Abstract
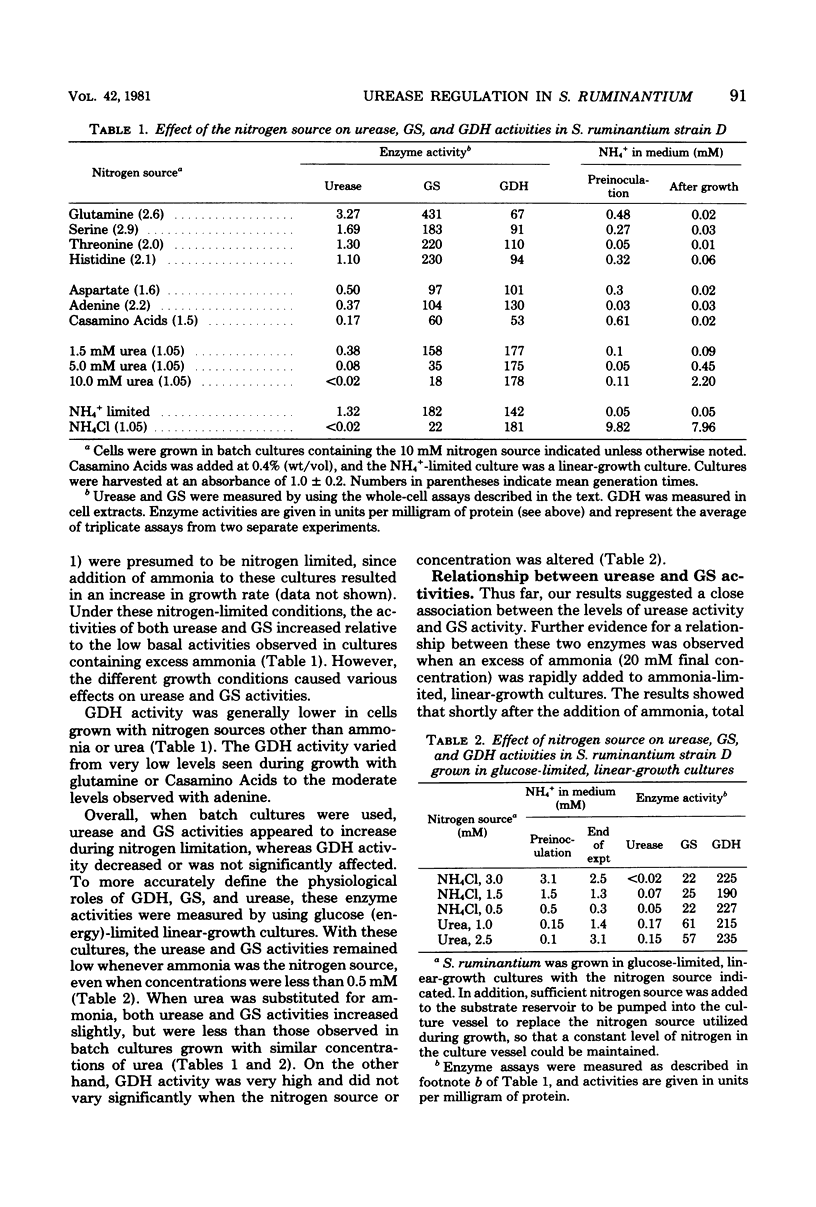
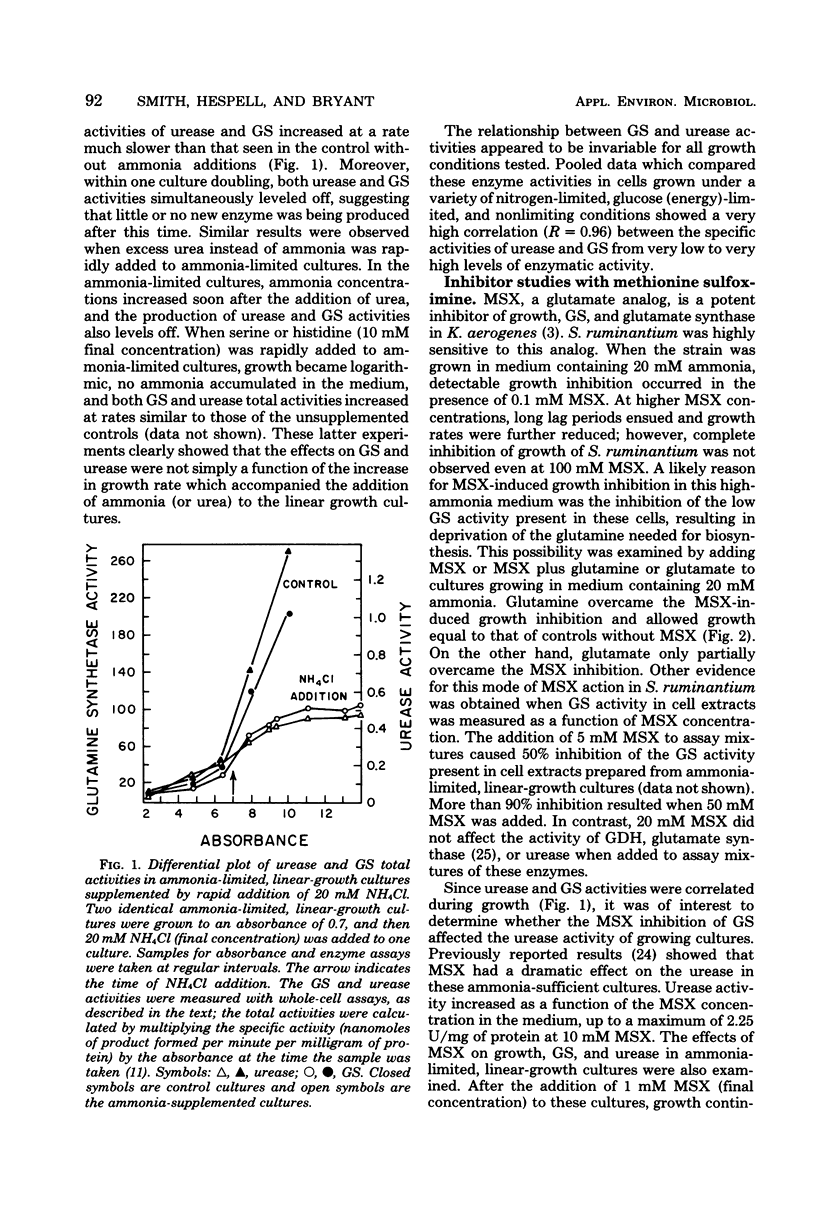
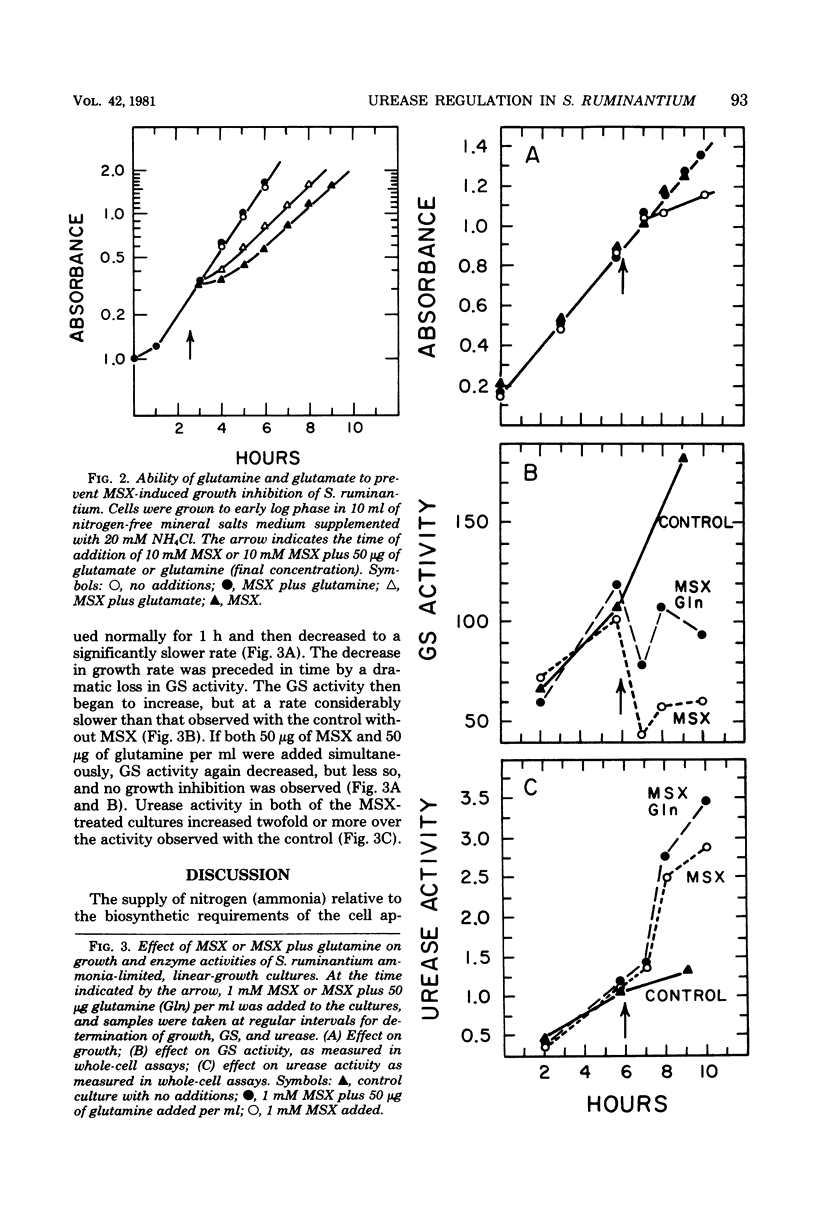
Urease and glutamine synthetase activities in Selenomonas ruminantium strain D were highest in cells grown in ammonia-limited, linear-growth cultures or when certain compounds other than ammonia served as the nitrogen source and limited the growth rate in batch cultures. Glutamate dehydrogenase activity was highest during glucose (energy)-limited growth or when ammonia was not growth limiting. A positive correlation (R = 0.96) between glutamine synthetase and urease activities was observed for a variety of growth conditions, and both enzyme activities were simultaneously repressed when excess ammonia was added to ammonia-limited, linear-growth cultures. The glutamate analog methionine sulfoximine (MSX), inhibited glutamine synthetase activity in vitro, but glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamate synthase, and urease activities were not affected. The addition of MSX (0.1 to 100 mM) to cultures growing with 20 mM ammonia resulted in growth rate inhibition that was dependent upon the concentration of MSX and was overcome by glutamine addition. Urease activity in MSX-inhibited cultures was increased significantly, suggesting that ammonia was not the direct repressor of urease activity. In ammonia-limited, linear-growth cultures, MSX addition resulted in growth inhibition, a decrease in GS activity, and an increase in urease activity. These results are discussed with respect to the importance of glutamine synthetase and glutamate dehydrogenase for ammonia assimilation under different growth conditions and the relationship of these enzymes to urease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. J. Biosynthesis of amono acids by ruminal microorganisms. J Anim Sci. 1969 Nov;29(5):797–807. doi: 10.2527/jas1969.295797x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M. Some nutritional characteristics of predominant culturable ruminal bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:605–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.605-614.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley J. E. Effect of methionine sulfoximine and methionine sulfone on glutamate synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.666-673.