Abstract
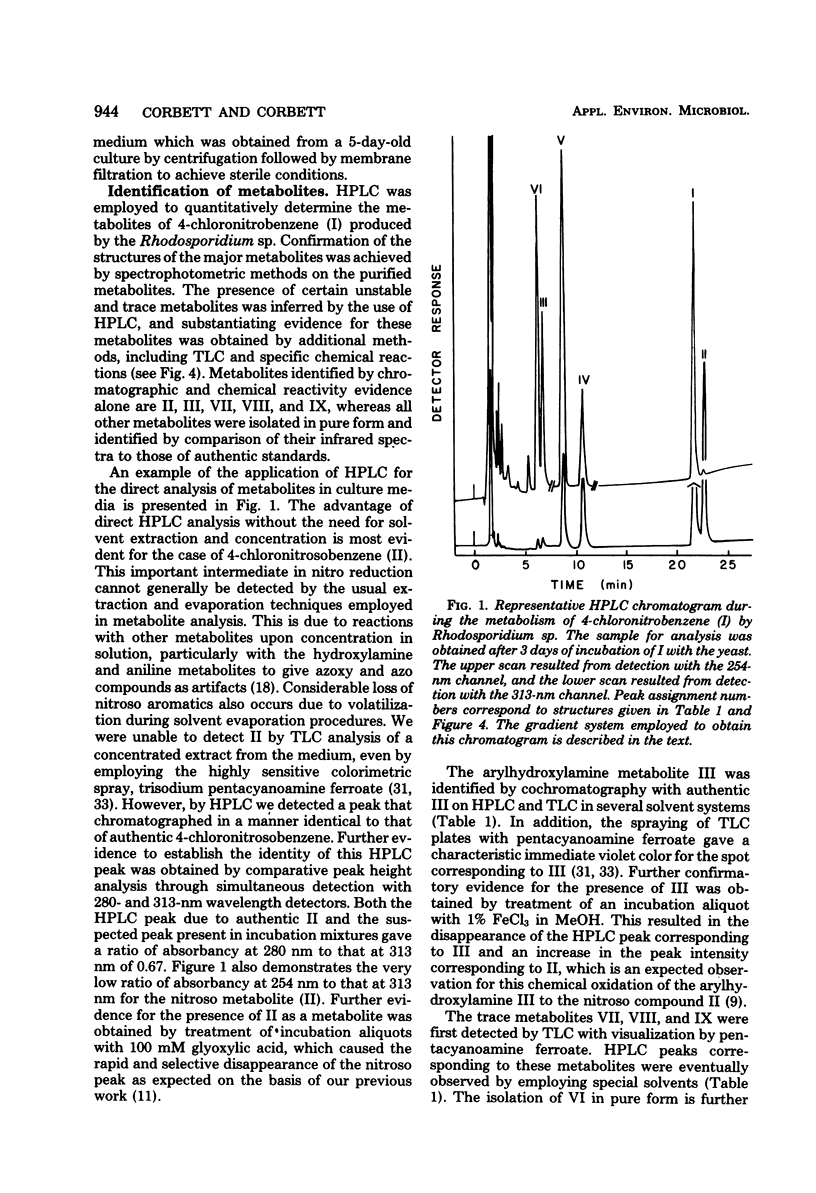
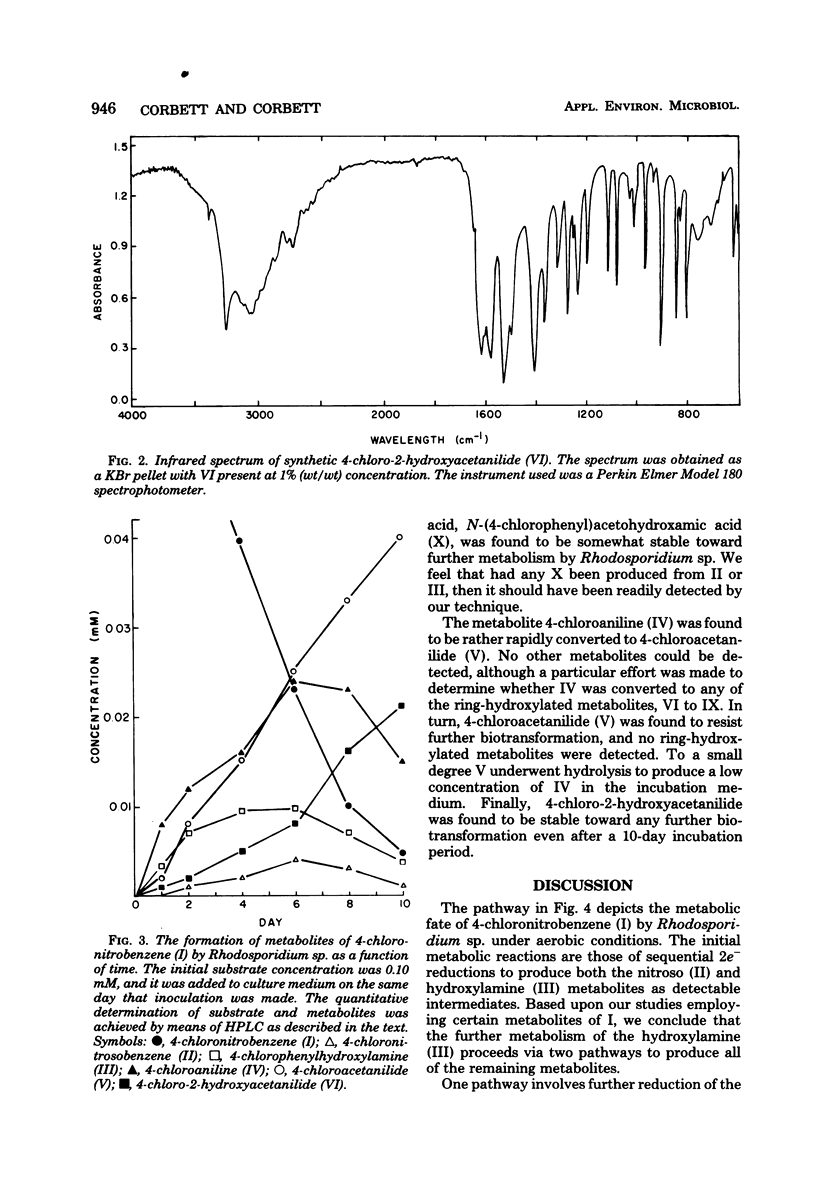
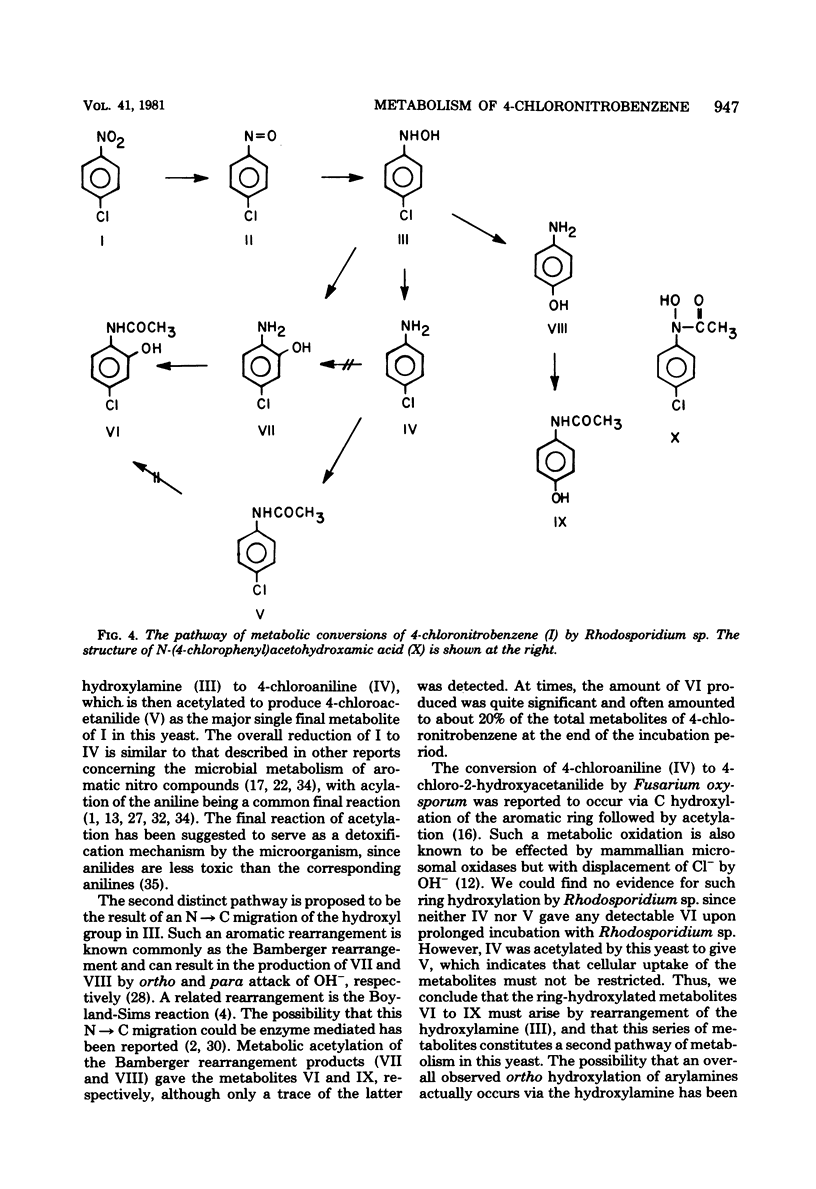
The yeast Rhodosporidium sp. metabolized 4-chloronitrobenzene by a reductive pathway to give 4-chloroacetanilide and 4-chloro-2-hydroxyacetanilide as the major final metabolites. The intermediate production of 4-chloronitrosobenzene, 4-chlorophenylhydroxylamine, and 4-chloroaniline was demonstrated by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Additional studies with selected metabolites established that the metabolite 4-chloro-2-hydroxyacetanilide was produced by an initial Bamberger rearrangement of the hydroxylamine metabolite, followed by acetylation. Direct C hydroxylation of the aromatic ring was not observed in this species. No hydroxamic acid production was detected, even though significant concentrations of the nitroso and hydroxylamine precursors to this functional group were observed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin M. K., Hutson D. H. The metabolism of 3-chloro-4-fluoro-aniline in dog and rat. Xenobiotica. 1980 Feb;10(2):135–144. doi: 10.3109/00498258009033739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu C. W., Lee L. H., Wang C. Y., Bryan G. T. Mutagenicity of some commercially available nitro compounds for Salmonella typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1978 Sep;58(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(78)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett M. D., Chipko B. R., Batchelor A. O. The action of chloride peroxidase on 4-chloroaniline. N-oxidation and ring halogenation. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):893–903. doi: 10.1042/bj1870893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett M. D., Chipko B. R. N-phenylglycolhydroxamate production by the action of transketolase on nitrosobenzene. