Abstract
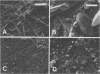
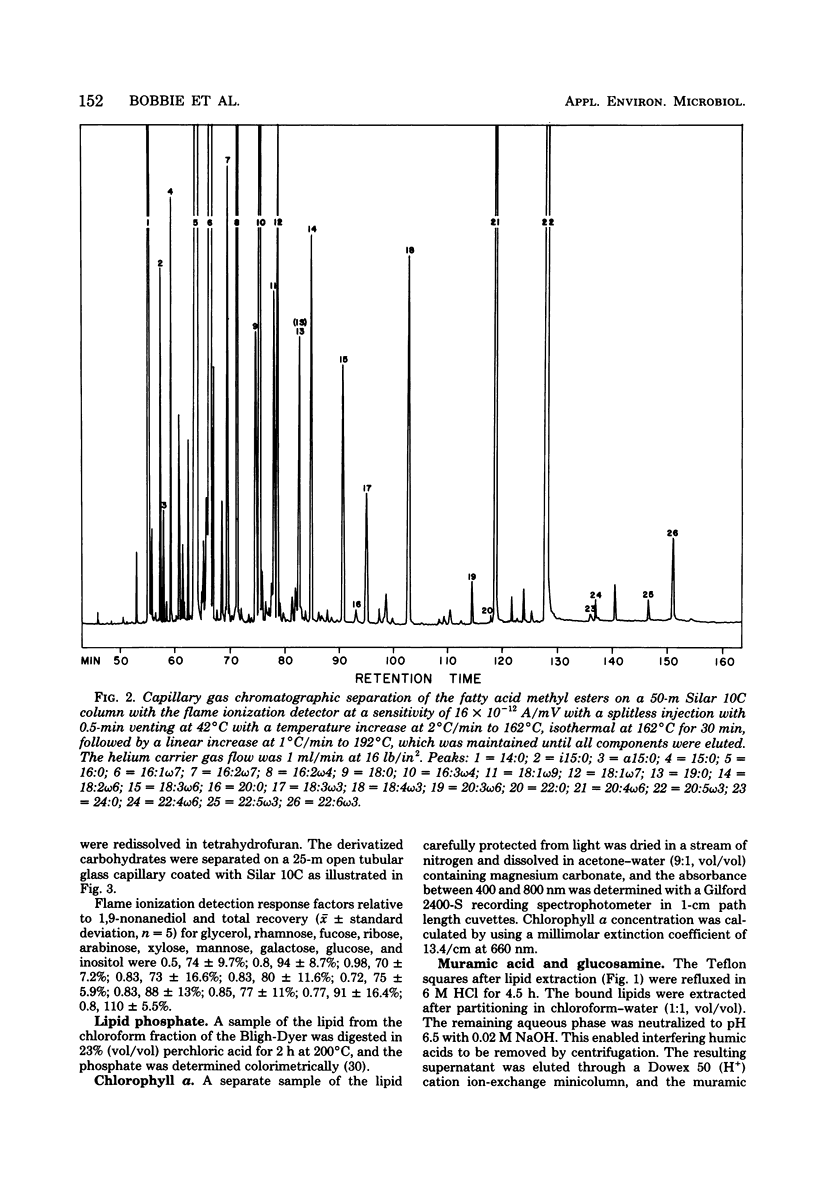
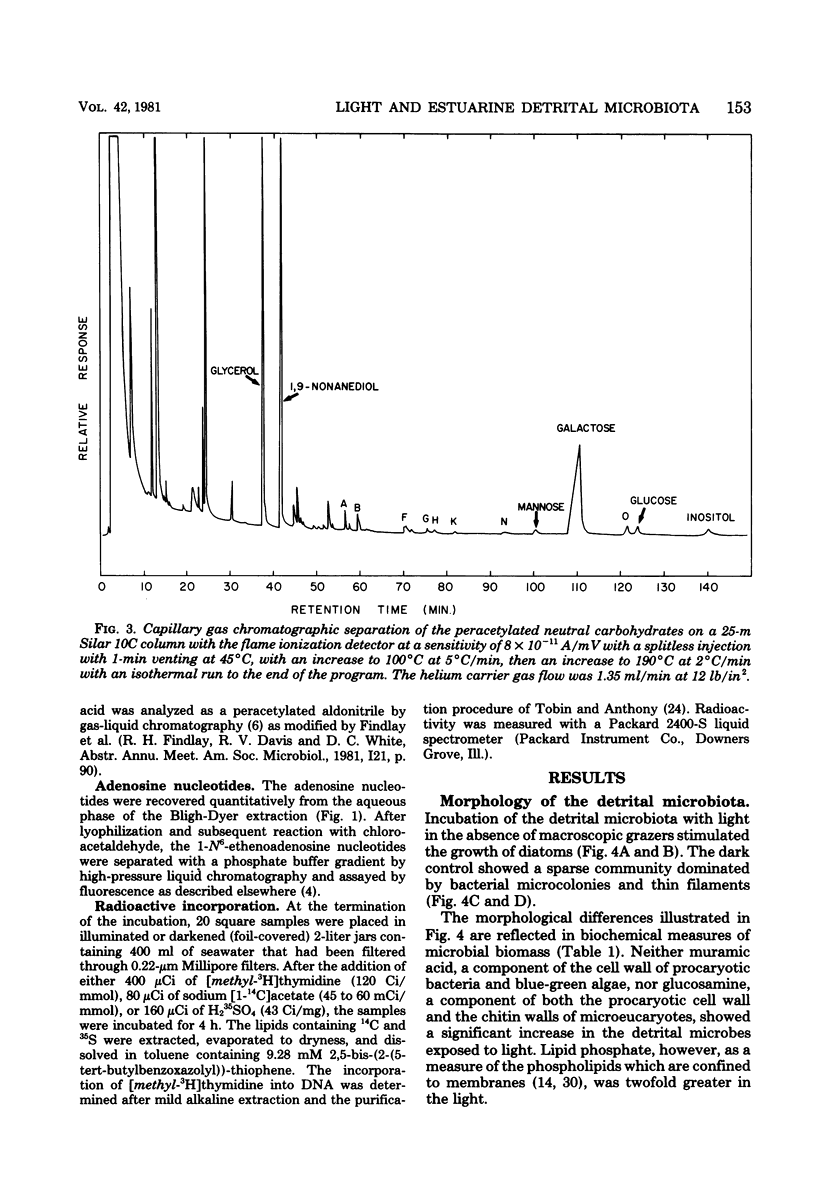
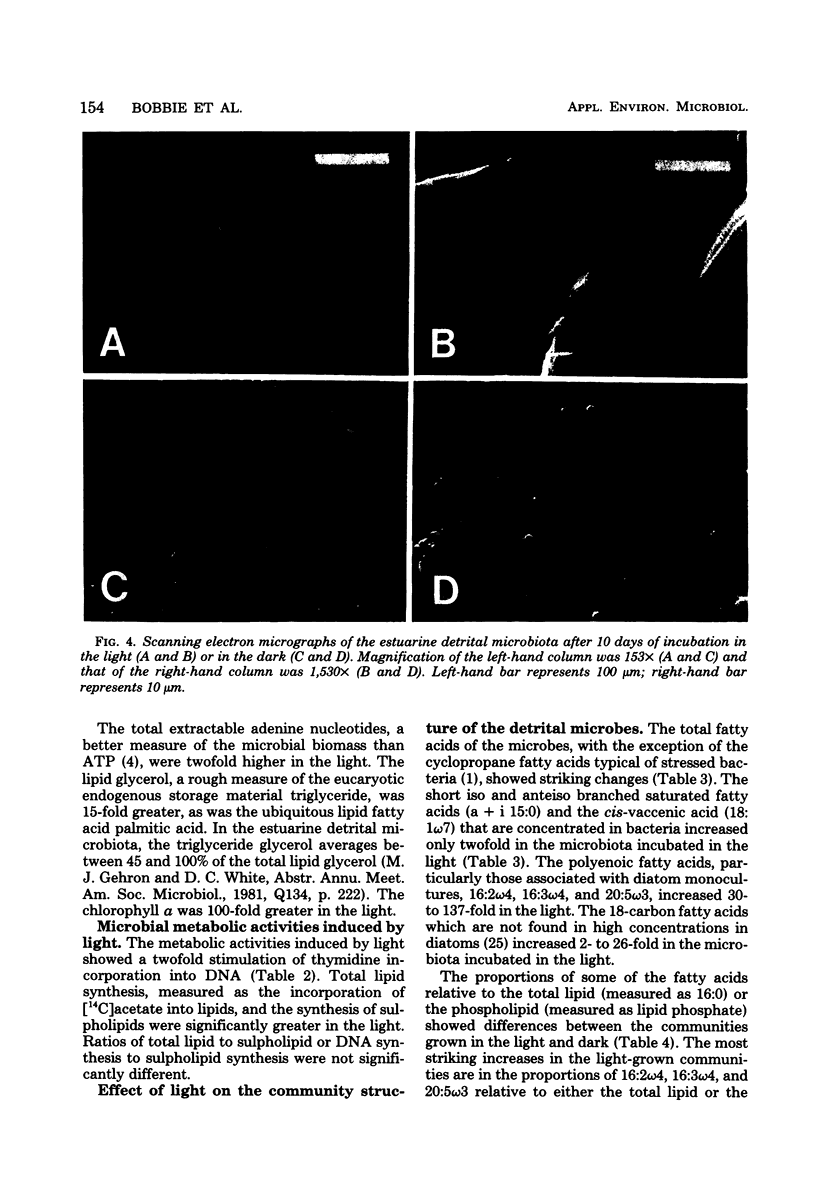
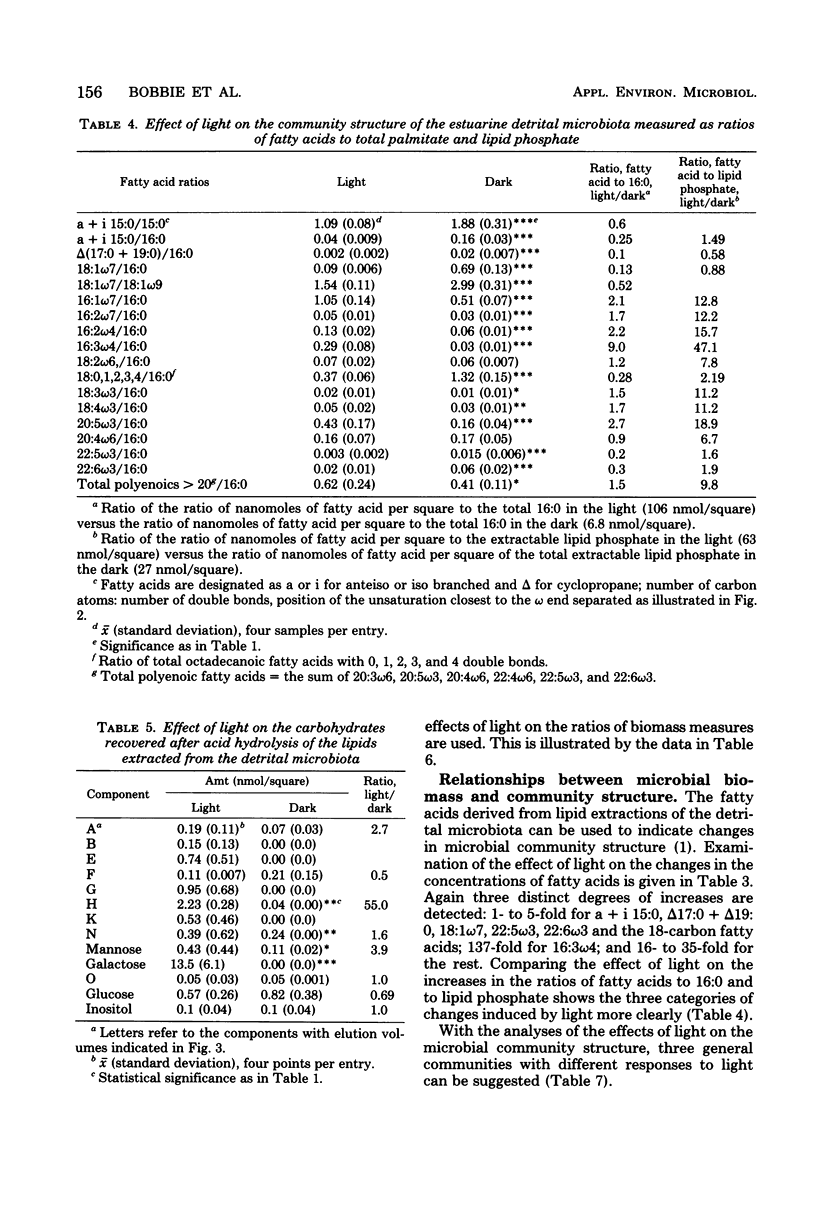
Comparison of estuarine detrital microbiota grown with and without light in the absence of macroscopic grazing showed shifts in the community structure that enabled correlation between various biochemical measures. Analysis of these biochemical measures showed that growth in light induces the smallest increases in procaryotic attributes such as muramic acid; wall glucosamine; lipid phosphate; total extractable adenosine nucleotides; short-branched, cyclopropane, and cis-vaccenic fatty acids; lipid glucose and mannose; the incorporation of acetate into lipid; and the formation of deoxyribonucleic acid from thymidine. Measures of the microfauna such as lipid inositol and the γ-linolenic series of polyenoic fatty acids also increased minimally in the light-grown microbiota. Measures of sulfo-lipid synthesis, lipid glycerol, total extractable palmitate, 18-carbon polyenoic fatty acids, and total polyenoic fatty acids longer than 20 carbons increased 10- to 15-fold