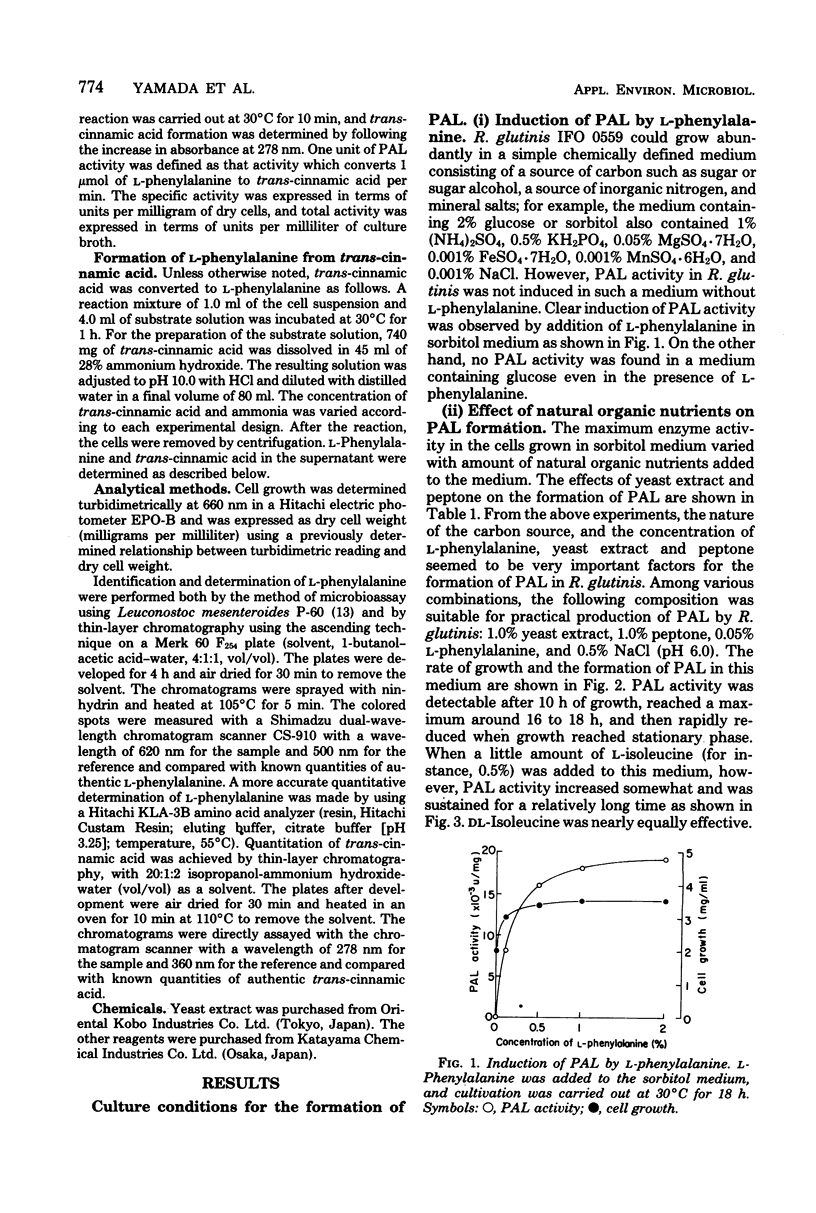
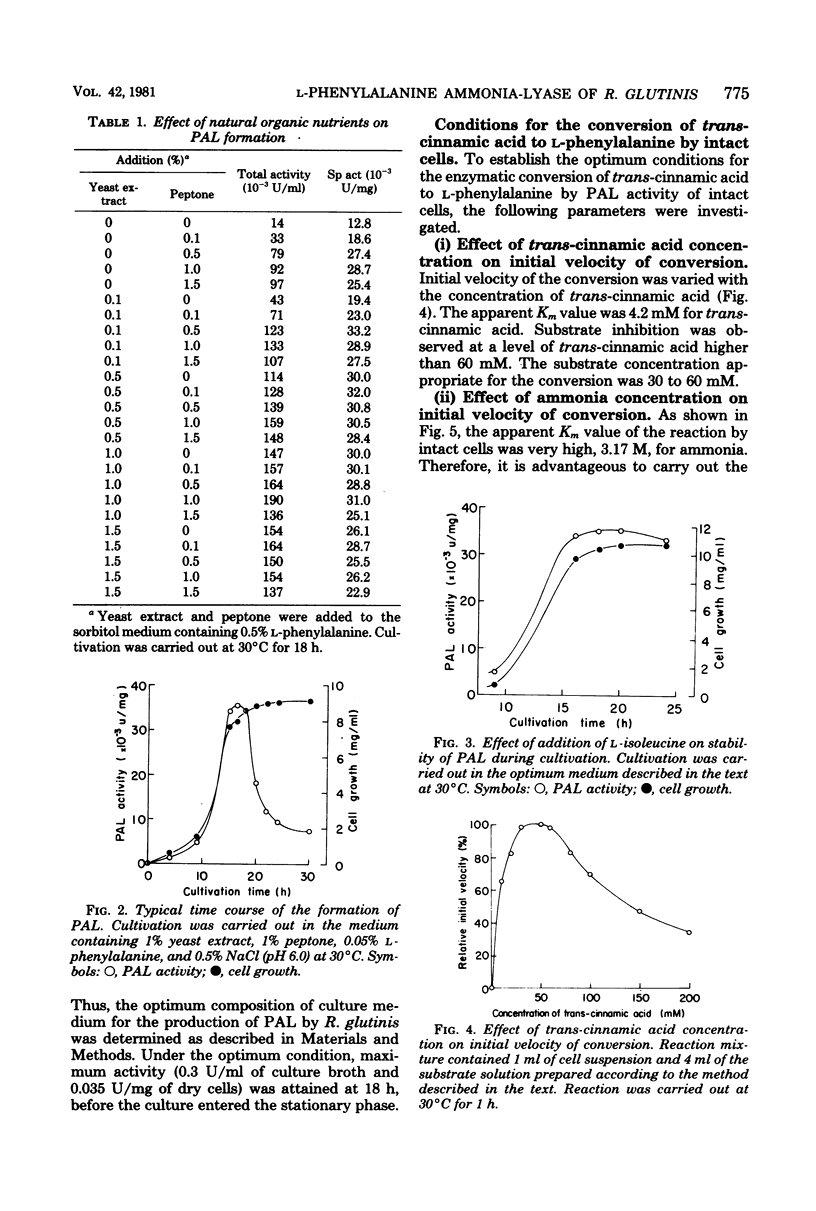
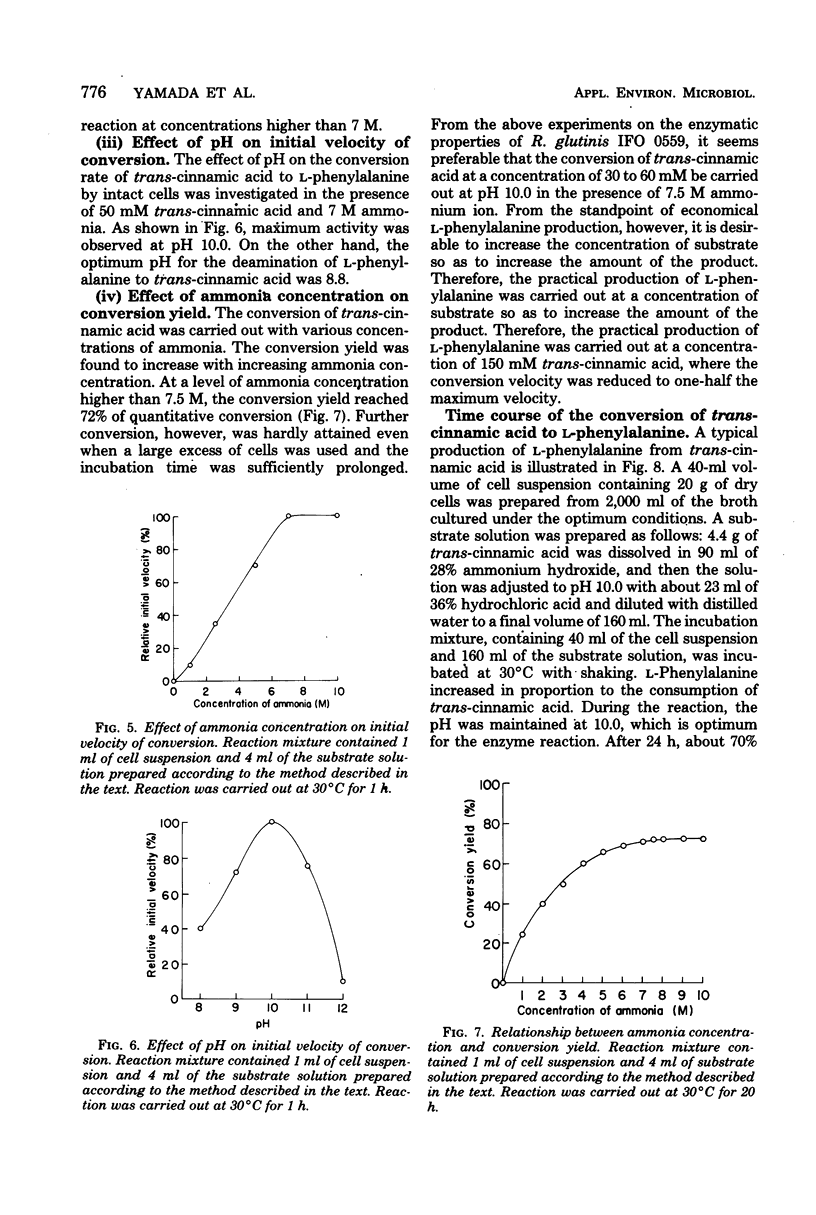
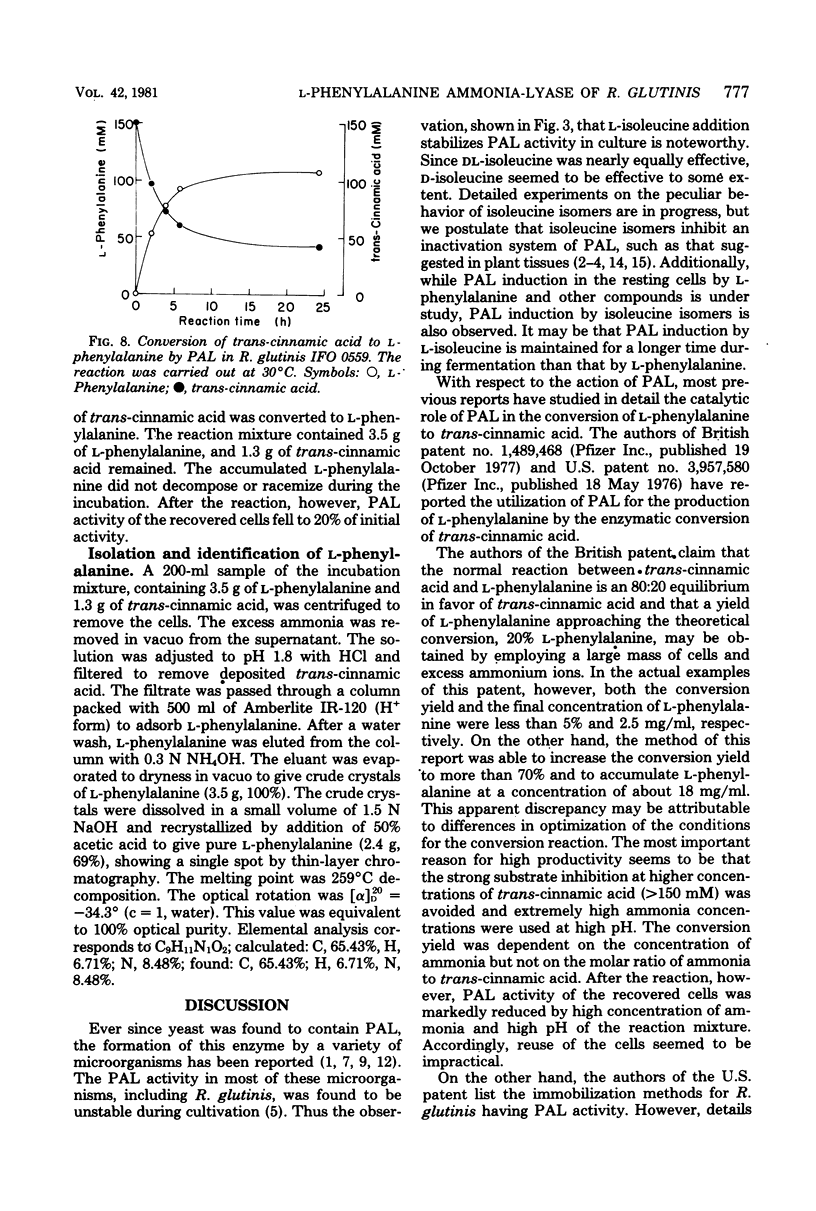
Abstract
An enzymatic method using l-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.5) for the rapid conversion of trans-cinnamic acid to l-phenylalanine has been investigated. With Rhodotorula glutinis, enzyme activity as high as 0.3 U/ml of culture broth was obtained. The enzyme activity was kept stable for a relatively long time during cultivation by the addition of l-isoleucine. Optimization of the parameters of the conversion reaction resulted in accumulation of 18 mg of l-phenylalanine per ml of reaction mixture. The conversion yield from trans-cinnamic acid was about 70%. The method may provide a rapid and practical way to produce l-phenylalanine useful as an essential amino acid.