Abstract
Glutamate is an essential neurotransmitter regulating brain functions. Excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT)-2 is one of the major glutamate transporters primarily expressed in astroglial cells. Dysfunction of EAAT2 is implicated in acute and chronic neurological disorders, including stroke/ischemia, temporal lobe epilepsy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer disease, human immunodeficiency virus 1-associated dementia, and growth of malignant gliomas. Ceftriaxone, one of the β-lactam antibiotics, is a stimulator of EAAT2 expression with neuroprotective effects in both in vitro and in vivo models based in part on its ability to inhibit neuronal cell death by glutamate excitotoxicity. Based on this consideration and its lack of toxicity, ceftriaxone has potential to manipulate glutamate transmission and ameliorate neurotoxicity. We investigated the mechanism by which ceftriaxone enhances EAAT2 expression in primary human fetal astrocytes (PHFA). Ceftriaxone elevated EAAT2 transcription in PHFA through the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway. The antibiotic promoted nuclear translocation of p65 and activation of NF-κB. The specific NF-κB binding site at the -272 position of the EAAT2 promoter was responsible for ceftriaxone-mediated EAAT2 induction. In addition, ceftriaxone increased glutamate uptake, a primary function of EAAT2, and EAAT2 small interference RNA completely inhibited ceftriaxone-induced glutamate uptake activity in PHFA. Taken together, our data indicate that ceftriaxone is a potent modulator of glutamate transport in PHFA through NF-κB-mediated EAAT2 promoter activation. These findings suggest a mechanism for ceftriaxone modulation of glutamate transport and for its potential effects on ameliorating specific neurodegenerative diseases through modulation of extracellular glutamate.
Glutamate plays a central role in brain physiology and pathology (1). It is the major mediator of excitatory signal transduction in the mammalian central nervous system and is implicated in most aspects of normal brain function, including cognition, memory, and learning (2). Glutamate exerts its signaling role by acting on glutamate receptors located on the surface of target cells. Accordingly, it is the glutamate concentration in the surrounding extracellular fluid that determines the extent of receptor stimulation. It is clinically relevant that the extracellular glutamate concentration is maintained at a low level, because excessive activation of glutamate receptors is harmful and glutamate is a potent neurotoxin at high concentration (2). The brain contains large quantities of glutamate, but only a small fraction of this glutamate is normally present in the extracellular fluid. Glutamate is constantly being released from cells and is continually being removed from the extracellular fluid (3). Glutamate transporters, also known as excitatory amino acid transporters, regulate this removal of glutamate from the extracellular fluid (3). Five excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT)4 cDNAs have been identified and cloned (EAAT1–5) (3). The predominant glutamate transporters in the brain are EAAT1 and EAAT2, also identified in the rodent as glutamate/aspartate transporter (GLAST) and glutamate transporter-1 (GLT-1), respectively, which are primarily expressed in astrocytes (3, 4).
Abnormalities in glutamate transport have been implicated in the pathogenesis of various neurological diseases (3, 5–18). Down-regulation of EAAT2 followed by accumulation of glutamate in the extracellular fluid and neuronal death have been documented in chronic, debilitative neurological disorders of diverse etiology, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (5–9, 18), Alzheimer disease (10), several forms of epilepsy (11), ischemia/stroke (12, 13), traumatic brain injury (13), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated dementia (14, 15), and hepatic encephalopathy (16, 17). HIV-1 infection of primary human fetal astrocytes (PHFA) results in down-regulation of both EAAT2 mRNA and protein and also decreases glutamate uptake in these cells (15). In a similar manner, treatment with tumor necrosis factor α, which might be secreted from HIV-infected macrophages, down-regulates both EAAT2 mRNA and protein and also reduces glutamate uptake in PHFA, suggesting an involvement of glutamate excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of HIV-associated dementia (15, 19).
