Abstract
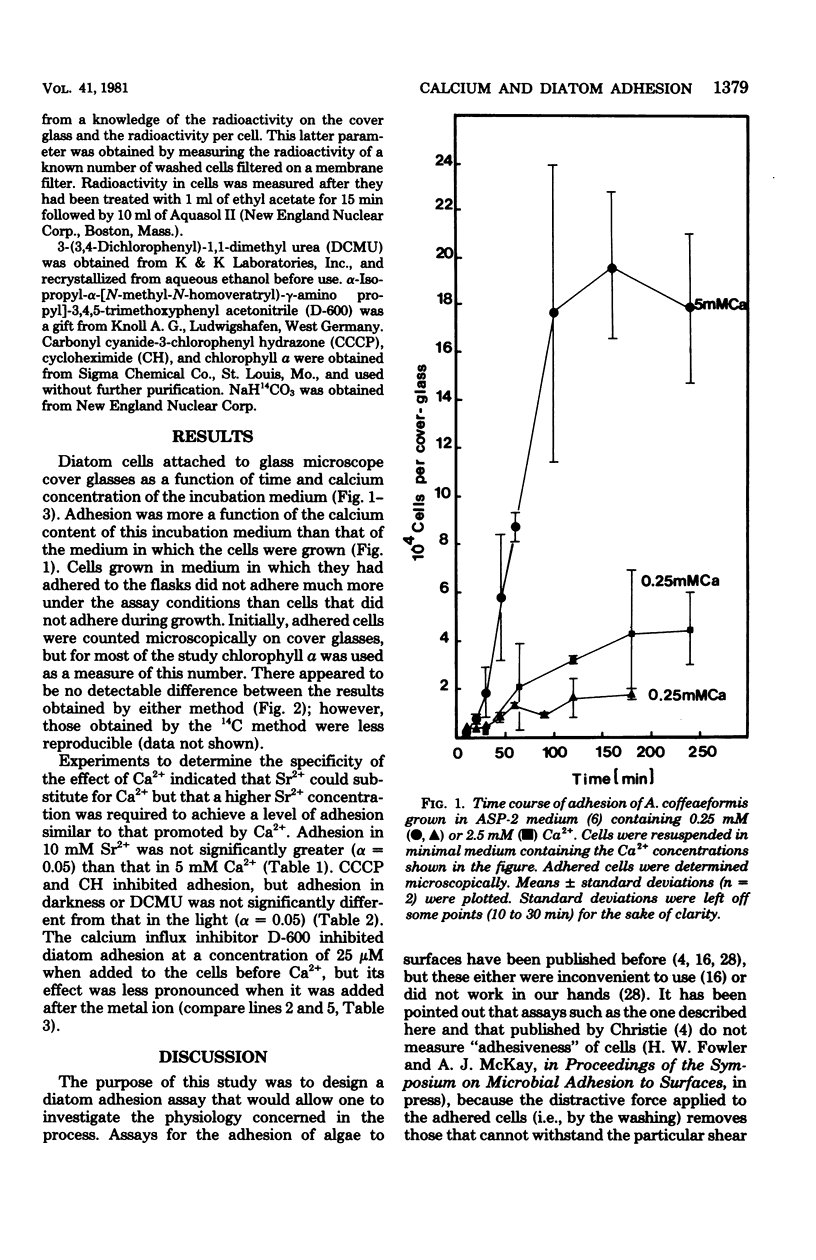
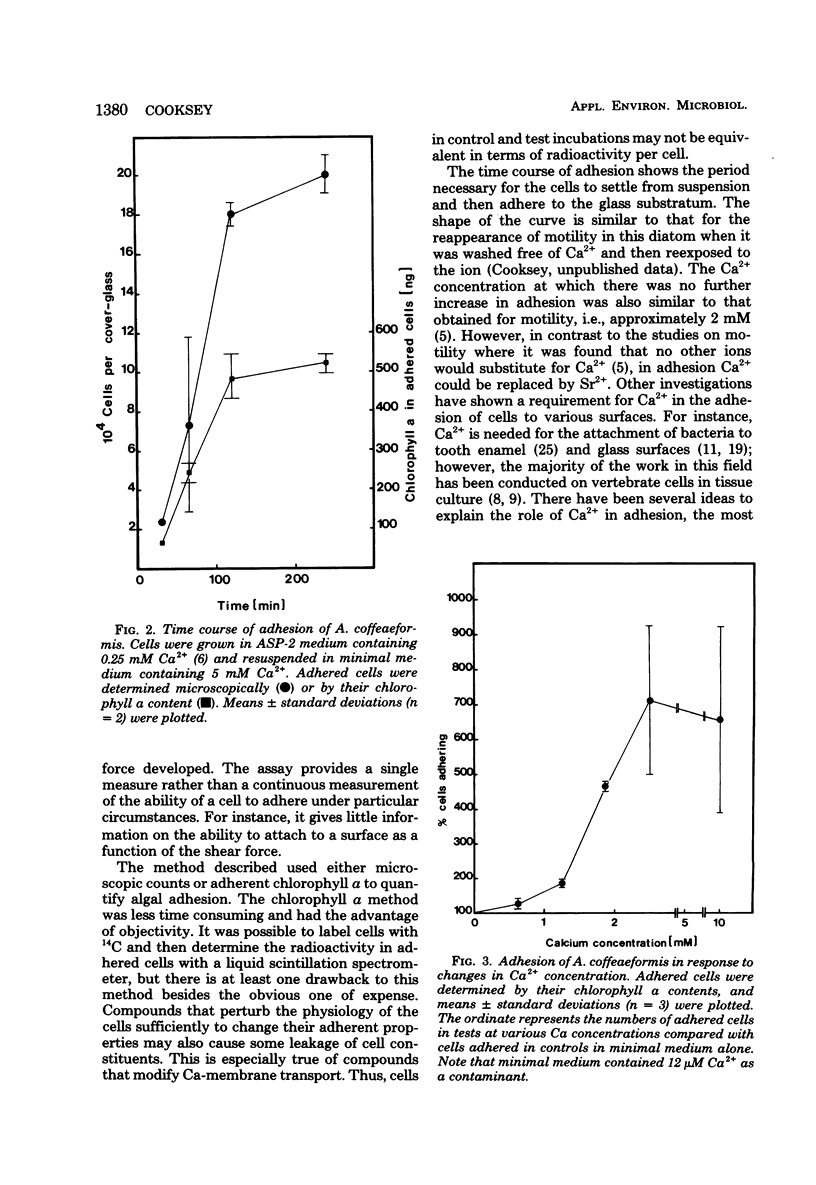
An assay for the adhesion of Amphora coffeaeformis (Bacillariophyceae) to glass is described. Ca2+ and Sr2+ promoted adhesion, but Ba2+ and Mn2+ were ineffective. Adhesion was inhibited by cycloheximide, carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenyl hydrazone, and α-isopropyl-α-[(N-methyl-N-homoveratryl)-γ-amino- propyl]-3,4,5-trimethyoxy phenyl acetonitrile (D-600), but not by 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1, 1-dimethyl urea or darkness. The assay has potential use in comparing chemical antifoulants.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooksey B., Cooksey K. E. Calcium is Necessary for Motility in the Diatom Amphora coffeaeformis. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jan;65(1):129–131. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culp L. A., Murray B. A., Rollins B. J. Fibronectin and proteoglycans as determinants of cell-substratum adhesion. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(3):401–427. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingell D., Garrod D. R. Effect of EDTA on electrophoretic mobility of slime mould cells and its relationship to current theories of cell adhesion. Nature. 1969 Jan 11;221(5176):192–193. doi: 10.1038/221192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. R., Norberg C. L., Segel I. H. Effect of cycloheximide on L-leucine transport by Penicillium chrysogenum: involvement of calcium. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):956–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.956-960.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marszalek D. S., Gerchakov S. M., Udey L. R. Influence of substrate composition on marine microfouling. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):987–995. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.987-995.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer C. J., van Breemen C., Casteels T. The action of lanthanum and D600 on the calcium exchange in the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig Taenia coli. Pflugers Arch. 1972;337(4):333–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00586650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon D. Cycloheximide is not a specific inhibitor of protein synthesis in vivo. Plant Physiol. 1975 May;55(5):815–821. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.5.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROVASOLI L., MCLAUGHLIN J. J., DROOP M. R. The development of artificial media for marine algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1957;25(4):392–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00446694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL M. R., SISLER H. D. INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN VITRO BY CYCLOHEXIMIDE. Nature. 1963 Nov 16;200:675–676. doi: 10.1038/200675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson T. R., Corpe W. A. Enhancement of adhesion of the marine Chlorella vulgaris to glass. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jul;21(7):1025–1031. doi: 10.1139/m75-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendelberger-Schieweg G., Hüttermann A., Haugli F. B. Muliple sites of action of cycloheximide in addition to inhibition of protein synthesis in Physarum polycephalum. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Jun;126(2):109–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00511215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobell C. E. The Effect of Solid Surfaces upon Bacterial Activity. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):39–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.39-56.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


