Abstract
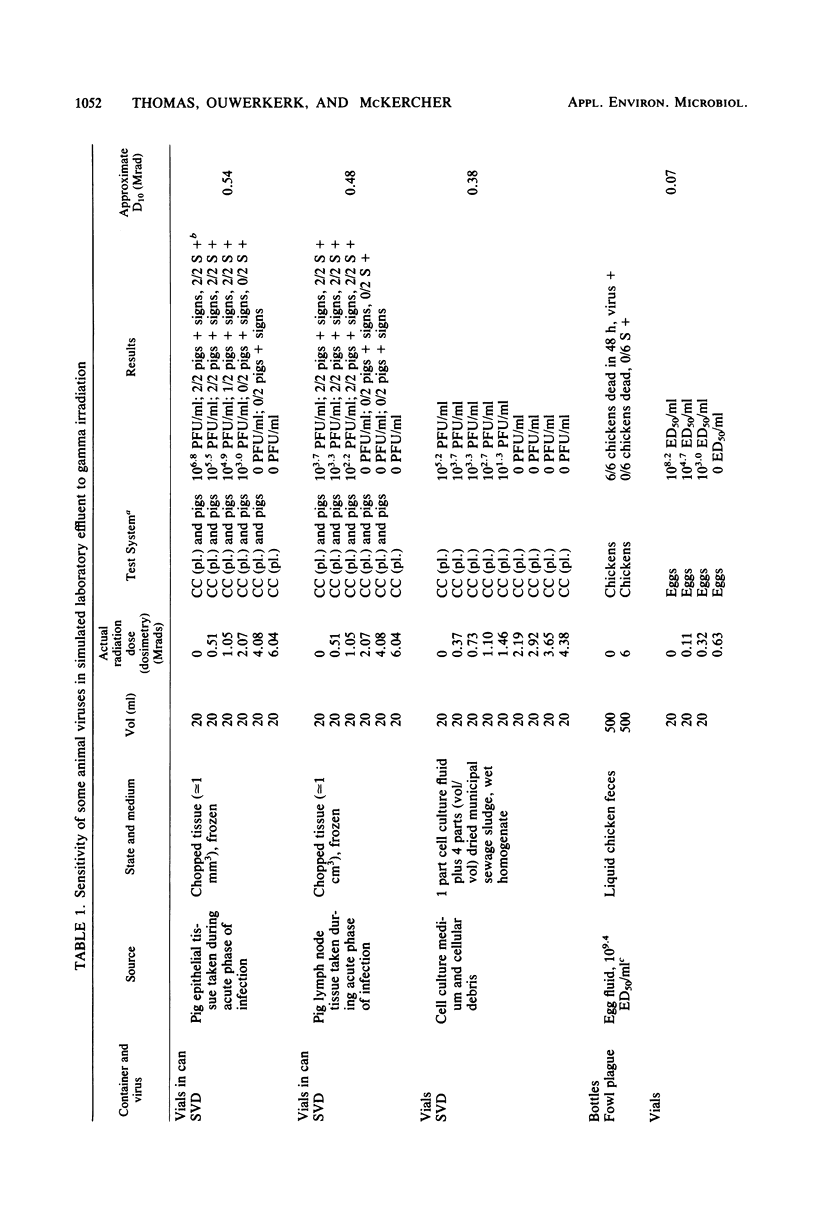
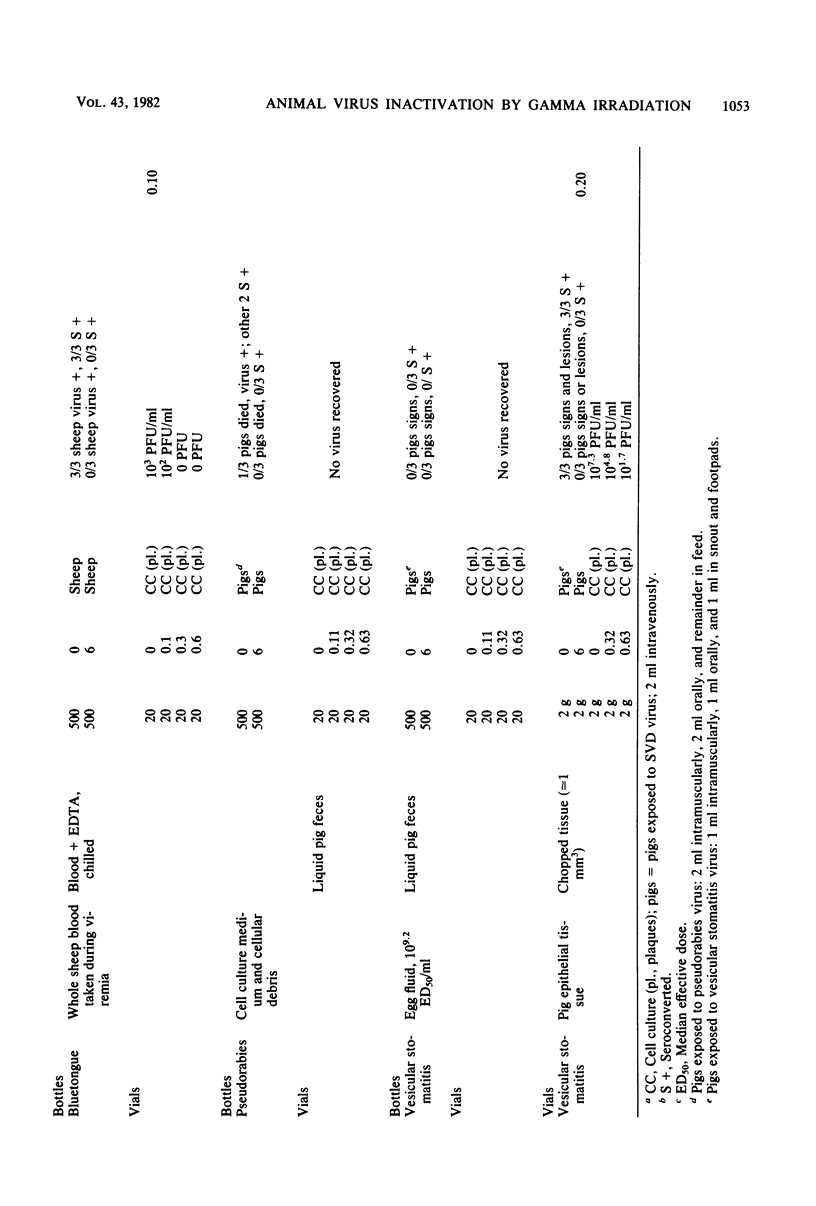
Several animal viruses were treated with gamma radiation from a 60Co source under conditions which might be found in effluent from an animal disease laboratory. Swine vesicular disease virus, vesicular stomatitis virus, and blue-tongue virus were irradiated in tissues from experimentally infected animals. Pseudorabies virus, fowl plague virus, swine vesicular disease virus, and vesicular stomatitis virus were irradiated in liquid animal feces. All were tested in animals and in vitro. The D10 values, that is, the doses required to reduce infectivity by 1 log10, were not apparently different from those expected from predictions based on other data and theoretical considerations. The existence of the viruses in pieces of tissue or in liquid feces made no difference in the efficacy of the gamma radiation for inactivating them. Under the "worst case" conditions (most protective for virus) simulated in this study, no infectious agents would survive 4.0 Mrads.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Howell P. G., Verwoerd D. W., Oellermann R. A. Plaque formation by bluetongue virus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1967 Dec;34(2):317–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN R. T., KEMPE L. L. Inactivation of some animal viruses with gamma radiation from cobalt-60. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):212–215. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLEY J. R. Preparation of non-infective soluble antigens with gamma radiation. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Apr;7:135–139. doi: 10.1139/m61-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Scarpino P. V., Fassolitis A. C., Larkin E. P., Peeler J. T. Gamma radiation inactivation of coxsackievirus B-2. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jul;26(1):14–17. doi: 10.1128/am.26.1.14-17.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F. C., Davies A. G., Dulac G. C., Willis N. G., Papp-Vid G., Girard A. Gamma ray inactivation of some animal viruses. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Oct;45(4):397–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L. Inactivation of poliovirus in wastewater sludge with radiation and thermoradiation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1218–1219. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1218-1219.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