Based on the role of glutamate transport by astrocytes in maintaining normal brain function, 1,040 Food and Drug Administration-approved drugs and nutritional agents were screened for bioactivity (19). These studies identified β-lactam antibiotics as potent stimulators of GLT-1 expression, not GLAST (20). β-Lactams and various semi-synthetic derivatives are effective antibiotics that act to inhibit bacterial synthetic pathways (21). The β-lactam ceftriaxone (CEF) increases both brain expression of EAAT2 and its biochemical and functional activity in vivo and is neuroprotective in vitro in models of ischemic injury and motor neuron degeneration, based in part on protection from glutamate toxicity (20, 22). CEF also delayed loss of neurons, increased muscle strength, and enhanced mouse survival in an animal model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (20). Moreover, this action appears to be mediated through increased transcription of the EAAT2 gene (19, 20). However, the precise manner by which CEF enhances EAAT2 gene expression remained unclear. In this study, we unravel the mechanism of CEF-induced EAAT2 gene expression and enhanced glutamate transport in PHFA.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Cell Cultures and Reagents—PHFA were generated from human fetal brain tissue obtained from elective abortions in full compliance with National Institutes of Health guidelines (19, 23, 24). PHFA were cultured as described (19, 23, 24). CEF and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate were purchased from Sigma. 6-Amino-4-(4-phenoxyphenyl-ethylamino) quinazoline (NF-κB activation inhibitor, quinazoline), NF-κB SN50 (cell-permeable inhibitor peptide), and NF-κB SN50M (control peptide) were purchased from Calbiochem. For the present studies, cells were cultured in antibiotic-free medium for at least 7 days before treatment with CEF.
Recombinant Adenovirus Constructs, Plasmids, and siRNAs— The recombinant replication-incompetent Ad.IκBα-mt32 was described previously (24). 5′-Deletion mutants of the human EAAT2 promoter were made with exonuclease III digestion by using the Erase-A-Base system (Promega) as described previously (19). The NFκBmt-272 construct was made using the QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene) in the context of the EAAT2Pro-954 construct according to the manufacturer's instructions. The sequences of primers used include: forward-5′-ATA GAG AGG GAT CGC CTG CAA ATC GCC AGC TCC GG-3′, reverse-5′-CCG GAG CTG GCG ATT TGC AGG CGA TCC CTC TCT AT-3′. The mutated sequences are underlined. The 3κB-Luc reporter vector and p65 expression vector were described previously (25, 26). Control siRNA-A, EAAT1 siRNA, EAAT2 siRNA, and p65 siRNA were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology.
Preparation of Cell Extracts and Western Blotting Analysis— Whole cell lysates were prepared and Western blotting was performed as described previously (23, 24). Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were prepared using Nuclear Extract kit (Active Motif) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The EAAT1 and EAAT2 proteins were detected using affinity-purified rabbit anti-peptide antibody generated against the C-terminal domains of EAAT1 and EAAT2, respectively. The domain sequence was described previously (4). Antibodies for p65 and IκBα were described previously (25). The antibodies for actin and Sp1 were purchased from Cell Signaling and Upstate, respectively. Protein expression was quantitatively analyzed via laser-scanning densitometry using National Institutes of Health Image Version 1.61 software. All results were normalized to actin or Sp1 expression.
Northern Blotting and Nuclear Run-on Assay—Total cellular RNA was extracted from cells using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. 20 μg of total RNA was used for Northern blotting as described previously (19). The nuclei were extracted using Nonidet P-40 lysis buffer, and nuclear run-on assays were performed as described previously (19).
Transient Transfection and Luciferase Assay—A total of 1 × 105 cells were seeded per well in 24-well plates and transfected with 880 ng of total DNA and 50 nm siRNA using Lipofectamine 2000 transfection reagent (Invitrogen) essentially according to the manufacturer's instructions. Luciferase assays were performed as described previously (23). Luciferase activity was normalized by β-galactosidase activity, and the data presented are the -fold activation ± standard deviation (S.D.) from at least three independent experiments performed in duplicate or triplicate.
