Abstract
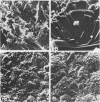
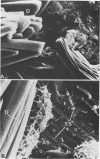
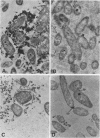
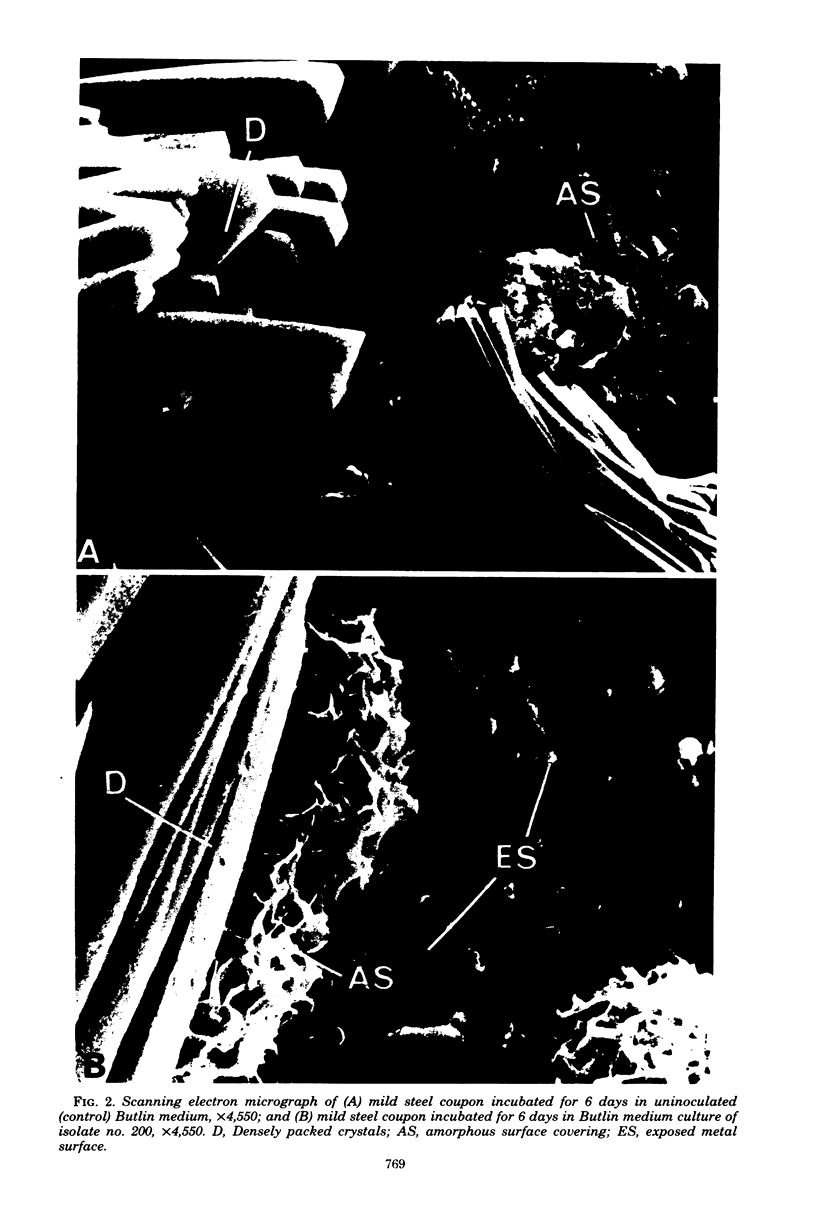
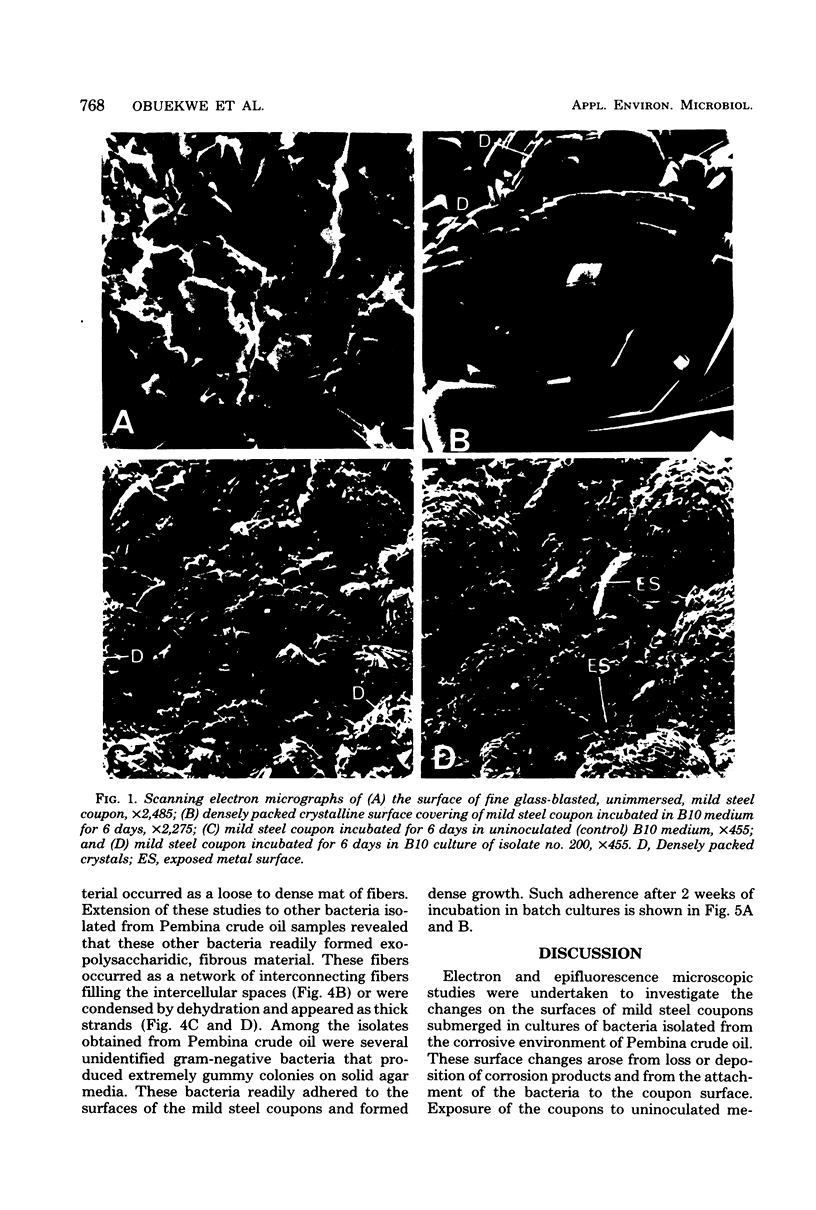
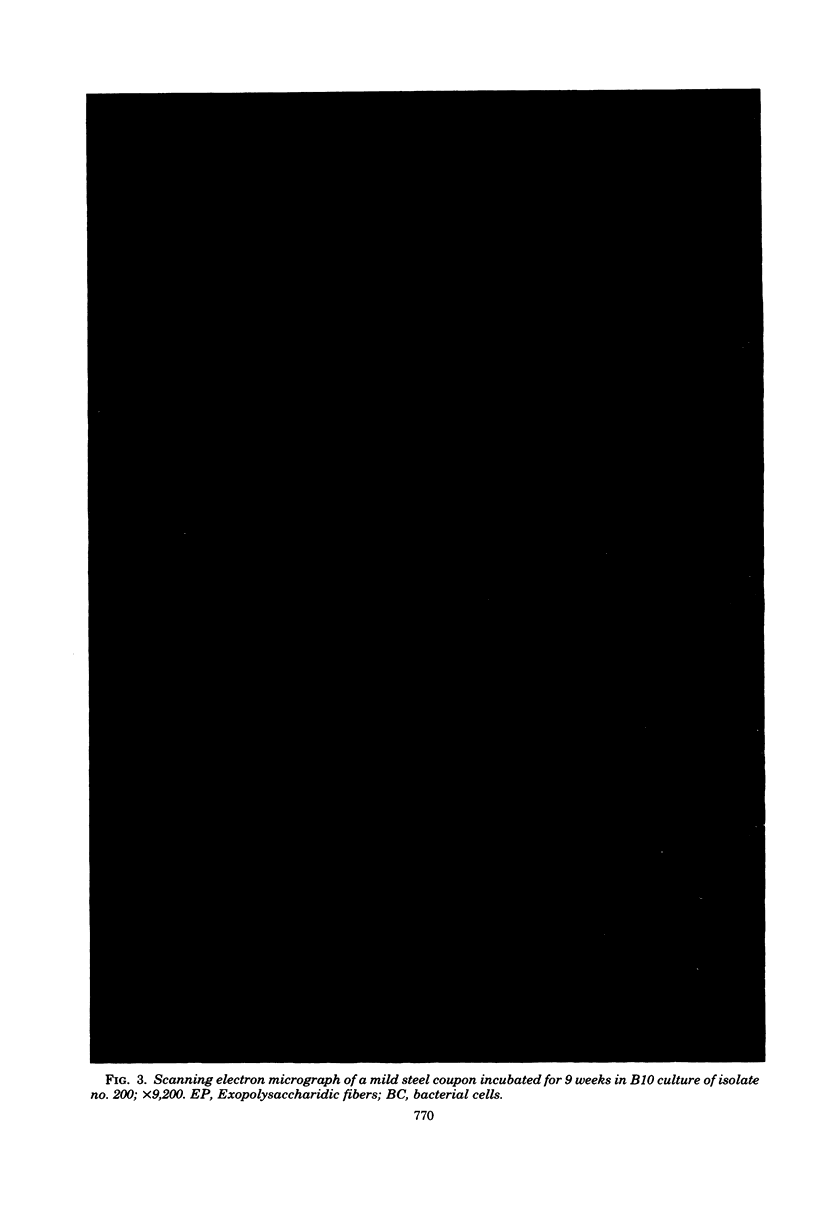
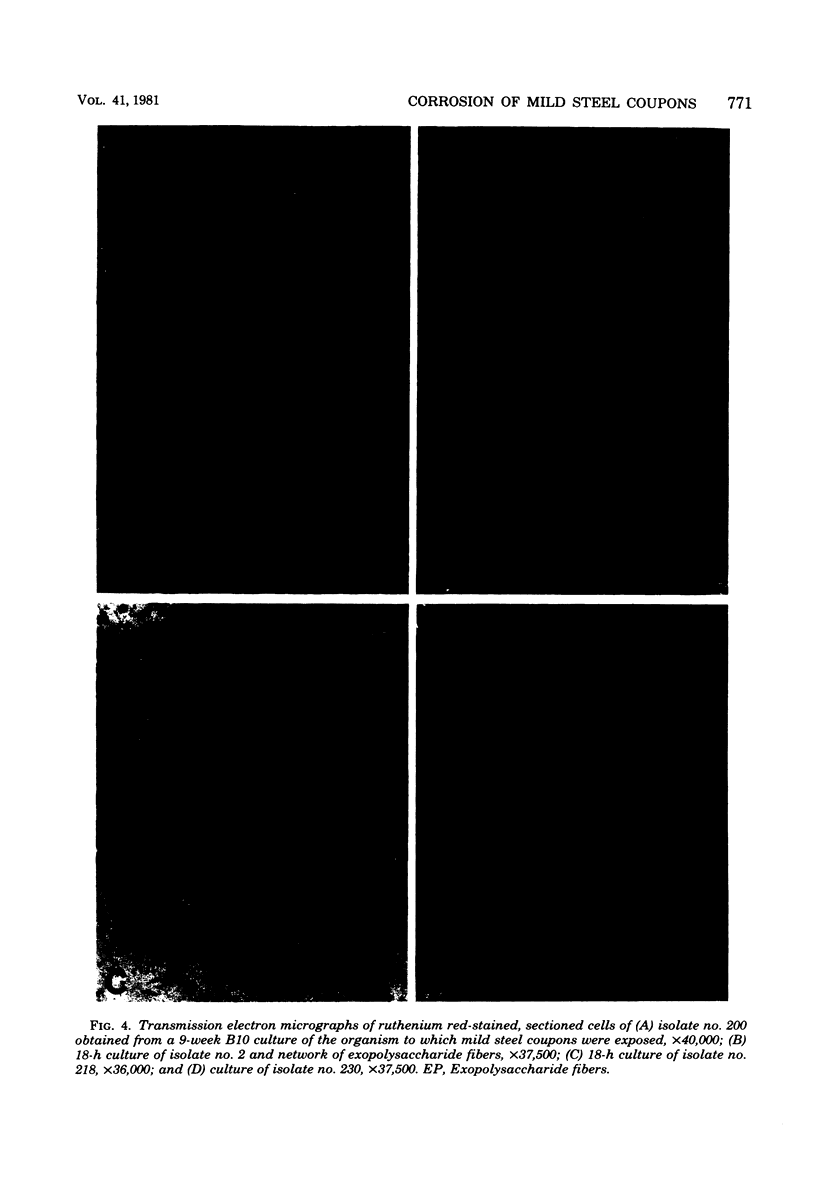
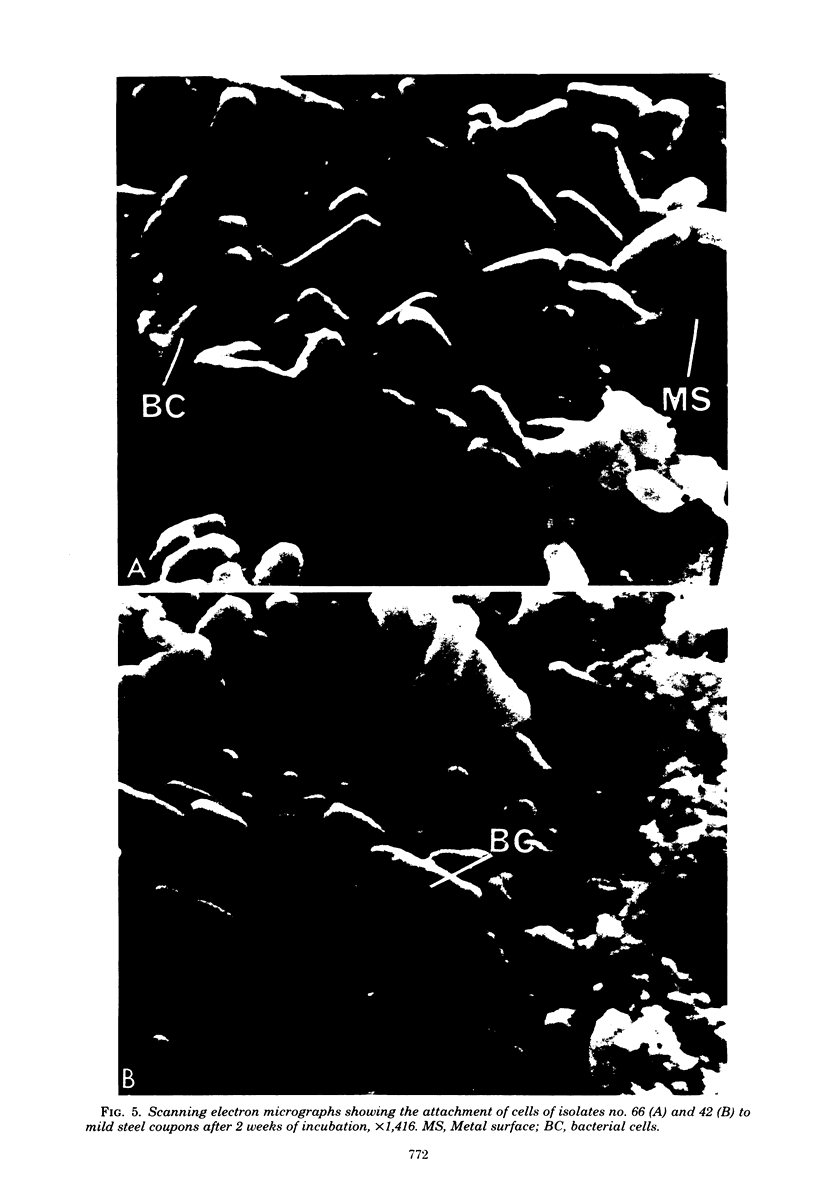
Changes which occur on the surface of mild steel coupons submerged in cultures of an Fe(III)-reducing bacterium, isolated from corroded pipe systems carrying crude oil, were studied microscopically to investigate the interaction between the corrosion-causing bacterium and the corroding mild steel coupon. Under micro-aerobic conditions and in the absence of the bacteria, a dense, crystalline, amorphous coat formed on the surface of the steel coupons. In the presence of bacteria the surface coat was extensively removed, exposing the bare metal to the environment. After about 2 weeks of exposure, the removal of the surface coating was