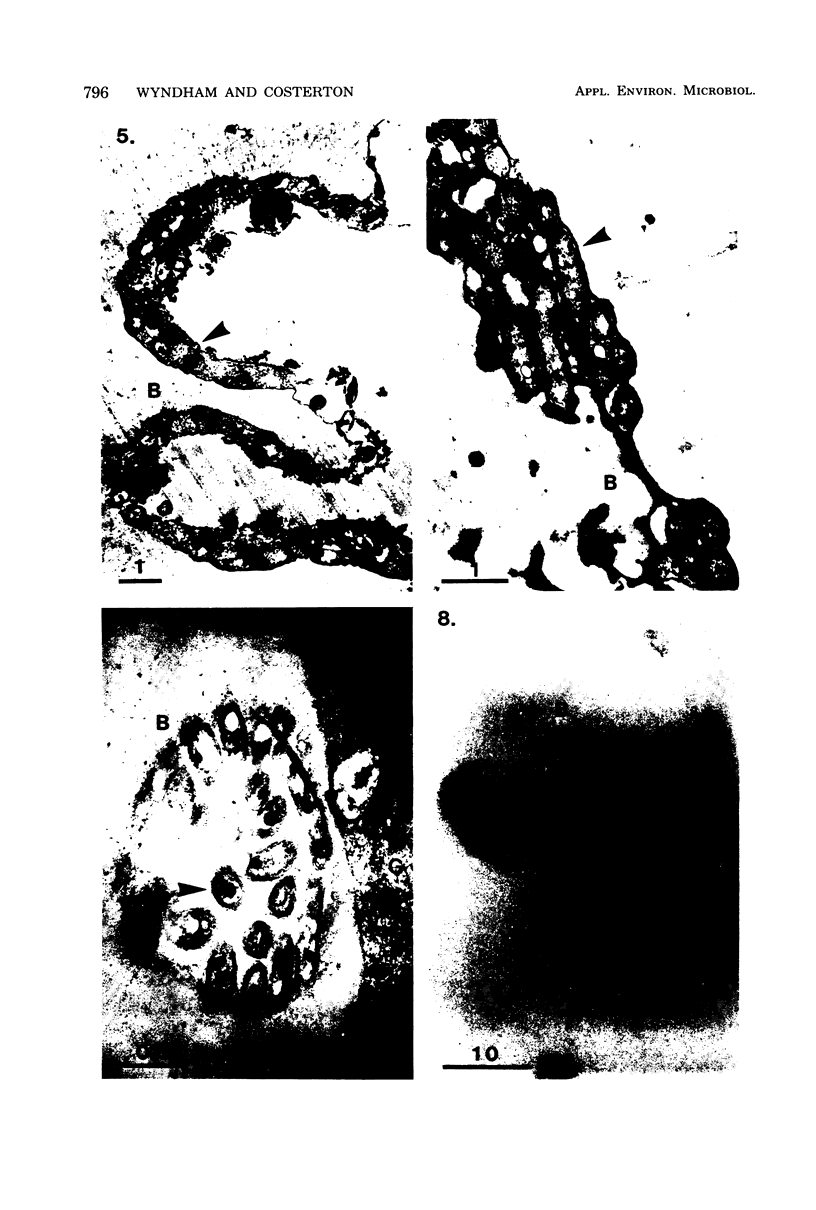
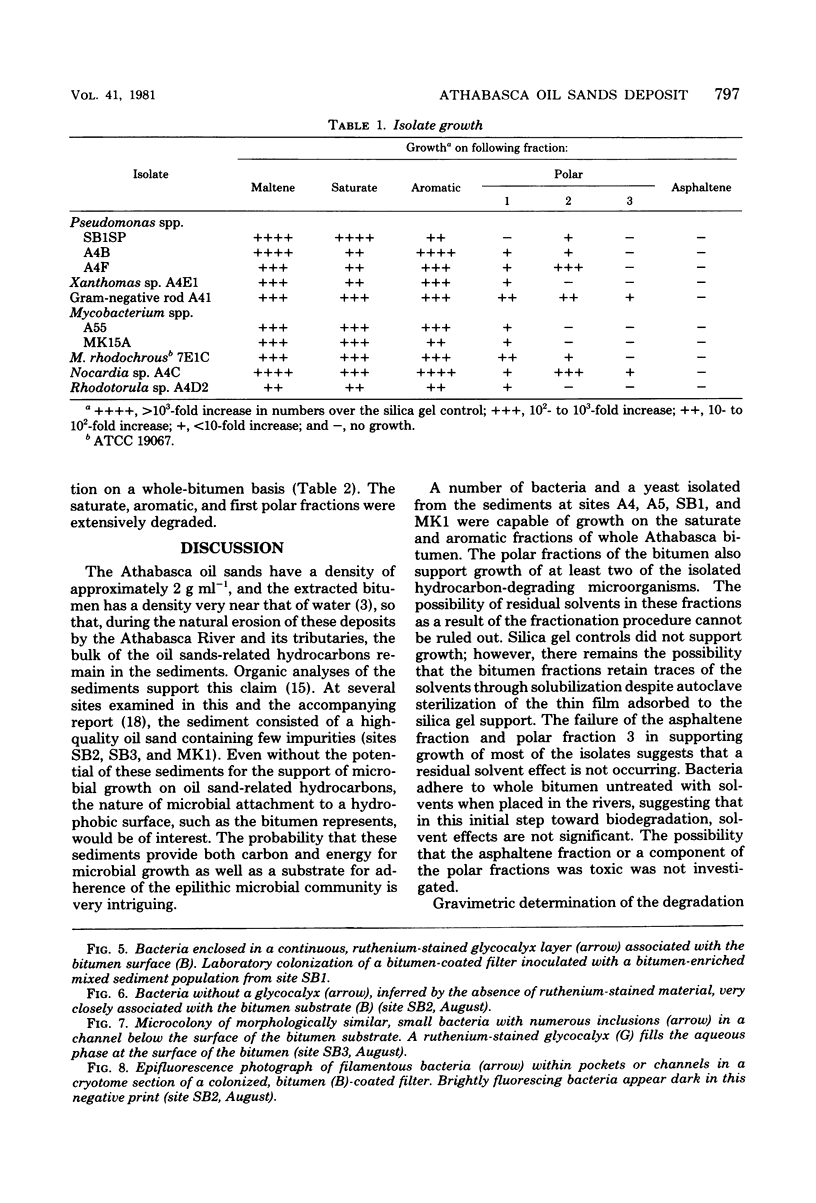
Abstract
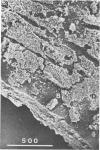
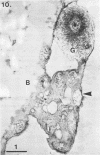
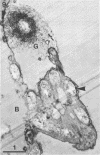
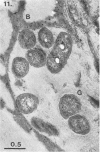
Bituminous hydrocarbons extracted from the Athabasca oil sands of north-eastern Alberta were adsorbed onto filter supports and placed at sites in the Athabasca River and its tributaries where these rivers come in contact with the oil sands formation. Colonization of the hydrocarbon surfaces at summer and winter ambient temperatures was examined by scanning and transmission electron microscopy as well as by epifluorescence microscopy of acridine orange-stained cross sections. Ruthenium red and alkaline bismuth stains visualized an association of bacteria with the hydrocarbon surface which was mediated by bacterial polysaccharides. Bacteria apparently lacking a glycocalyx were also found closely associated with the surface of the hydrophobic substrate and in channels within the substrate. A solvent precipitation and column chromatographic fractionation of the bitumen was followed by cross-tests for growth on the fractions by various isolated sediment microorganisms, as determined by epifluorescence count. All fractions except the asphaltenes supported the growth of at least two of the isolates, although fractionation of degraded bitumen revealed that the saturate, aromatic, and first polar fractions were preferentially degraded.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainsworth S. K., Ito S., Karnovsky M. J. Alkaline bismuth reagent for high resolution ultrastructural demonstration of periodate-reactive sites. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Dec;20(12):995–1005. doi: 10.1177/20.12.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartha R. The microbiology of aquatic oil spills. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1977;22:225–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardini G., Jurtshuk P. Cytochrome P-450 involvement in the oxidation of n-octane b cell-free extracts of Corynebacterium sp. strain 7E1C. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):6070–6072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Ingram J. M., Costerton J. W. Alkaline phosphatase localization and spheroplast formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Dec;16(12):1319–1324. doi: 10.1139/m70-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter S. C., Sullivan J. D., Williams J., Watson S. W. Influence of substrate wettability on the attachment of marine bacteria to various surfaces. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):298–308. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.298-308.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. S., Finnerty W. R. Microbial assimilation of hydrocarbons. I. The fine-structure of a hydrocarbon oxidizing Acinetobacter sp. Arch Microbiol. 1975;102(2):75–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00428349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C., Cruickshank R. H. Cell surface hydrophobicity and the orientation of certain bacteria at interfaces. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Apr 8;91(1):29–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00409536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. F. Petroleum: tar quantities floating in the northwestern atlantic taken with a new quantitative neuston net. Science. 1971 Jul 30;173(3995):430–432. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3995.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAEUBLI W. A new embedding technique for electron microscopy, combining a water-soluble epoxy resin (Durcupan) with water-insoluble Araldite. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jan;16:197–201. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. D., Colwell R. R., Petrakis L. Microbial petroleum degradation: application of computerized mass spectrometry. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Nov;21(11):1760–1767. doi: 10.1139/m75-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlake D. W., Jobson A., Phillippe R., Cook F. D. Biodegradability and crude oil composition. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Jul;20(7):915–928. doi: 10.1139/m74-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyndham R. C., Costerton J. W. Heterotrophic potentials and hydrocarbon biodegradation potentials of sediment microorganisms within the athabasca oil sands deposit. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):783–790. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.783-790.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerberg A., Diver A., Peeri Z., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: chemical and physical properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.414-420.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]