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay—Nuclear extracts were prepared using Nuclear Extract kit (Active Motif) according to the manufacturer's instructions; electrophoretic mobility shift assay was performed as described previously (23). The sequences of oligonucleotides used as probes include: -583 probe, 5′-AGA CGG AGG GGC ATC CCG GGT CTC-3′; -334 probe, 5′-GGT TAA AGG AGT TGC CCG AGG CGG-3′; -272 probe, 5′-AGA GGG ATC GCC TGC AAA TCC CCA GCT C-3′; and -251 probe, 5′-TCC GGC GGG GCT AAA CCT TGC AAT-3′. The sequences of the -272 M probe containing a mutated NF-κB binding site at the -272 position of the EAAT2 promoter are 5′-AGA GGG ATC GCC TGC AAA TCG CCA GCT C-3′. The mutated sequence is underlined. For supershift experiments, 2 μl of anti-p65 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was added to the reaction mixture and was incubated for 15 min at 4 °C before the addition of probe.
Immunofluorescence Microscopy—PHFA seeded onto 4-well chamber slides were infected with Ad.vec or Ad.IκBα-mt32 at 10 plaque-forming units/cell and then treated with or without CEF. Two days later, the cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline. Immunofluorescence staining was done with anti-p65 antibody and mounted with mounting medium containing 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole as described (25). Images were taken with a confocal laser scanning microscope LSM multiphoton 510 (Zeiss).
Glutamate Uptake Assay—PHFA were plated in triplicate at 1 × 105 cells/well in 12-well plates, grown up to ∼75% confluence, and equilibrated at 25 °C in incubation medium, 0.125 m NaCl, 4.5 mm KCl, 1.2 mm CaCl2, 1.2 mm MgCl2, and 5 mm glucose, buffered to pH 7.4 with sodium phosphate. Assays to determine glutamate uptake were performed as described previously (15, 20). The results are expressed in pmol glutamate/mg protein/min.
Statistical Analysis—Results are expressed as means ± S.D. of at least three independent experiments. The unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test was performed for statistical evaluations. p <0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
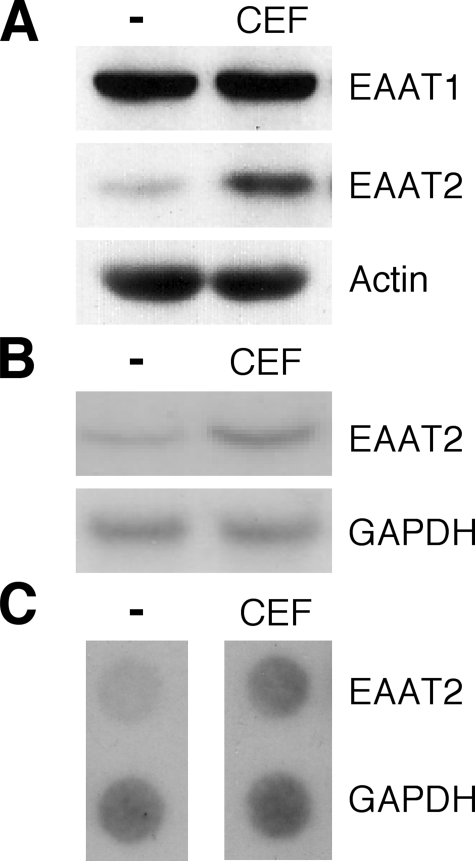
Human EAAT2 Expression Is Induced by CEF in PHFA—To investigate whether CEF induces EAAT1 and EAAT2 expression in PHFA, the effect of CEF on EAAT1 and EAAT2 protein level was determined. As shown in Fig. 1A, treatment of PHFA with CEF significantly enhanced EAAT2 protein levels (∼3-fold). However, CEF had no effect on EAAT1 expression in PHFA (Fig. 1A), confirming previous data indicating that CEF did not regulate GLAST expression in the rat (20). To determine whether CEF-mediated EAAT2 protein accumulation was associated with an increase in EAAT2-specific mRNA expression, total RNA from PHFA treated with or without CEF was isolated and examined by Northern blotting. As shown in Fig. 1B, EAAT2 mRNA was increased ∼3.5-fold in CEF-treated PHFA. This induction was caused by enhanced transcription (∼2.3-fold) as confirmed by performing nuclear run-on assays (Fig. 1C). These results confirm that human EAAT2 expression is induced by CEF at a transcriptional level in PHFA.