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 1;165(2):263–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1650263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett M. D., Chipko B. R., Paul J. H. The production of hydroxamic acid metabolites of nitrosobenzene by Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1978 Jan-Feb;1(3):259–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett M. D., Chipko B. R. Quantitative determination of N-arylaceto- and N-arylglycolhydroxamic acids in biochemical reaction mixtures. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90722-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Guroff G., Udenfriend S., Witkop B. Hydroxylation of alkyl and halogen substituted anilines and acetanilides by microsomal hydroxylases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Jan;17(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell J. W., Hunter I. L., Tallman A. S. Marine basidiomycetous yeasts (Rhodosporidium spp. n.) with tetrapolar and multiple allelic bipolar mating systems. Can J Microbiol. 1973 May;19(5):643–657. doi: 10.1139/m73-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. D., Plimmer J. R., Klingebiel U. I. Microbial oxidation of 4-chloroaniline. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 Jan-Feb;21(1):127–132. doi: 10.1021/jf60185a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiese M., Taeger K. The fate of phenylhydroxylamine in human red cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976;292(1):59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00506490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick N. G., Feeherry F. E., Levinson H. S. Microbial transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and other nitroaromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):949–958. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.949-958.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. G., Pohl L. R., Krishna G. The requirement of the gut flora in nitrobenzene-induced methemoglobinemia in rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 May 1;25(9):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90507-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel S., Bollag J. M. Formylation and acetylation of 4-chloroaniline by a Streptomyces sp. Acta Microbiol Pol. 1977;26(1):59–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Uchiyama M. Pathway of nitro reduction of parathion by spinach homogenate. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 Mar-Apr;23(2):281–286. doi: 10.1021/jf60198a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweedy B. G., Loeppky C., Ross J. A. Metobromuron: acetylation of the aniline moiety as a detoxification mechanism. Science. 1970 Apr 24;168(3930):482–483. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3930.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehleke H., Nestel K. Hydroxylamino- und Nitrosobiphenyl: Biologische Oxydationsprodukte von 4-Aminobiphenyl und Zwischenprodukte der Reduktion von 4-Nitrobiphenyl. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1967;257(2):151–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Alfen N. K., Kosuge T. Microbial metabolism of the fungicide 2,6-dichloro-4-nitroaniline. J Agric Food Chem. 1974 Mar-Apr;22(2):221–224. doi: 10.1021/jf60192a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


