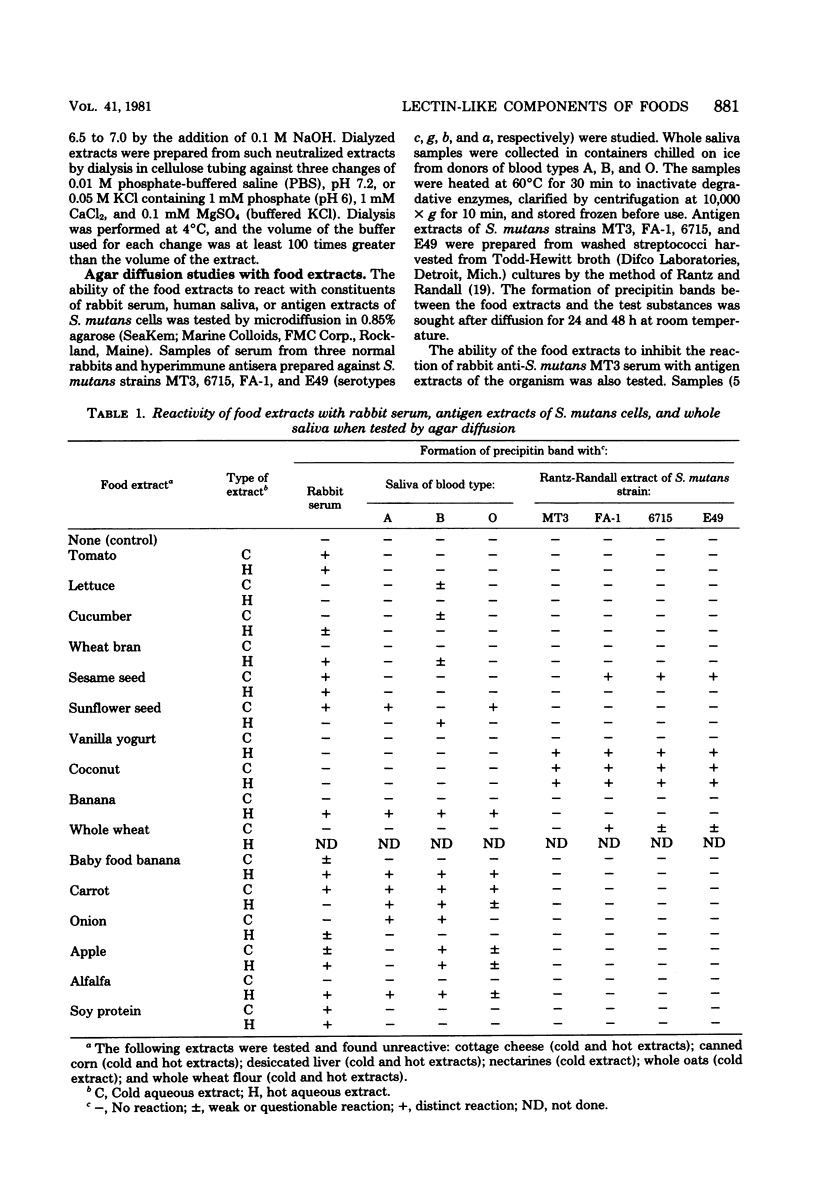
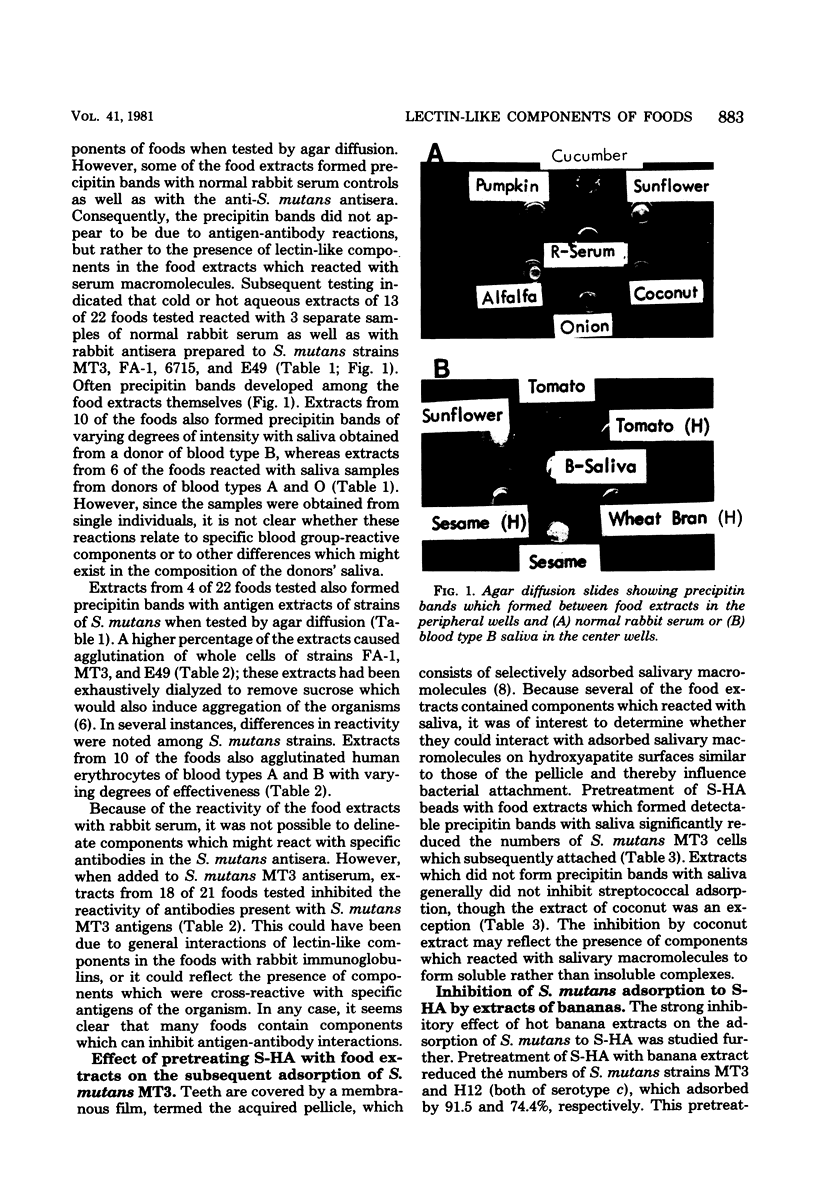
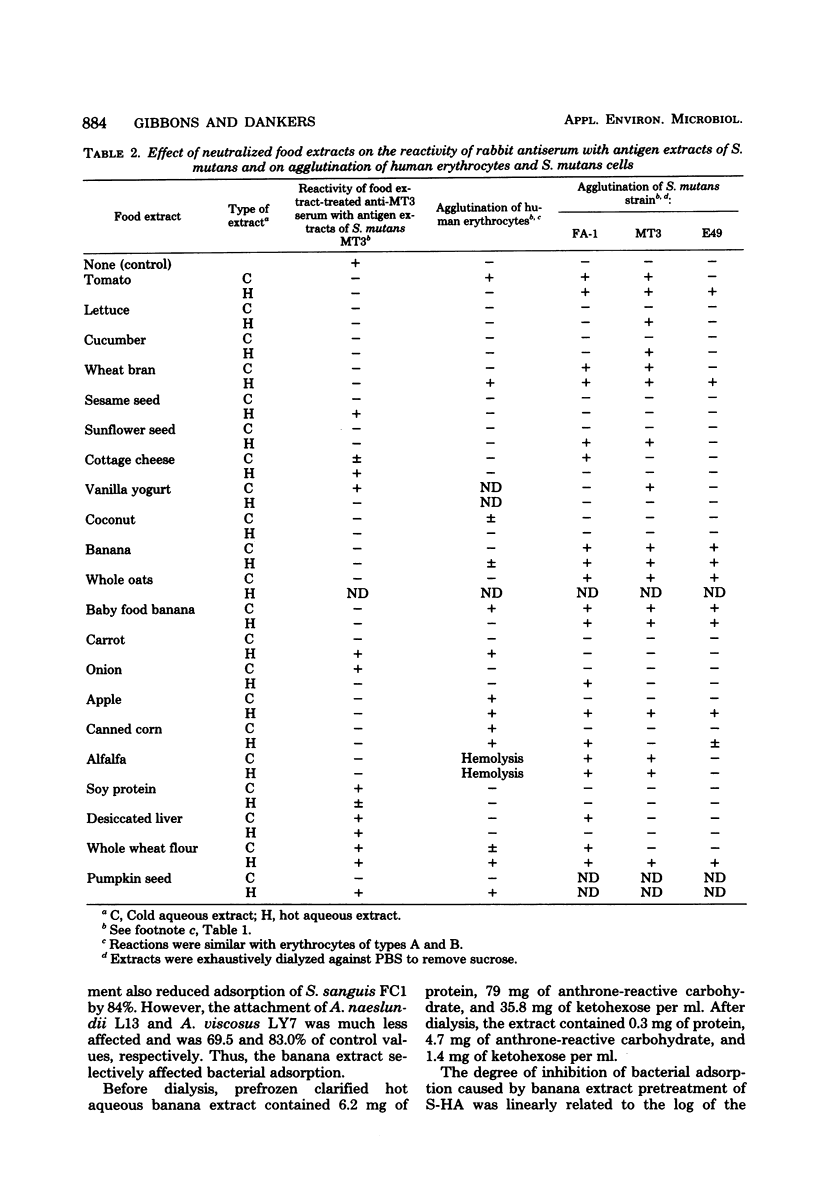
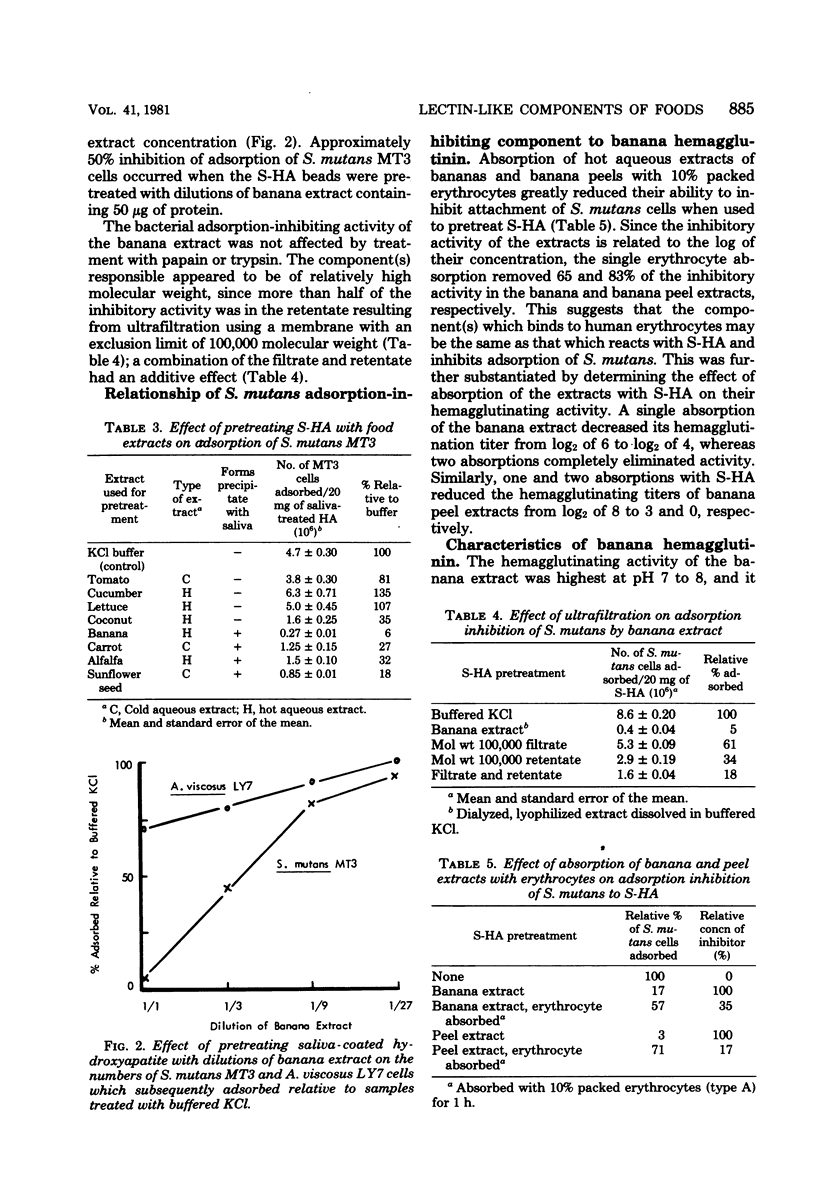
Abstract
Hot and cold aqueous extracts were prepared from 22 commonly ingested fruits, vegetables, and seeds. When tested by agar diffusion, extracts from 13 and 10 of the foods formed precipitin bands with samples of normal rabbit serum and human saliva, respectively; extracts from four of the foods also reacted with antigen extracts of strains of Streptococcus mutans. When added to rabbit antiserum, extracts from 18 of 21 foods tested inhibited reactivity with antigen extracts derived from S. mutans MT3. Extracts from 16 foods agglutinated whole S. mutans cells, whereas those from 10 foods agglutinated human erythrocytes of blood types A and B. The lectin-like activities of extracts which reacted with human saliva were studied further. Pretreatment of saliva-coated hydroxyapatite (S-HA) beads with extracts of bananas, coconuts, carrots, alfalfa, and sunflower seeds markedly reduced the subsequent adsorption of S. mutans MT3. Pretreatment of S-HA with banana extract also strongly inhibited adsorption of S. mutans H12 and S. sanguis C1, but it had little effect on attachment of Actinomyces naeslundii L13 or A. viscosus LY7. Absorption experiments indicated that the component(s) in banana extract responsible for inhibiting streptococcal adsorption to S-HA was identical to that which bound to human erythrocytes. The banana hemagglutinin exhibited highest activity between pH 7 and 8, and it was inhibited by high concentrations of glucosamine, galactosamine, and, to a lesser