Abstract
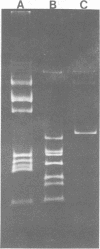
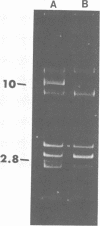
Restriction and modification have been demonstrated in Streptococcus cremoris KH cells when infected by Streptococcus lactis C2 phage (designated c2) at an efficiency of plating of 2 × 10−7. The growth of c2 phage through KH cells produces modified progeny phage capable of unrestricted growth on KH cells. The ability of single-colony isolates of S. cremoris KH cultures to restrict and modify c2 phage was found to be variable. From 2 to 6.5% of colonies isolated were partially deficient in restrictive capacity, permitting a greater plaquing ability by c2 phage of 1.8 to 2.9 log cycles. No completely restrictionless mutants were isolated from 1,000 colonies examined. Mutants were shown to be deficient in both restriction and modification capabilities of the same specificity. The frequent occurrence of a genotypic change that resulted in the loss of both restriction and modification capacities indicated the involvement of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in genetically determining this specific restriction and modification system. S. cremoris KH was found to harbor 11 plasmid molecules, with molecular weights (×106) estimated to be 50, 41, 24, 18, 10, 7.4, 3.3, 3.0, 2.8, 2.5, and 1.5. Of the 27 mutants examined, 25 were missing the 10-megadalton plasmid. This consistent plasmid difference among the majority of mutants isolated supports the involvement of this plasmid in restriction and modification. Plasmid linkage of restriction and modification systems provides a genetic mechanism for the rapid development of phage-sensitive starter cultures due to the inherent instability of extrachromosomal elements.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Plasmids, loss of lactose metabolism, and appearance of partial and full lactose-fermenting revertants in Streptococcus cremoris B1. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):367–377. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.367-377.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister D., Glover S. W. The isolation and properties of non-restricting mutants of two different host specificities associated with drug resistance factors. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):63–71. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussemaer J. P., Schrauwen P. P., Sourrouille J. L., Guy P. Multiple modification/restriction systems in lactic streptococci and their significance in defining a phage-typing system. J Dairy Res. 1980 Oct;47(3):401–409. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900021294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J., Davies F. L. High-frequency conjugation associated with Streptococcus lactis donor cell aggregation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1260–1264. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1260-1264.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Sutton L. Restriction and modification determined by a Pseudomonas R plasmid. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):115–116. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W. Serological studies of a host range mutant of a lactic streptococcal bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):785–789. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.785-789.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempler G. M., McKay L. L. Characterization of Plasmid Deoxyribonucleic Acid in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis: Evidence for Plasmid-Linked Citrate Utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):316–323. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.316-323.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R., McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Improved lysis of group N streptococci for isolation and rapid characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):592–600. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.592-600.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen L. D., McKay L. L. Isolation and characterization of plasmid DNA in Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):944–952. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.944-952.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie R. J. Lysogenic strains of group N lactic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):210–217. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.210-217.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Efstathiou J. D. Transductional evidence for plasmid linkage of lactose metabolism in streptococcus lactis C2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.45-52.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Plasmid distribution and evidence for a proteinase plasmid in Streptococcus lactis C2-1. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):546–548. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.546-548.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Walsh P. M. Conjugal transfer of genetic information in group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.84-91.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Zottola E. A. Loss of lactose metabolism in lactic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jun;23(6):1090–1096. doi: 10.1128/am.23.6.1090-1096.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Cords B. R., Baldwin K. A. Transduction of lactose metabolism in Streptococcus lactis C2. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):810–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.810-815.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C., Heffron F., Falkow S. Transposition of a plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid sequence that mediates ampicillin resistance: independence from host rec functions and orientation of insertion. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):425–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.425-434.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Restriction and modification in group N streptococci: effect of heat on development of modified lytic bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):500–506. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.500-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. M. THE STREPTOCOCCI. Bacteriol Rev. 1937 Dec;1(1):3–97. doi: 10.1128/br.1.1.3-97.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha R. P. Alteration of Host Specificity to Lytic Bacteriophages in Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):326–332. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.326-332.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van Leeuwen W. J., Guinée P. A. Interference with propagation of typing bacteriophages by extrachromosomal elements in Salmonella typhimurium: bacteriophage type 505. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1414–1426. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1414-1426.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]