FIGURE 1.
CEF induces EAAT2 expression in primary human fetal astrocytes. PHFA cells were cultured in antibiotic-free medium for at least 7 days prior to all experiments reported in this study. Cells were treated with 10 μm CEF for 2 days. A, cell lysates were prepared, and EAAT1 and EAAT2 protein expressions were analyzed. Actin was used as an internal control. B, total cellular RNA was extracted and subjected to Northern blotting for EAAT2 mRNA expression. C, nuclei were extracted, and the isolated nuclei were used to label preinitiated RNA transcription with [α-32P]UTP in vitro, and the purified RNA was hybridized to a dot blot carrying an equivalent amount of panel DNA probes. The transcript rate of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) served as a control.
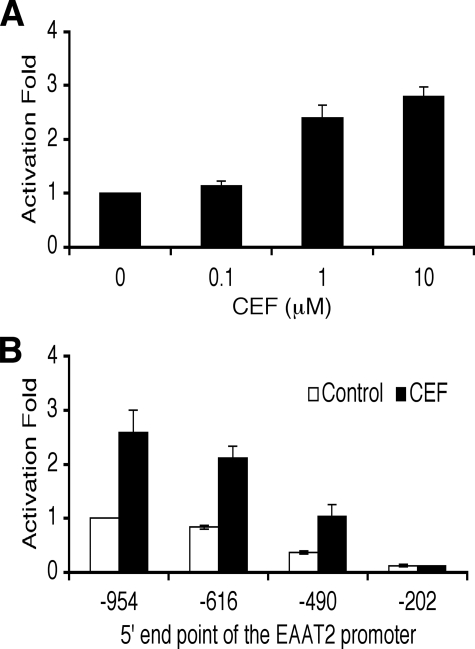
CEF Activates the Human EAAT2 Promoter—To determine whether CEF activates the human EAAT2 promoter, an EAAT2 promoter-driven luciferase reporter vector (EAAT2Pro-954) was transiently transfected into PHFA cultured in antibiotic-free medium for at least 7 days. CEF treatment induced EAAT2 promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner up to ∼2.5-fold (Fig. 2A), documenting a significant transcriptional response of the EAAT2 promoter to this β-lactam antibiotic. We next determined in more detail the cis elements in the EAAT2 promoter essential for response to CEF. A series of 5′-deletion mutants of the EAAT2 promoter-reporter construct were transiently transfected into PHFA, and the transfected cells were treated with CEF (Fig. 2B). The basal promoter activity of each -490 and -202 deletion mutant significantly reduced in a similar pattern as reported previously, indicating that four NF-κB binding sites in the -616/-203 region of the EAAT2 promoter are important for the basal promoter activity (Fig. 2B) (19, 26). In addition, deletion from -490 to -203 resulted in a loss of CEF-induced promoter activity (Fig. 2B). These results suggest that transcription factors binding to the -490/-203 region are capable of regulating induction of the EAAT2 promoter in response to CEF.
FIGURE 2.
CEF activates the EAAT2 promoter. A, PHFA cells were transfected with the EAAT2Pro-954 together with a pSV-β-galactosidase plasmid as an internal control. One day after transfection, cells were treated with various concentrations of CEF for 2 days as indicated. Values are presented as -fold-normalized activity relative to that of the untreated cells taken as 1. B, PHFA cells were transfected with different EAAT2 promoter deletion-reporter constructs with pSV-β-galactosidase as an internal control. One day after transfection, cells were treated with 10 μm CEF for 2 days. Values are presented as -fold-normalized activity relative to that of the EAAT2Pro-954 in untreated cells taken as 1. Error bars indicate S.D.
