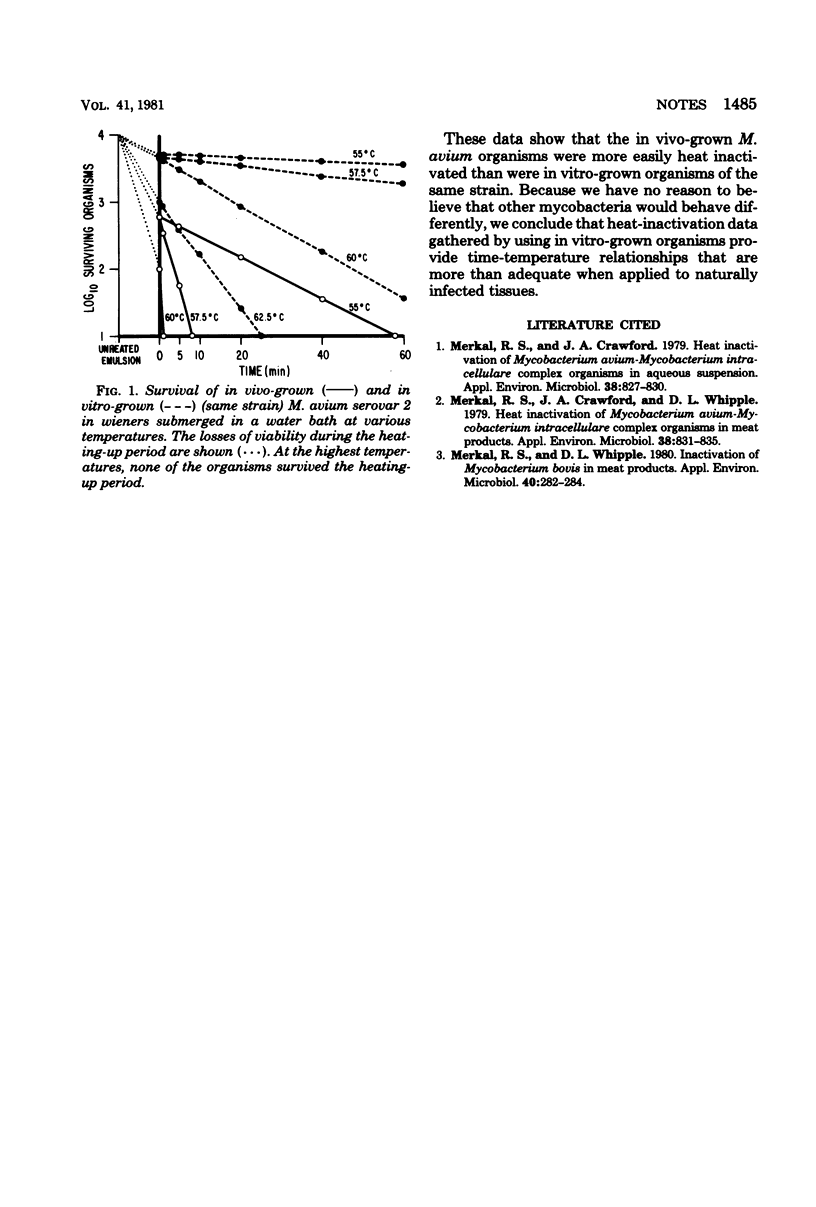
Abstract
Heat inactivation of mycobacteria from lesions and from culture was compared in meat products. In vivo-grown organisms were more easily heat inactivated than were in vitro-grown organisms.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Merkal R. S., Crawford J. A. Heat inactivation of Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare complex organisms in aqueous suspension. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):827–830. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.827-830.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S., Crawford J. A., Whipple D. L. Heat inactivation of Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare complex organisms in meat products. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):831–835. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.831-835.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S., Whipple D. L. Inactivation of Mycobacterium bovis in meat products. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):282–284. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.282-284.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