in algae and fungi. Chlorophyll a, lipid galactose, and the 16- and 20- carbon polyenoic fatty acids characteristic of diatoms increased maximally in the light. This increase of diatom measure correlated with the sheets of diatoms detected by scanning electron microscopy.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bobbie R. J., White D. C. Characterization of benthic microbial community structure by high-resolution gas chromatography of Fatty Acid methyl esters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1212–1222. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1212-1222.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon J. J., de Leeuw J. W., Hoek G. J., Vosjan J. H. Significance and taxonomic value of iso and anteiso monoenoic fatty acids and branded beta-hydroxy acids in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1183-1191.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. M., White D. C. Fluorometric determination of adenosine nucleotide derivatives as measures of the microfouling, detrital, and sedimentary microbial biomass and physiological status. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):539–548. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.539-548.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio S. D., Mayberry W. R., White D. C. Muramic Acid assay in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):349–350. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.349-350.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. L., James A. T. Metabolism of trans-3-hexadecenoic acid in broad bean. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jan 2;50(2):325–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb09807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herron J. S., King J. D., White D. C. Recovery of Poly-beta-Hydroxybutyrate from Estuarine Microflora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.251-257.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. Bacterial lipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1964;2:17–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. D., White D. C. Muramic acid as a measure of microbial biomass in estuarine and marine samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):777–783. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.777-783.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. D., White D. C., Taylor C. W. Use of lipid composition and metabolism to examine structure and activity of estuarine detrital microflora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1177–1183. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1177-1183.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. J., White D. C. Effects of grazing by estuarine gammaridean amphipods on the microbiota of allochthonous detritus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):659–671. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.659-671.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickels J. S., King J. D., White D. C. Poly-beta-Hydroxybutyrate Accumulation as a Measure of Unbalanced Growth of the Estuarine Detrital Microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):459–465. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.459-465.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N. Lipid composition as a guide to the classification of bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1974;17(0):63–108. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70555-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]