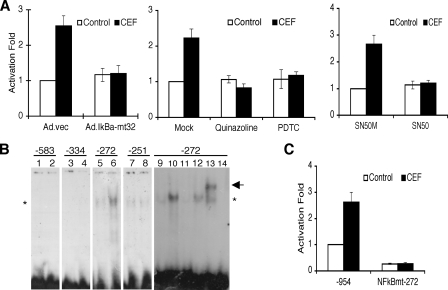
NF-κB Is Important for CEF-mediated EAAT2 Promoter Activation—We reported previously that NF-κB plays a crucial role in positive and negative regulation of the EAAT2 promoter (26). Accordingly, we examined whether NF-κB is a basis of the CEF-mediated EAAT2 promoter activation by using NF-κB genetic and pharmacological inhibitors. The addition of NF-κB inhibitors Ad.IκBα-mt32, quinazoline, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, and SN50 significantly inhibited CEF-mediated EAAT2 promoter activation with little change in basal EAAT2 promoter activity in PHFA (Fig. 3A). These results indicate that NF-κB is involved in CEF-mediated EAAT2 promoter activation.
FIGURE 3.
NF-κB is crucial for CEF-induced EAAT2 expression. A, PHFA were infected with Ad.vec or Ad.IκBα-mt32. The infected cells (left) or uninfected PHFA (middle and right) were transfected with EAAT2Pro-954 together with pSV-β-galactosidase as an internal control. One day after transfection, cells were treated with 10 μm CEF together with the indicated inhibitors (middle, 5 μm quinalzoline or 20 μm pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate; right, 5 μm SN50M or SN50) for 2 days. Values are presented as –fold-normalized activity relative to that of the EAAT2Pro-954 in Ad.vec-infected (left), mock-treated (middle), or SN50M-treated (right) cells. B, PHFA were treated with 10 μm CEF for 4 days, and nuclear extracts were prepared. Nuclear extracts were mixed with each radiolabeled oligonucleotide containing the NF-κB binding site located at -583, -334, -272, or -251 of the EAAT2 promoter as follows: lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9, untreated nuclear extracts; lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10–13, CEF-treated nuclear extracts; lane 14, no extracts added. For competition assays, a 100-fold excess of corresponding unlabeled probe (lane 11) or unlabeled probe encompassing the mutated NF-κB site (lane 12) was added. Supershift analysis was performed with an anti-p65 antibody (lane 13). The asterisk and arrow indicate, respectively, NF-κB and a supershift band. C, PHFA were transfected with either the EAAT2Pro-954 or NF-κBmt-272 construct together with pSV-β-galactosidase as an internal control. One day after transfection, cells were treated with 10 μm CEF for 2 days. Values are represented as –fold-normalized activity to that of the EAAT2Pro-954 in untreated cells taken as 1. Error bars indicate S.D.