followed by colonization of the metal surface by the bacteria. Colonization was mediated by fibrous, exopolysaccharidic material formed by the bacteria. Extension of studies to other bacteria isolated from crude oil and corroded pipes reveals that the formation of exopolysaccharide fibers and possession of adherent properties are common characteristics of bacteria from crude oil systems.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geesey G. G., Richardson W. T., Yeomans H. G., Irvin R. T., Costerton J. W. Microscopic examination of natural sessile bacterial populations from an alpine stream. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1733–1736. doi: 10.1139/m77-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Berman K. S., Knoettner P., Kapsimalis B. Dental caries and alveolar bone loss in gnotobiotic rats infected with capsule forming streptococci of human origin. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Jun;11(6):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. C., Roth I. L., Sanders W. M., 3rd Electron microscopic study of a slime layer. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):316–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.316-325.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie E. B., Brown K. N., Lam J., Costerton J. W. Morphological stabilization of capsules of group B streptococci, types Ia, Ib, II, and III, with specific antibody. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):609–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.609-617.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCowan R. P., Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Adherent bacterial populations on the bovine rumen wall: distribution patterns of adherent bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):233–241. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.233-241.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbandian J., Freedman M. L., Tanzer J. M., Lovelace S. M. Ultrastructure of Mutants of Streptococcus mutans with Reference to Agglutination, Adhesion, and Extracellular Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1170–1179. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1170-1179.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDERSEN J. W., BAKER B. E. Hydrolysis. Nature. 1952 May 31;169(4309):928–928. doi: 10.1038/169928a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson H., Irvin R., Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J. Ultrastructure and adhesion properties of Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):278–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.278-287.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobell C. E., Allen E. C. The Significance of Marine Bacteria in the Fouling of Submerged Surfaces. J Bacteriol. 1935 Mar;29(3):239–251. doi: 10.1128/jb.29.3.239-251.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]