Abstract
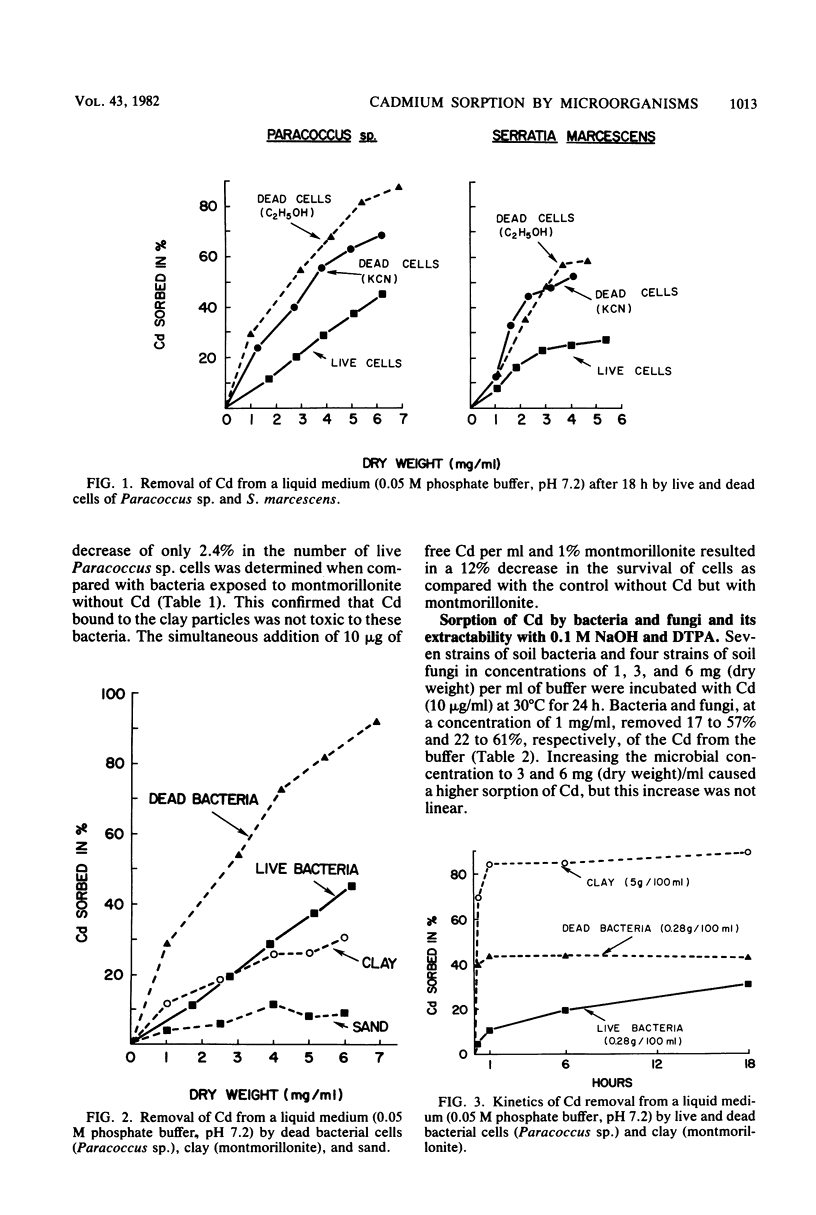
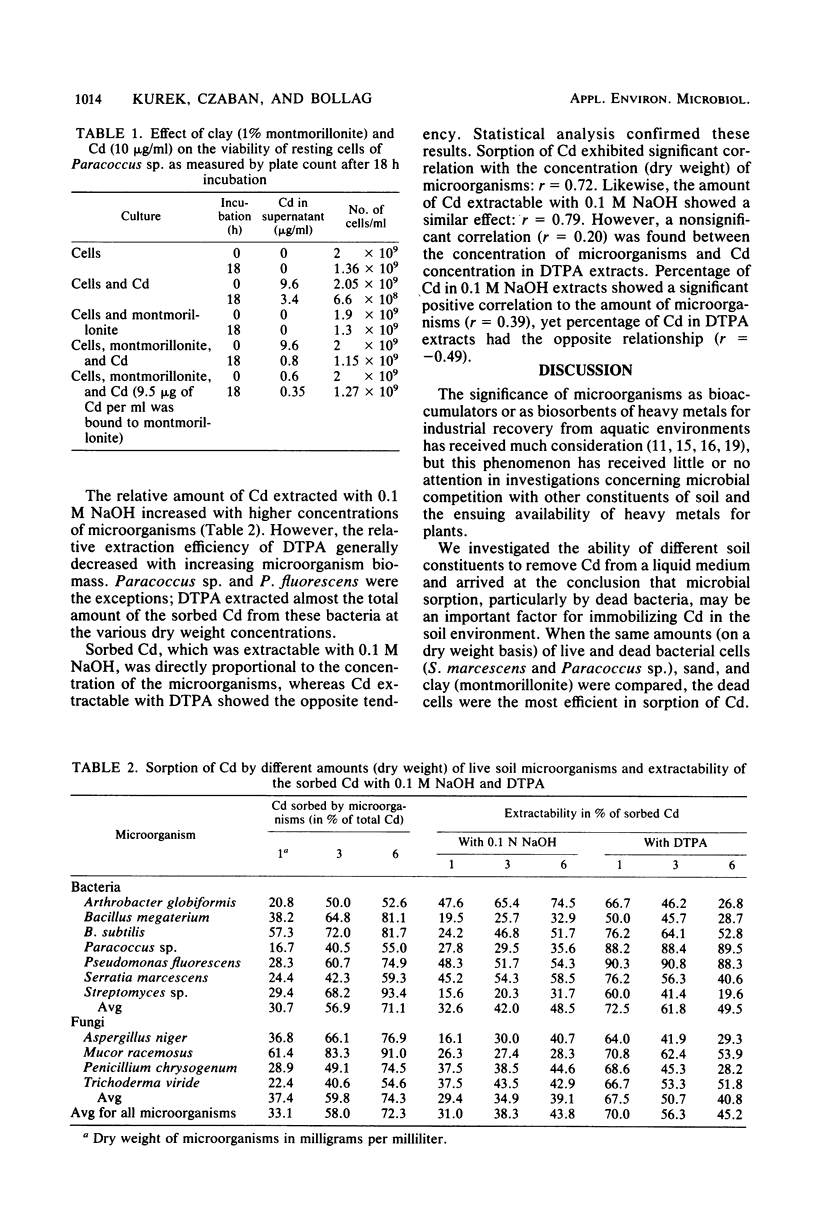
The fate of cadmium in soil is influenced to a great extent by microbial activity. Microorganisms were compared with abiotic soil components for their ability to sorb Cd from a liquid medium. When the same amount (on a dry weight basis) of bacterial cells (Serratia marcescens and Paracoccus sp.), clay (montmorillonite), or sand was separately incubated in 0.05 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.2, containing 10 ppm of Cd (10 μg/ml), bacterial cells removed the largest quantity of Cd. Dead cells sorbed much more Cd from the medium than live cells. A comparative study of Cd removal from the medium by seven soil bacteria and four fungi did not indicate appreciable differences. With increasing microbial biomass, the relative efficiency of 0.1 M NaOH as an extractant of sorbed Cd increased, whereas the extraction efficiency of 0.005 M DTPA (diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid) decreased. It appeared that NaOH and DTPA extracted different chemical forms of Cd. This assumption was supported by vastly different correlation coefficients in the relative amount of Cd extracted by the two solvents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doyle J. J., Marshall R. T., Pfander W. H. Effects of cadmium on the growth and uptake of cadmium by microorganisms. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):562–564. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.562-564.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer M., Sarofim A. F., Fassett D. W., Hammond P., Shacklette H. T., Nisbet I. C., Epstein S. Environmental impact of cadmium: a review by the Panel on Hazardous Trace Substances. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 May;7:253–323. doi: 10.1289/ehp.747253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Roth C. Plasmid-linked resistance to inorganic salts in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1335-1342.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramamoorthy S., Springthorpe S., Kushner D. J. Competition for mercury between river sediment and bacteria. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1977 May;17(5):505–511. doi: 10.1007/BF01685971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Shumate S. E., Parrott J. R. Microbial Cells as Biosorbents for Heavy Metals: Accumulation of Uranium by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):237–245. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.237-245.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tynecka Z., Zajac J., Goś Z. Plasmid dependent impermeability barrier to cadmium ions in Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Microbiol Pol A. 1975;7(1):11–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