NF-κB Binding Site at the -272 Position of the EAAT2 Promoter Responds to CEF—The results described above indicate that the human EAAT2 promoter is activated by CEF and the NF-κB signaling pathway mediates this CEF-induced EAAT2 promoter activation. A previous report showed that three NF-κB binding sites are in the -490/-203 region of the EAAT2 promoter and the other one is at the -583 position of the EAAT2 promoter (26). To determine which site(s) is responsible for this activation, we performed electrophoretic mobility shfit assay using double-stranded oligonucleotide probes containing each NF-κB binding site from the -490/-203 region and -583 position of the EAAT2 promoter. As shown in Fig. 3B, the intensity of DNA-protein complexes generated by the -583, -334, and -251 probes, containing the NF-κB binding sites at the -583, -334, and -251 positions, respectively, did not change following CEF treatment in comparison with non-treated PHFA nuclear extracts. However, the intensity of one band generated by the -272 probe, containing the NF-κB binding site at the -272 position of the EAAT2 promoter, was significantly higher in CEF-treated nuclear extracts as compared with non-treated nuclear extracts (Fig. 3B). To further characterize this increased DNA-protein complex from CEF-treated PHFA nuclear extracts, an unlabeled -272 probe and a -272 M probe containing mutation in the -272 NF-κB binding site were used as competitors in electrophoretic mobility shift assay. As shown in Fig. 3B, lane 11, unlabeled probe 2 completely competed the increased DNA-protein complex. In contrast, the -272 M probe had little effect on nucleoprotein complex formation (Fig. 3B, lane 12). These results indicate that the NF-κB binding site at the -272 position of the EAAT2 promoter confers the CEF-mediated differential transcription factor binding. Supershift experiments with anti-p65 antibody resulted in a retarded mobility of the complex (indicated by arrow), demonstrating the presence of p65, a subunit of NF-κB in the nucleoprotein complex (lane 13). Taken together, these data indicate that CEF increases binding of NF-κB to the -272 NF-κB binding site in the EAAT2 promoter. To clarify the role of the -272 NF-κB binding site of the EAAT2 promoter, a mutant EAAT2 promoter-reporter construct (NFκBmt-272) containing a mutation in the -272 NF-κB binding site was generated (Fig. 3C). This construct was transiently transfected into PHFA, and the transfected cells were treated with or without CEF. As shown in Fig. 3C, the NFκBmt-272 abolished response to CEF. In addition, the mutation of the -272 NF-κB binding site significantly reduced the basal EAAT2 promoter activity, confirming as previously shown that four NF-κB sites are important for the basal activity of the EAAT2 promoter (26). These results indicate that the NF-κB binding site at the -272 position is critical for basal EAAT2 promoter activity as well as CEF-mediated EAAT2 promoter activation.
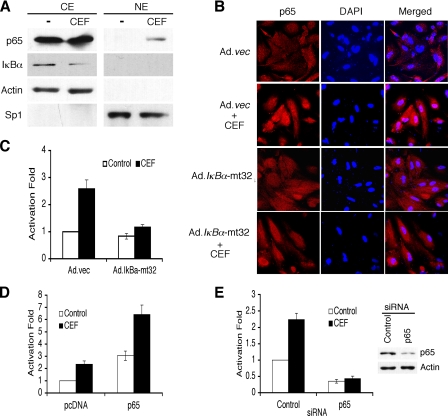
CEF Activates NF-κB via IκBα Degradation and p65 Translocation—In general, NF-κB is activated through the proteasomal degradation of the cytoplasmic inhibitor IκB proteins binding to the NF-κB complex (27). The resulting proteasomal degradation of IκB proteins liberates IκB-bound NF-κB, which translocates to the nucleus to drive expression of target genes (27). To determine whether CEF-induced NF-κB activation also proceeds through a similar canonical pathway, the expression of IκBα and the p65 subunit of NF-κB were examined by Western blot analysis. As shown in Fig. 4A, the level of IκBα in cytoplasmic extracts of PHFA was decreased significantly following treatment with CEF (∼1.9-fold ± 0.43). However, the level of p65 protein was unchanged in the cytoplasmic extracts and increased significantly in the nuclear extracts after CEF treatment of PHFA (∼3.4-fold ± 0.91) (Fig. 4A). In immunofluorescence studies using anti-p65 antibody, slight cytoplasmic and no nuclear staining were detected in untreated PHFA, but staining in the nucleus increased significantly in CEF-treated PHFA (Fig. 4B). In addition, Ad.IκBα-mt32 infection inhibited CEF-mediated p65 nuclear translocation (Fig. 4B). These results point out that CEF treatment induces the translocation of p65 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in PHFA, indicating NF-κB activation. To confirm whether CEF can induce the transcriptional activity of NF-κB, we employed a 3κB-Luc reporter vector containing three NF-κB consensus binding sites. As shown in Fig. 4C, CEF enhanced the transcriptional activity of NF-κBupto ∼2.5-fold and Ad.IκBα-mt32 infection, a dominant negative inhibitor of NF-κB, abolished CEF-mediated NF-κB activation. To clarify the role of p65 in CEF-medicated EAAT2 promoter activation, we investigated whether p65 overexpression or knocking down p65 affects CEF-mediated EAAT2 promoter activation. As shown in Fig. 4D, p65 overexpression activated the EAAT2 promoter and also further augmented the CEF-induced EAAT2 promoter activation (Fig. 4D). In addition, p65 siRNA abolished CEF-induced EAAT2 promoter activation (Fig. 4E). The activity of p65 siRNA was confirmed by measuring p65 protein levels as shown in Fig. 4E (∼75% reduction). These results suggest that CEF induces NF-κB activation through induction of the p65 nuclear translocation and the expression of its downstream target genes, including EAAT2.