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bezanson G. S., Desaty D., Emes A. V., Vining L. C. Biosynthesis of cinnamamide and detection of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in Streptomyces verticillatus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Mar;16(3):147–151. doi: 10.1139/m70-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke S. O., Hoagland R. E., Elmore C. D. Effects of Glyphosate on Metabolism of Phenolic Compounds: V. l-alpha-AMINOOXY-beta-PHENYLPROPIONIC ACID AND GLYPHOSATE EFFECTS ON PHENYLALANINE AMMONIA-LYASE IN SOYBEAN SEEDLINGS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jan;65(1):17–21. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz R. R., Hodgins D. S., Abell C. W. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Induction and purification from yeast and clearance in mammals. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4646–4650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havir E. A., Hanson K. R. L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. II. Mechanism and kinetic properties of the enzyme from potato tubers. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1904–1914. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalghatgi K. K., Subba Rao P. V. Microbial L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Purification, subunit structure and kinetic properties of the enzyme from Rhizoctonia solani. Biochem J. 1975 Jul;149(1):65–72. doi: 10.1042/bj1490065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalghatgi K. K., Subba Rao P. V. Regulation of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from Rhizoctonia solani. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):568–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.568-578.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K., Rao P. V., Towers G. H. Degradation of phenylalanine and tyrosine by Sporobolomyces roseus. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):507–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1060507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


