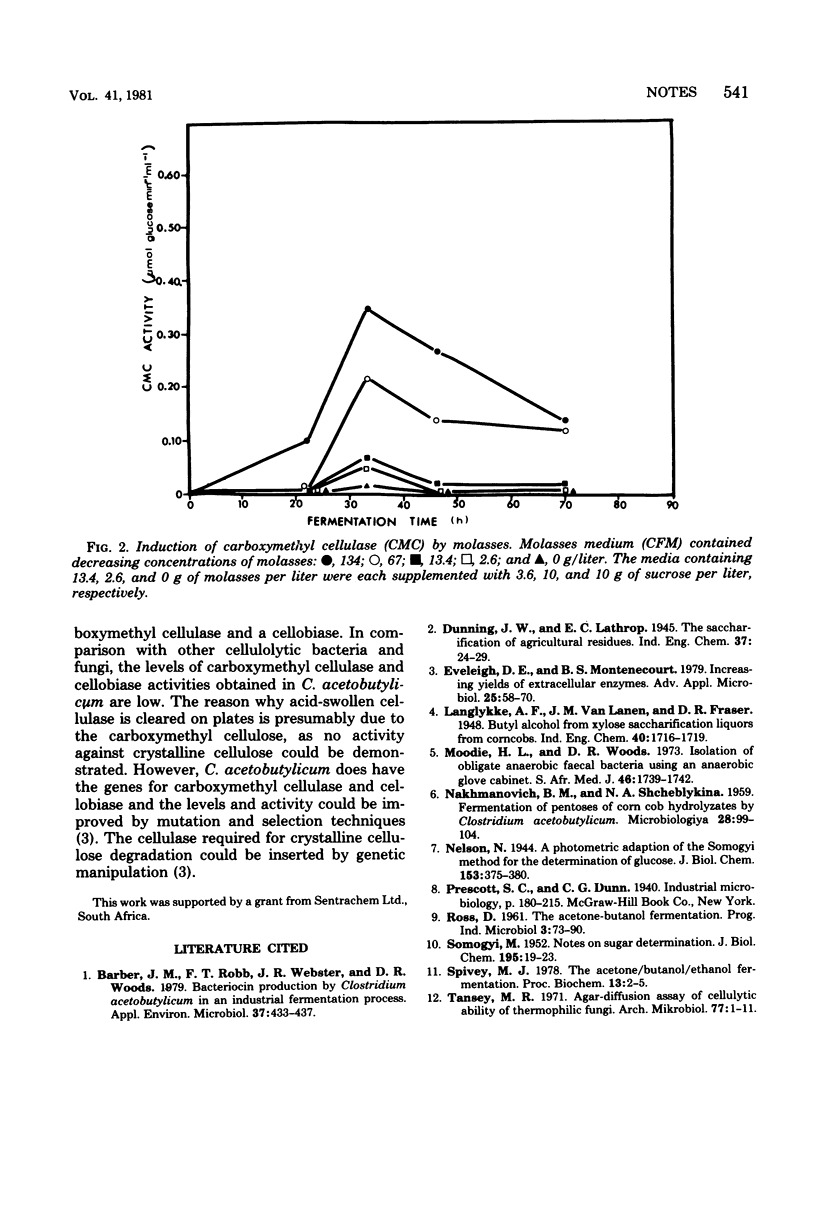
The production of a carboxymethyl cellulase and a cellobiase by Clostridium acetobutylicum was demonstrated. In liquid medium the carboxymethyl cellulase was induced by molasses, and it was not repressed by glucose. Optimum carboxymethyl cellulase activity occurred at pH 4.6 and 37 degrees C.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Moodie H. L., Woods D. R. Isolation of obligate anaerobic faecal bacteria using an anaerobic glove cabinet. S Afr Med J. 1973 Sep 29;47(38):1739–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS D. The acetone-butanol fermentation. Prog Ind Microbiol. 1961;3:71–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