FIGURE 4.
CEF activates NF-κB. A, PHFA were treated with 10 μm CEF for 4 days. Nuclear extracts (NE) and cytoplasmic extracts (CE) were prepared and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Actin and Sp1 were used as the internal control for CE and NE, respectively. B, PHFA cells were infected with Ad.vec or Ad.IκBα-mt32 and then incubated with 10 μm CEF for 2 days. The p65 immunostaining and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining were evaluated by confocal microscopy. C, PHFA were infected with Ad.vec or Ad.IκBα-mt32. The infected cells were transfected with 3κB-Luc, containing three tandem NF-κB binding sites, together with pSV-β-galactosidase as an internal control. One day after transfection, the cells were treated with 10 μm CEF for 2 days. Values are presented as -fold-normalized activity relative to that of 3κB-Luc in Ad.vec-infected cells untreated with CEF taken as 1. D, PHFA were transfected with the EAAT2Pro-954 and pcDNA or p65 expression vector together with a pSV-β-galactosidase plasmid as an internal control. One day after transfection, cells were treated with 10 μm CEF for 2 days. Values are presented as -fold-normalized activity relative to that of the pcDNA-transfected and untreated cells taken as 1. E, PHFA were transfected with the EAAT2Pro-954 and control siRNA or p65 siRNA together with a pSV-β-galactosidase plasmid as an internal control. One day after transfection, cells were treated with 10 μm CEF for 2 days. Values are presented as -fold-normalized activity relative to that of the control siRNA-transfected and untreated cells taken as 1. The cell lysates treated with control and p65 siRNA were used for Western blotting. Error bars indicate S.D.
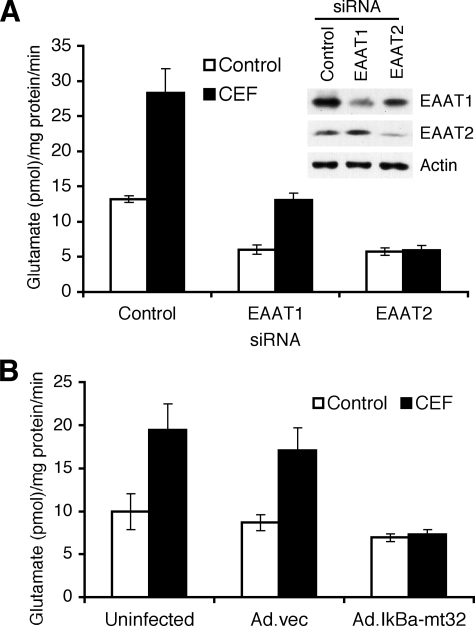
CEF Elevates Glutamate Transporter Activity in PHFA— Glutamate transporters are preferentially localized to astroglial membranes, although in some cases increased protein expression is not always mirrored by concomitant membrane localization and functional activity (28). Based on this consideration, we investigated whether CEF-mediated EAAT2 expression could induce the functional activity of EAAT2 as a glutamate transporter. As shown in Fig. 5A, CEF treatment increased l-[3H]glutamate transport in PHFA, and this increased glutamate transporter activity was inhibited by EAAT2 siRNA, but not EAAT1 siRNA. EAAT1 and EAAT2 siRNA also decreased basal glutamate uptake in PHFA (Fig. 5A). The activity of EAAT1 and EAAT2 siRNA was confirmed by measuring EAAT1 and EAAT2 expression as shown in Fig. 5A. In addition, inhibition of NF-κB using Ad.IκBα-mt32 completely abrogated the CEF-mediated increase of glutamate uptake activity (Fig. 5B). These results indicate that CEF can induce glutamate transporter activity in PHFA cells by induction of EAAT2 gene expression through the NF-κB signaling pathway.