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1324–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANEY A. L., MARBACH E. P. Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin Chem. 1962 Apr;8:130–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell D. R., Bryant M. P. Medium without rumen fluid for nonselective enumeration and isolation of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Sep;14(5):794–801. doi: 10.1128/am.14.5.794-801.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalupa W., Clark J., Opliger P., Lavker R. Ammonia metabolism in rumen bacteria and mucosa from sheep fed soy protein or urea. J Nutr. 1970 Feb;100(2):161–169. doi: 10.1093/jn/100.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Wallace R. J. The mechanism of passage of endogenous urea through the rumen wall and the role of ureolytic epithelial bacteria in the urea flux. Br J Nutr. 1979 Nov;42(3):553–557. doi: 10.1079/bjn19790147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Magasanik B. Urease of Klebsiella aerogenes: control of its synthesis by glutamine synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):446–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.446-452.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES G. A., MACLEOD R. A., BLACKWOOD A. C. UREOLYTIC RUMEN BACTERIA. I. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE MICROFLORA FROM A UREA-FED SHEEP. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Jun;10:371–378. doi: 10.1139/m64-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John A., Isaacson H. R., Bryant M. P. Isolation and characteristics of a ureolytic strain of Selenomonas ruminatium. J Dairy Sci. 1974 Sep;57(9):1003–1014. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(74)85001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltwasser H., Krämer J., Conger W. R. Control of urease formation in certain aerobic bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;81(2):178–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00412327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVENSON S. M., CROWLEY L. V., HOROWITZ R. E., MALM O. J. The metabolism of carbon-labeled urea in the germ free rat. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):2061–2062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B., Prival M. J., Brenchley J. E., Tyler B. M., DeLeo A. B., Streicher S. L., Bender R. A., Paris C. G. Glutamine synthetase as a regulator of enzyme synthesis. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):119–138. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152808-9.50010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W., Brown C. M. 'Glutamine(amide):2-oxoglutarate amino transferase oxido-reductase (NADP); an enzyme involved in the synthesis of glutamate by some bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):187–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahel G., Zelenetz A. D., Tyler B. M. gltB gene and regulation of nitrogen metabolism by glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):139–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.139-148.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. M., Smith J. A. The utilization of urea in the bovine rumen. 2. The conversion of urea to ammonia. Biochem J. 1943 Apr;37(1):148–153. doi: 10.1042/bj0370148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior P. J. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella aerogenes: studies with the continuous-culture technique. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):407–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.407-418.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Bryant M. P. Introduction to metabolic activities of intestinal bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):149–157. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Isolation of ureolytic Peptostreptococcus productus from feces using defined medium; failure of common urease tests. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):594–599. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.594-599.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visek W. J. Effects of urea hydrolysis on cell life-span and metabolism. Fed Proc. 1972 May-Jun;31(3):1178–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozny M. A., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Urease assay and urease-producing species of anaerobes in the bovine rumen and human feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1097–1104. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1097-1104.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


