Abstract
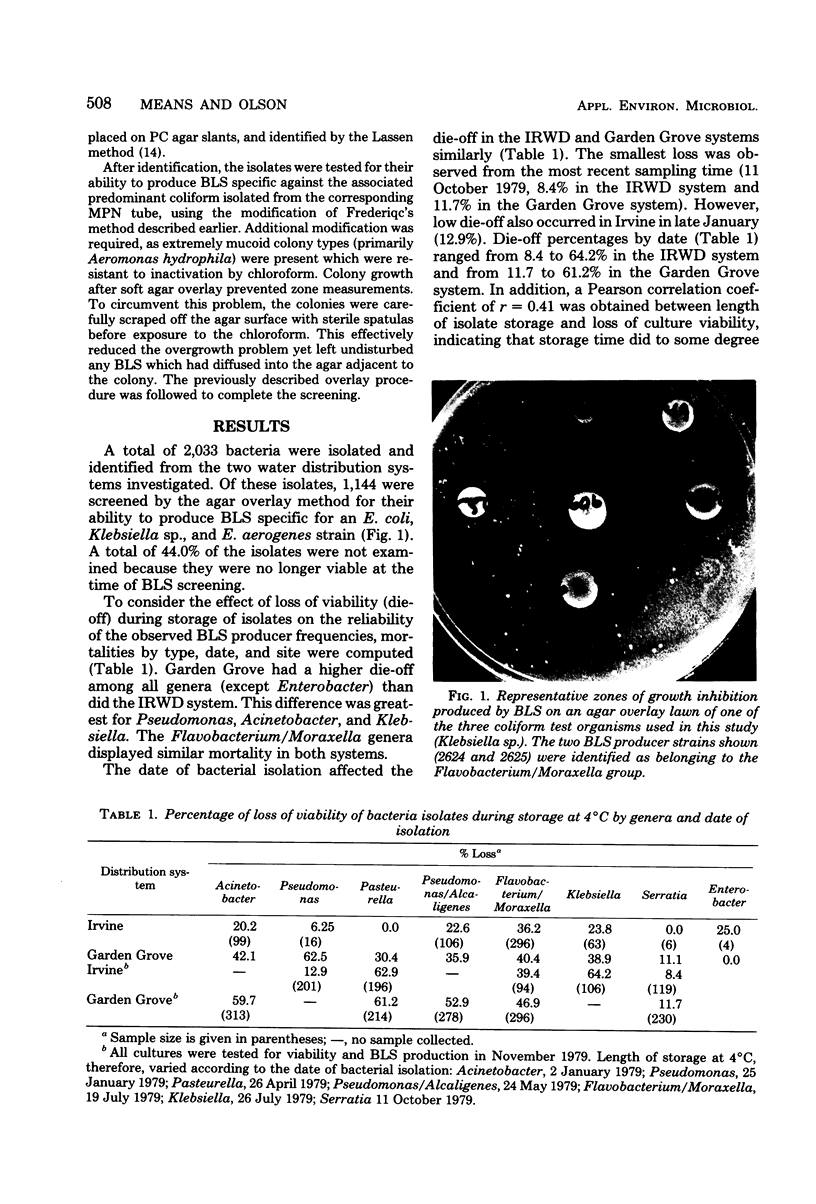
Bacterial isolates from an unchlorinated potable groundwater system and a chlorinated surface water system were screened by an agar overlay method for the ability to produce bacteriocin-like substances (BLS) inhibitory to the growth of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella sp., and Enterobacter aerogenes. The production of coliform-specific BLS by noncoliform bacteria varied with the site and date of isolation as well as the genus of the producer strain. A total of 448 bacterial isolates were screened from the chlorinated system, and 22.1% produced BLS specific for at least one of the three coliforms. In the unchlorinated system, 7.9% (n = 696) possessed this ability. Flavobacterium/Moraxella comprised 57.1% of all bacteria (from both systems) producing BLS. The possibility that BLS interfere with coliform detection in standard bacteriological water quality tests is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind A., Burrows J. R. Suggested procedure allowing use of plastic petri dishes in bacteriocin typing. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):970–970. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.970-.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Influence of environmental stress on enumeration of indicator bacteria from natural waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):186–194. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.186-194.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLUCCI A. F., SCARPINO P. V., PRAMER D. Evaluation of factors affecting survival of Escherichia coli in sea water. V. Studies with heat- and filter-sterilized sea water. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Sep;9:400–404. doi: 10.1128/am.9.5.400-404.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies R. R., Govan J. R. Typing of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by pyocine production. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(2):339–345. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges A. J. An examination of single-hit and multi-hit hypotheses in relation to the possible kinetics of colicin adsorption. J Theor Biol. 1966 Aug;11(3):383–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligler I. J. Non-Lactose Fermenting Bacteria from Polluted Wells and Subsoil. J Bacteriol. 1919 Jan;4(1):35–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.4.1.35-42.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen J. Rapid identification of gram-negative rods using a three-tube method combined with a dichotomic key. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1975 Dec;83(6):525–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R., Yankfsky S., Jannasch H. W. Lysis of Escherichia coli by marine micro-organisms. Nature. 1967 Aug 19;215(5103):891–893. doi: 10.1038/215891a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., NAKAMURA M. Reversibility of inhibition of nucleic acids and protein synthesis by colicin K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:306–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson B. H. Enchanced accuracy of coliform testing in seawater by a modification of the most-probable-number method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):438–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.438-444.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. F., Olson B. H. Scanning electron microscope evidence for bacterial colonization of a drinking-water distribution system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):274–287. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.274-287.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]