Abstract
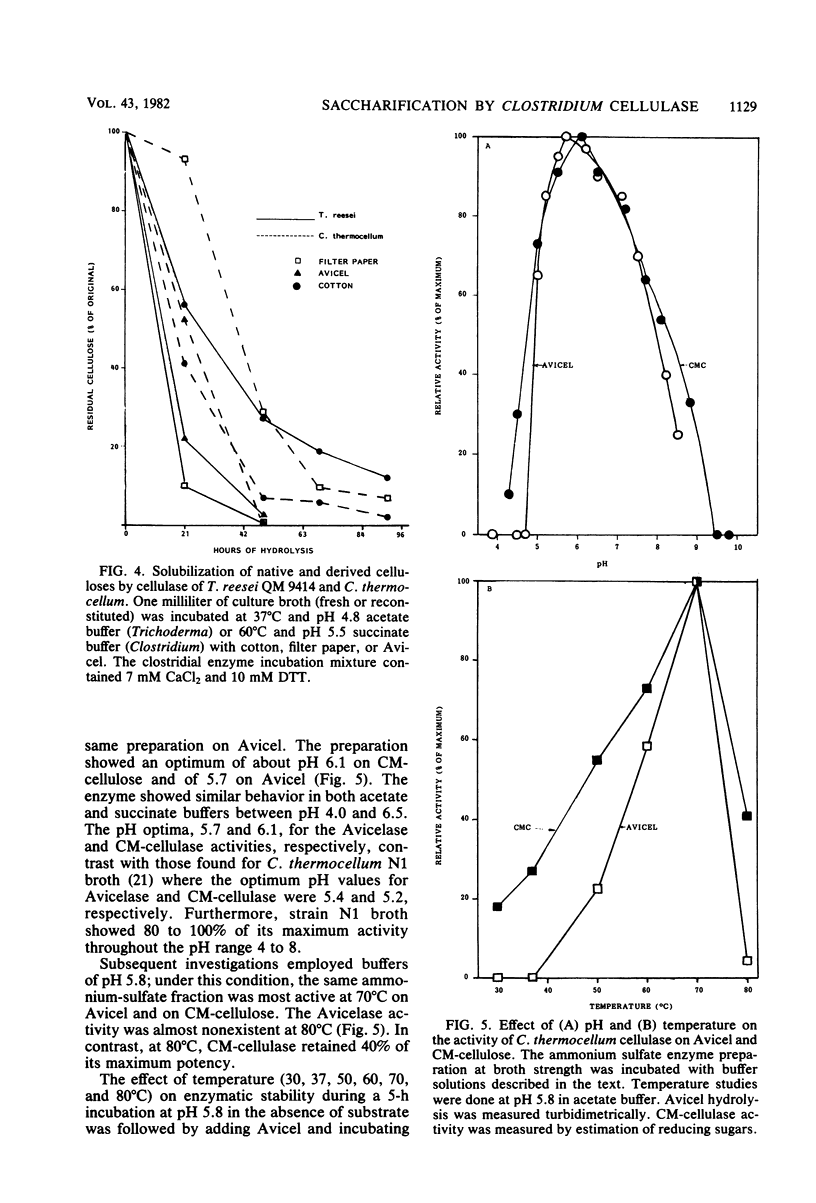
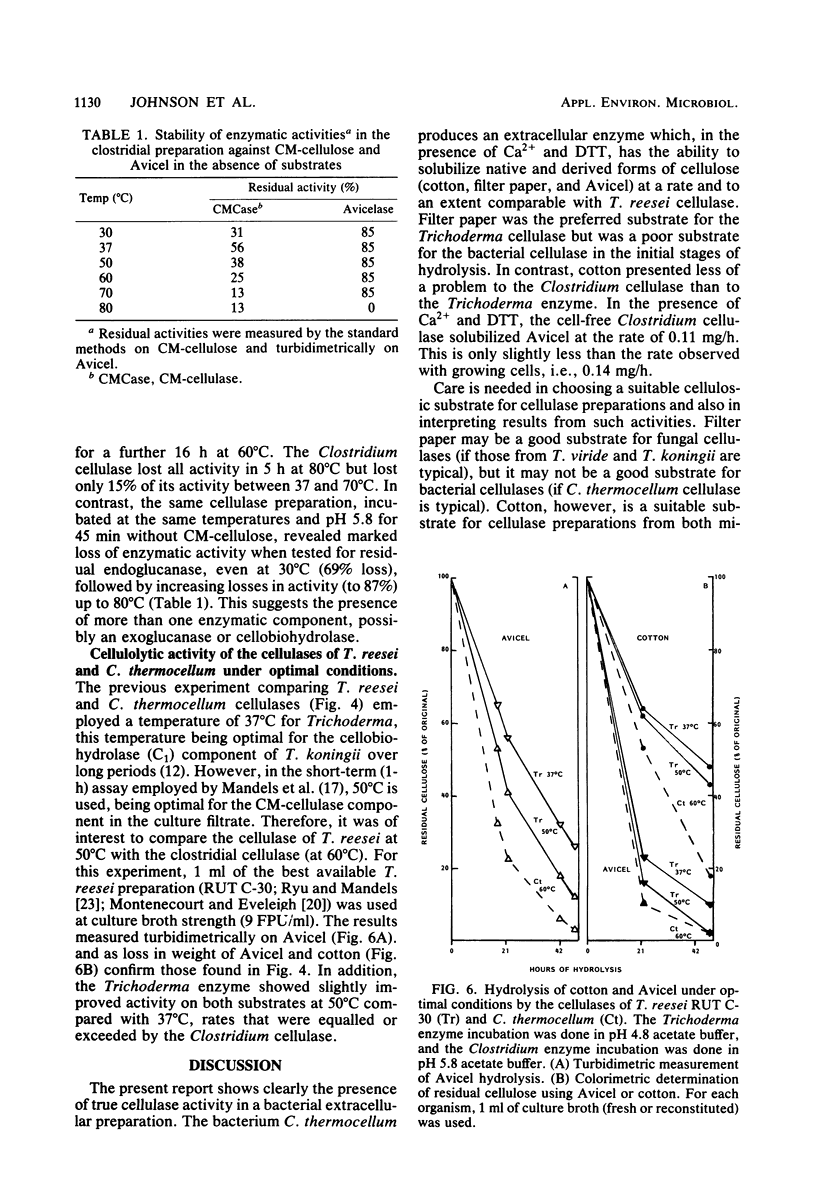
True cellulase activity has been demonstrated in cell-free preparations from the thermophilic anaerobe Clostridium thermocellum. Such activity depends upon the presence of Ca2+ and a thiol-reducing agent of which dithiothreitol is the most promising. Under these conditions, native (cotton) and derived forms of cellulose (Avicel and filter paper) were all extensively solubilized at rates comparable with cellulase from Trichoderma reesei. Maximum activity of the Clostridium cellulase was displayed at 70°C and at pH 5.7 and 6.1 on Avicel and carboxymethylcellulose, respectively. In the absence of substrate at temperatures up to 70°C, carboxymethylcellulase was much more unstable than the Avicel-hydrolyzing activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Cellulolytic activity of the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):517–530. doi: 10.1139/m81-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G., BRYANT M. P. THE CELLULOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF PURE STRAINS OF BACTERIA FROM THE RUMEN OF CATTLE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:441–448. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G. HYDROLYSIS OF FIBROUS COTTON AND REPRECIPITATED CELLULOSE BY CELLULOLYTIC ENZYMES FROM SOIL MICRO-ORGANISMS. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:270–281. doi: 10.1042/bj0950270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell G., Griffin M. The nature and mode of action of the cellulolytic component C1 of Trichoderma koningii on native cellulose. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):587–594. doi: 10.1042/bj1350587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell G., Riaz M. Interactions between components of the cellulase complex of Trichoderma koningii on native substrates. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;78(4):295–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00412270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell G. Solubilization of native and derived forms of cellulose by cell-free microbial enzymes. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):315–320. doi: 10.1042/bj1000315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Tang J. Sensitive assay for cellulase and dextranase. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jun;73(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandels M., Andreotti R., Roche C. Measurement of saccharifying cellulase. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp. 1976;(6):21–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBEE R. H. The anaerobic thermophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):51–63. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.51-63.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Weimer T. K., Zeikus J. G. Cellulolytic and physiological properties of Clostridium thermocellum. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00429622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng T. K., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of Extracellular Cellulase Activities of Clostridium thermocellum LQRI and Trichoderma reesei QM9414. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):231–240. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.231-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Fermentation of cellulose and cellobiose by Clostridium thermocellum in the absence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):289–297. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.289-297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]