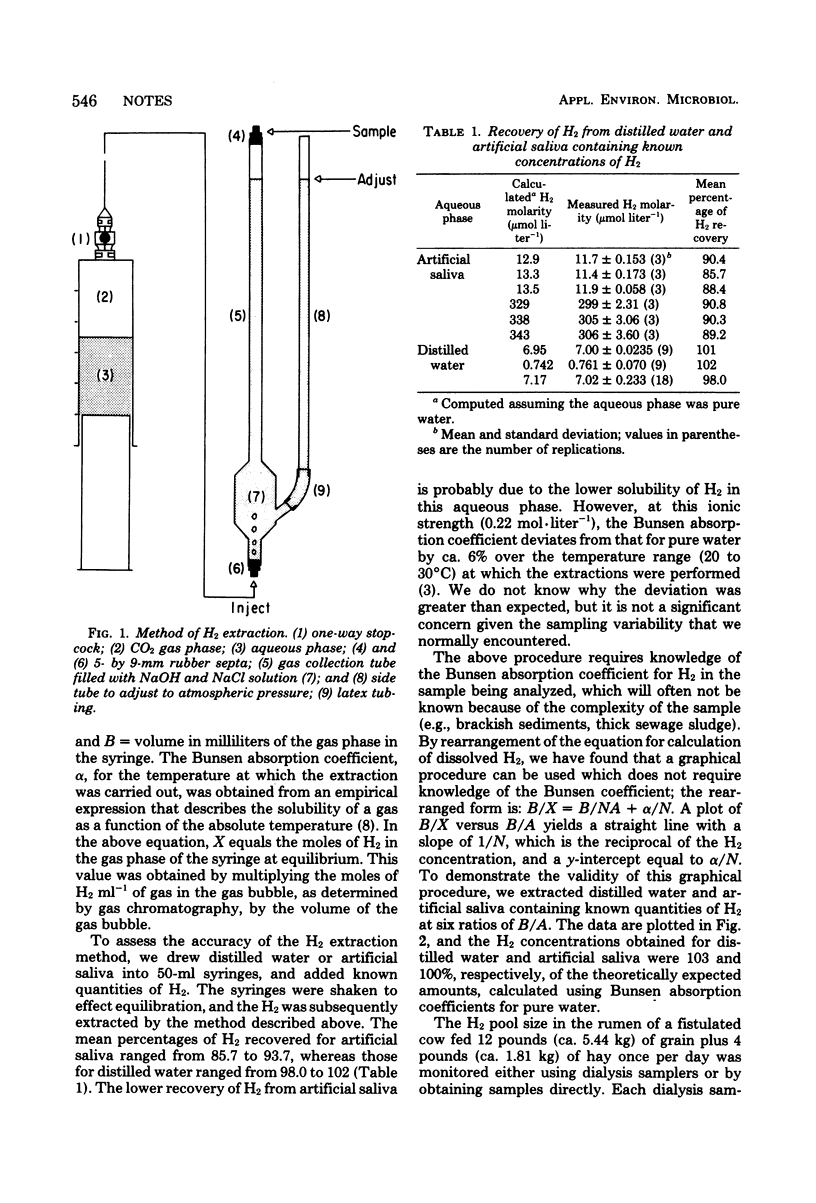
Abstract
A method of transferring dissolved H2 to a CO2 headspace and then absorbing out the CO2 to concentrate the H2 before gas chromatographic analysis was developed to measure low concentrations of dissolved H2. A detection limit of 10 pmol of H2 ml-1 of water was achieved. When used ot monitor H2 changes in a bovine rumen, a 10-fold increase in H2 was noted 1 h after feeding and then declined rapidly to the normal steady-state concentration of 1 microM.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Czerkawski J. W., Breckenridge G. Determination of concentration of hydrogen and some other cases dissolved in biological fluids. Lab Pract. 1971 May;20(5):403–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E. Hydrogen as an intermediate in the rumen fermentation. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):158–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00406327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall E. I. Studies on ruminant saliva. 1. The composition and output of sheep's saliva. Biochem J. 1948;43(1):99–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin M. J. Metabolic interactions among intestinal microorganisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1320–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



