Abstract
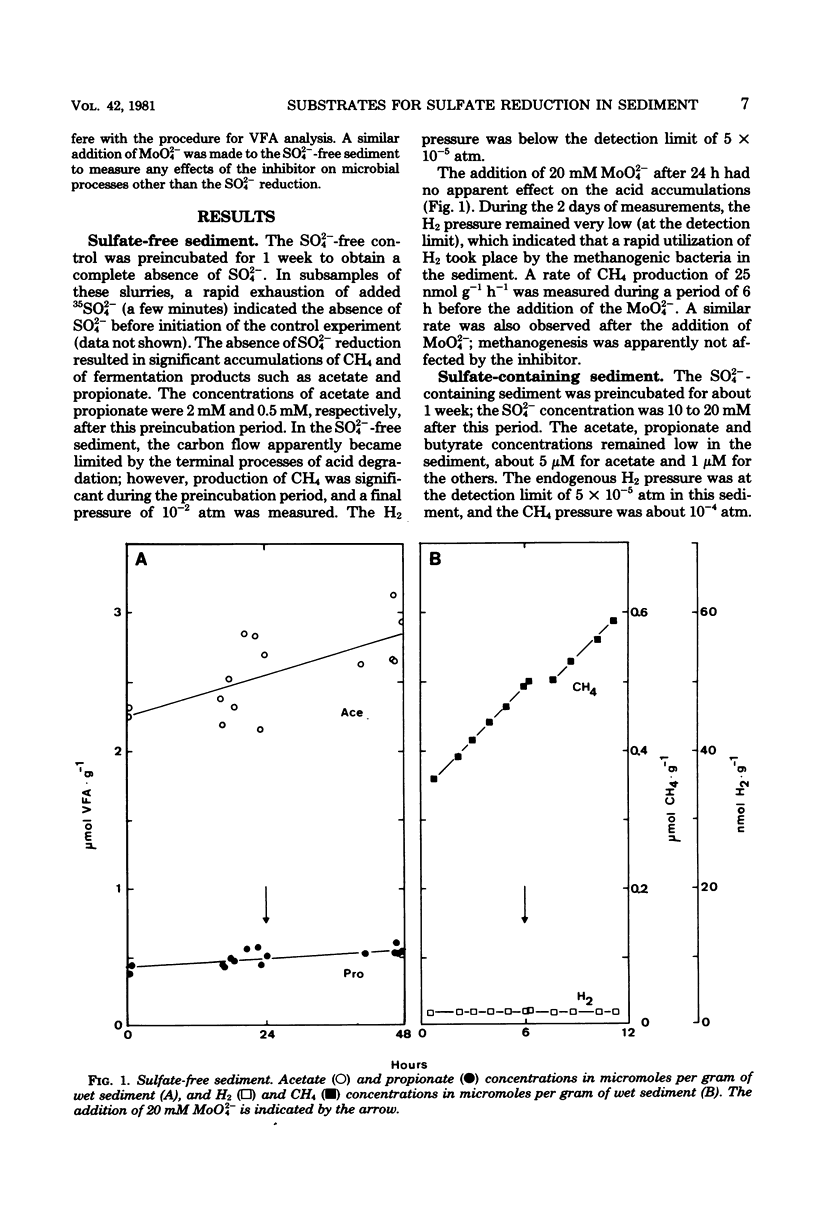
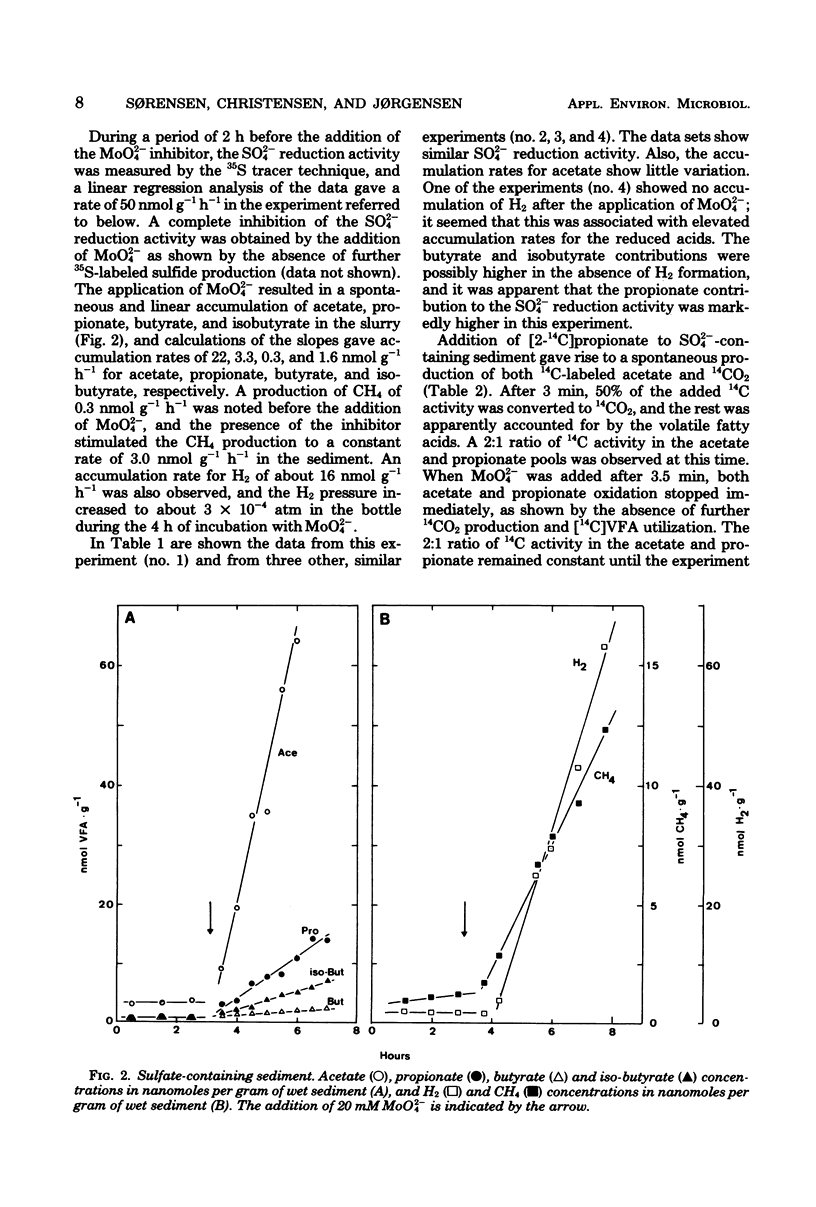
The addition of 20 mM MoO42− (molybdate) to a reduced marine sediment completely inhibited the SO42− reduction activity by about 50 nmol g−1 h−1 (wet sediment). Acetate accumulated at a constant rate of about 25 nmol g−1 h−1 immediately after MoO42− addition and gave a measure of the preceding utilization rate of acetate by the SO42−-reducing bacteria. Similarly, propionate and butyrate (including isobutyrate) accumulated at constant rates of 3 to 7 and 2 to 4 nmol g−1 h−1, respectively. The rate of H2 accumulation was variable, and a range of 0 to 16 nmol g−1 h−1 was recorded. An immediate increase of the methanogenic activity by 2 to 3 nmol g−1 h−1 was apparently due to a release of the competition for H2 by the absence of SO42− reduction. If propionate and butyrate were completely oxidized by the SO42−-reducing bacteria, the stoichiometry of the reactions would indicate that H2, acetate, propionate, and butyrate account for 5 to 10, 40 to 50, 10 to 20, and 10 to 20%, respectively, of the electron donors for the SO42−-reducing bacteria. If the oxidations were incomplete, however, the contributions by propionate and butyrate would only be 5 to 10% each, and the acetate could account for as much as two-thirds of the SO42− reduction. The presence of MoO42− seemed not to affect the fermentative and methanogenic activities; an MoO42− inhibition technique seems promising in the search for the natural substrates of SO42− reduction in sediments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram J. W., Nedwell D. B. Hydrogen as a substrate for methanogenesis and sulphate reduction in anaerobic saltmarsh sediment. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):93–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00689357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram J. W., Nedwell D. B. Inhibition of methanogenesis by sulphate reducing bacteria competing for transferred hydrogen. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):89–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00689356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Campbell L. L., Reddy C. A., Crabill M. R. Growth of desulfovibrio in lactate or ethanol media low in sulfate in association with H2-utilizing methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1162–1169. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1162-1169.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappenberg T. E. Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. II. Inhibition experiments. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(2):297–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00394388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappenberg T. E., Prins R. A. Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. 3. Experiments with 14C-labeled substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(3):457–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00399358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E., Smith W., Bauchop T., Yu I., Rabinowitz J. C. Formate as an intermediate in the bovine rumen fermentation. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.389-397.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar H. F., Wuhrmann K. Kinetic parameters and relative turnovers of some important catabolic reactions in digesting sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.1-7.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountfort D. O., Asher R. A., Mays E. L., Tiedje J. M. Carbon and electron flow in mud and sandflat intertidal sediments at delaware inlet, nelson, new zealand. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):686–694. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.686-694.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdel F., Pfennig N. A new anaerobic, sporing, acetate-oxidizing, sulfate-reducing bacterium, Desulfotomaculum (emend.) acetoxidans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Feb 4;112(1):119–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00446665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Anaerobic metabolism of immediate methane precursors in Lake Mendota. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):244–253. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.244-253.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Effect of sulfate on carbon and electron flow during microbial methanogenesis in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.275-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