extent, mannosamine. Other sugars tested had no effect. The selective bacterial adsorption-inhibiting effect noted for banana extract was also observed in studies with purified lectins. Thus, pretreating S-HA with wheat germ agglutinin and concanavalin A inhibited adsorption of S. mutans MT3 cells, whereas peanut agglutinin, Ulex agglutinin, Dolichos agglutinin, and soybean agglutinin had little effect; none of these lectins affected attachment of A. viscosus LY7. Collectively, the observations suggest that many foods contain lectins which can interact with components of human saliva and S. mutans cells. Because of their potential to influence host-parasite interactions in the mouth and elsewhere in the gastrointestinal canal, these reactions warrant further study.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bammann L. L., Gibbons R. J. Immunoglobulin A antibodies reactive with Streptococcus mutans in saliva of adults, children, and predentate infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):538–543. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.538-543.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D. Daucus carrota (carrot)--a selective bacteriosorbent. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:327–333. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Bammann L. L., Gibbons R. J. Comparative estimates of bacterial affinities and adsorption sites on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):846–853. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.846-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Leung W. L., Fillery E. D., Grove D. A. Mannose-contaminating agglutinin for Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.427-434.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Fitzgerald R. J. Dextran-induced agglutination of Streptococcus mutans, and its potential role in the formation of microbial dental plaques. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.341-346.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Qureshi J. V. Virulence-related physiological changes and antigenic variation in populations of Streptococcus mutans colonizing gnotobiotic rats. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1082–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1082-1091.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Gill K., Slade H. D. Binding of lectins to Streptococcus mutans cells and type-specific polysaccharides, and effect on adherence. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.708-716.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYES P. H., JORDAN H. V. PERIODONTAL LESIONS IN THE SYRIAN HAMSTER. III. FINDINGS RELATED TO AN INFECTIOUS AND TRANSMISSIBLE COMPONENT. Arch Oral Biol. 1964 Jul-Aug;9:377–400. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(64)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler W., Prokop O., Kühnemund O. Routine identification of group-C streptococci by means of an agglutinin (protectin) from the albumen gland of the edible snail, Helix pomatia. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):127–130. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liener I. E. Phytohemagglutinins: their nutritional significance. J Agric Food Chem. 1974 Jan-Feb;22(1):17–22. doi: 10.1021/jf60191a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Sharon N. The biochemistry of plant lectins (phytohemagglutinins). Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42(0):541–574. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottensooser F., Nakamizo Y., Sato M., Miyamoto Y., Takizawa K. Lectins detecting group C streptococci. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):971–973. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.971-973.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi J. V., Goldner M., Riche W. H., Hargreaves J. A. Streptococcus mutans serotypes in young schoolchildren. Caries Res. 1977;11(3):141–152. doi: 10.1159/000260260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer R. L., Keller K. F., Doyle R. J. Lectins in diagnostic microbiology: use of wheat germ agglutinin for laboratory identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):669–672. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.669-672.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson D. L., Thorne D. R., Loh H. H. Lectins: endogenous carbohydrate-binding proteins from vertebrate tissues: functional role in recognition processes? Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(9):727–748. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staat R. H., Doyle R. J., Langley S. D., Suddick R. P. Modification of in vitro adherence of Streptococcus mutans by plant lectins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:639–647. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Handel E. Determination of fructose and fructose-yielding carbohydrates with cold anthrone. Anal Biochem. 1967 Apr;19(1):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]