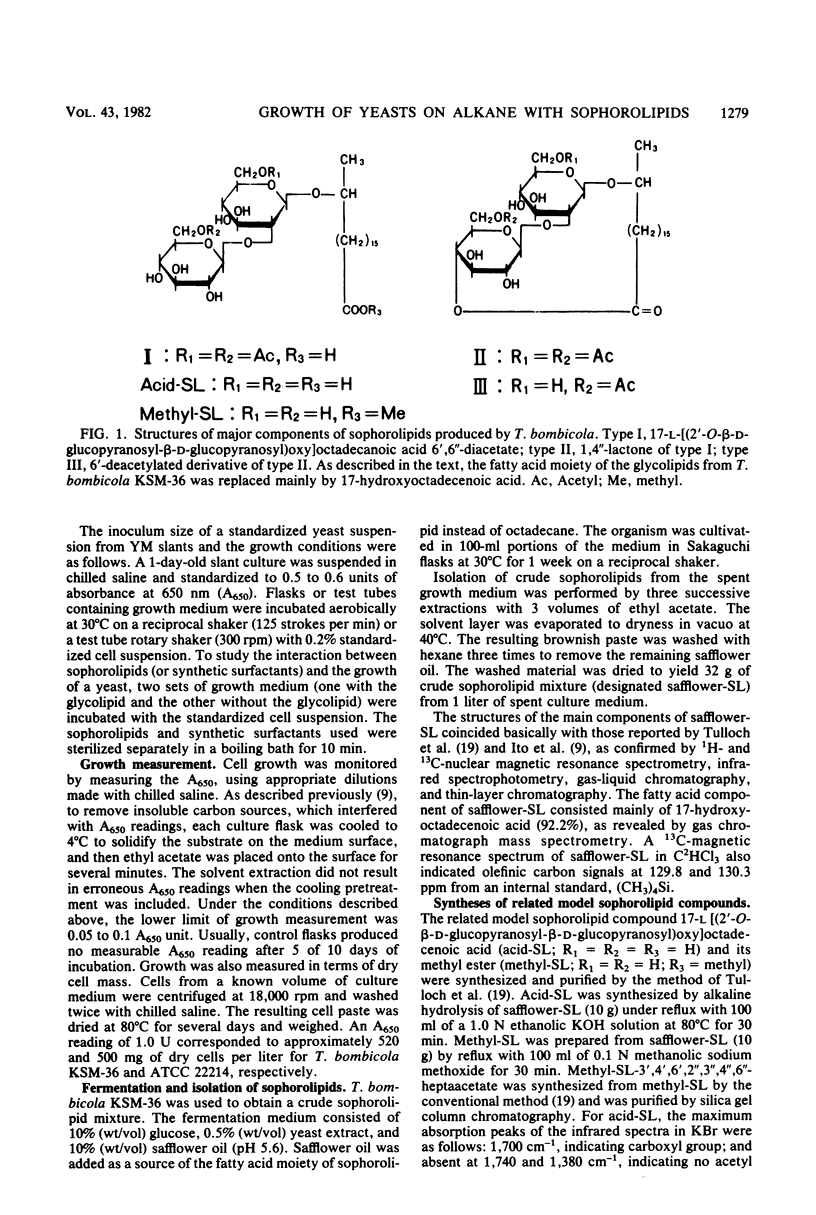
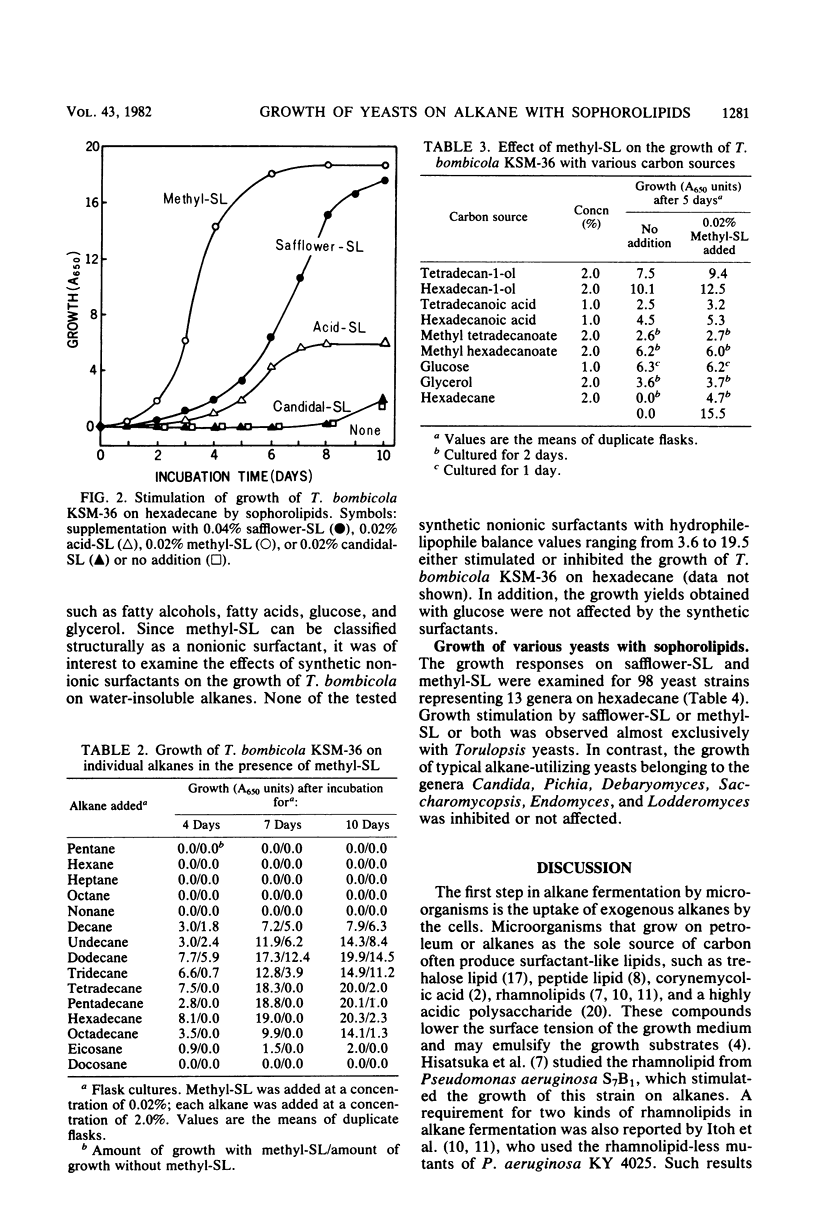
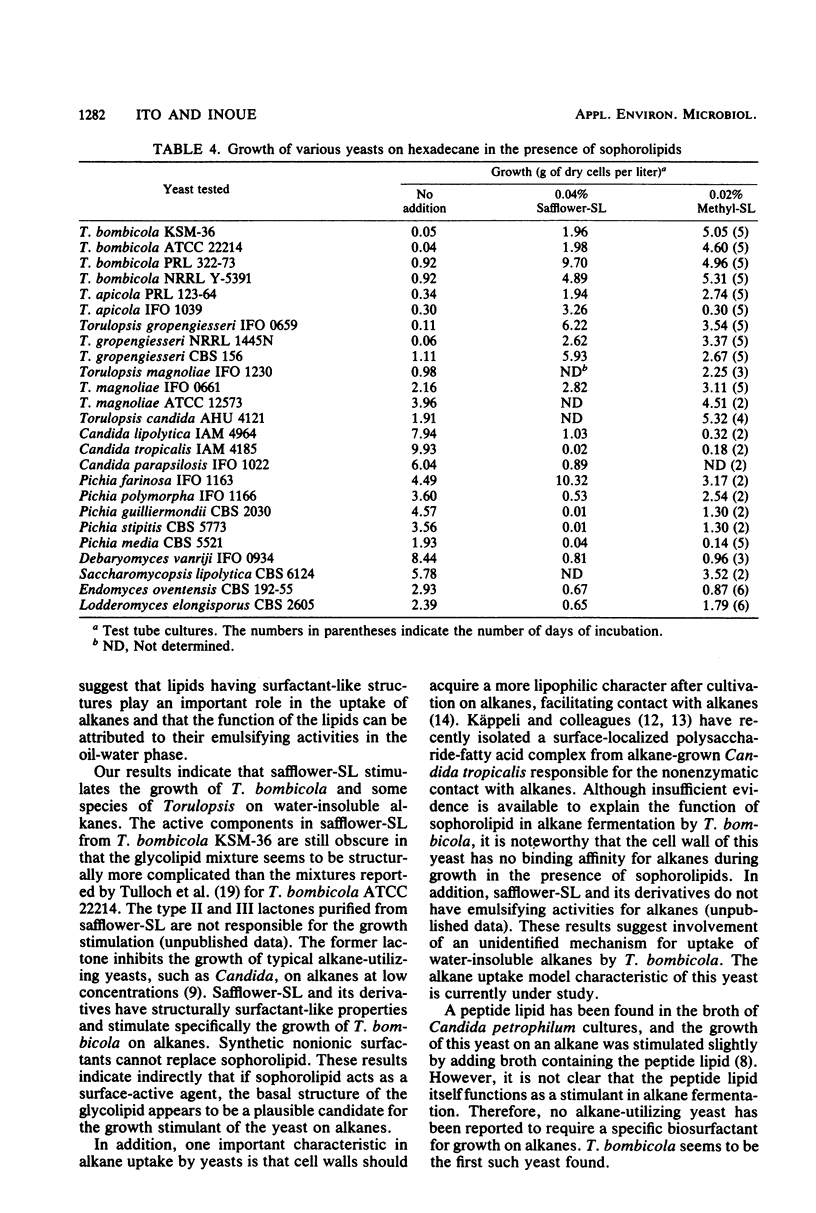
Abstract
Torulopsis bombicola produces extracellular sophorolipids when it is grown on water-insoluble alkanes. Sophorolipids and related model compounds, which were not themselves used for growth, were found to stimulate markedly the growth of T. bombicola on alkanes. This stimulatory effect was restricted to growth on C10 to C20 alkanes, whereas no significantly influence was observed for growth on fatty alcohols, fatty acids, glucose, or glycerol. The nonionic methyl ester of the glycolipid supported the greatest cell yield. However, a number of synthetic nonionic surfactants were unable to replace the glycolipid. When organisms were grown on hexadecane, stimulation of growth by sophorolipids was observed almost exclusively with strains of Torulopsis yeasts. In contrast, the growth of other typical alkane-utilizing yeasts, such as candida and Pichia strains, was inhibited or not affected. It appears that sophorolipids are involved in alkane dissimilation by T. bombicola through an undetermined mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper D. G., Zajic J. E., Gerson D. F. Production of surface-active lipids by Corynebacterium lepus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):4–10. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.4-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI MENNA M. E. Two new species of yeasts from New Zealand. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):269–272. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esders T. W., Light R. J. Glucosyl- and acetyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of glycolipids from Candida bogoriensis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1375–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz E., Tulloch A. P., Spencer J. F. Stereospecific hydroxylation of long chain compounds by a species of Torulopsis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):882–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Honda H., Tomita F., Suzuki T. Rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown on n-paraffin (mixture of C 12 , C 13 and C 14 fractions). J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Dec;24(12):855–859. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käppeli O., Fiechter A. Component from the cell surface of the hydrocarbon-utilizing yeast Candida tropicalis with possible relation to hydrocarbon transport. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):917–921. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.917-921.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käppeli O., Müller M., Fiechter A. Chemical and structural alterations at the cell surface of Candida tropicalis, induced by hydrocarbon substrate. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):952–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.952-958.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J. F., Gorin P. A., Tulloch A. P. Torulopsis bombicola sp.n. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(1):129–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02069014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stodola F. H., Deinema M. H., Spencer J. F. Extracellular lipids of yeasts. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Sep;31(3):194–213. doi: 10.1128/br.31.3.194-213.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerberg A., Diver A., Peeri Z., Gutnick D. L., Rosenberg E. Emulsifier of Arthrobacter RAG-1: chemical and physical properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):414–420. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.414-420.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