FIGURE 5.
CEF induces glutamate uptake in PHFA. A, PHFA were transfected with control, EAAT1, or EAAT2 siRNA, and then the transfected cells were treated with 10 μm CEF. Two days later, glutamate uptake levels were measured as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Accordingly, cell lysates from PHFA transfected with control, EAAT1, or EAAT2 siRNA were prepared and EAAT1 and EAAT2 expressions were analyzed. B, PHFA were infected with Ad.vec or Ad.IκBα-mt32, and then the uninfected or infected cells were treated with 10 μm CEF. Two days later, glutamate uptake levels were measured. Error bars indicate S.D.
DISCUSSION
Glutamate excitotoxicity is implicated in central nervous system abnormalities, including trauma, stroke, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington disease, Alzheimer disease, epilepsy, HIV-associated dementia, and immune-mediated damage in multiple sclerosis (10, 12, 29–36). However, the mechanism by which astrocytes regulate glutamate transport and prevent glutamate damage to neurons remains to be defined. One way astrocytes affect neuronal function is through the EAAT2 transporter and its capacity to maintain stimulatory, but nontoxic, levels of free intrasynaptic l-glutamate in the area adjacent to neurons (29, 37, 38). Abnormalities in this process result in the accumulation of extracellular glutamate in synaptic clefts and over-excitation death of neurons in the process of glutamate excitotoxicity (29, 37, 38). Therefore, it is crucial to understand the regulation of EAAT2 expression in astrocytes and define ways of controlling this process. A recent report also suggested that regulation in expression and activity of EAAT2 by caspase-3 are possible mechanisms responsible for the impairment of glutamate uptake in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (39).
Previous reports showed that one of the most active β-lactam antibiotics and a representative cephalosporin, CEF, was neuroprotective in vitro and in vivo and its EC50 for increasing EAAT2 expression was 3.5 μm, which is comparable with the known central nervous system levels attainable with therapy for meningitis, indicating that β-lactam antibiotics could serve unique functions as potential neurotherapeutics (20, 22, 40, 41). In the present study, we elucidate the mechanism by which CEF induces EAAT2 expression.
In a previous report we documented that CEF induces GLT-1, but not GLAST, expression in the rodent system (20). As shown in Fig. 1A, CEF induces the expression of EAAT2, but not EAAT1, in PHFA, confirming that CEF uniquely stimulates EAAT2 expression in human astrocytes as it does GLT-1 in rodents. CEF induces EAAT2 expression at the transcriptional level (Figs. 1, B and C, and 2A). Recently, data have been presented indicating that β-lactam antibiotics ampicillin and penicillin induce EAAT2 expression at the translational level (42). The discrepancies between these observations and our present results probably reflect the different cell types, experimental protocols, and chemicals employed. Tian et al. (42) used primary cortical neuron and astrocyte mixed cells from rodents treated with ampicillin and penicillin, whereas the present study employed PHFA and CEF. Both results, however, suggest that β-lactam antibiotics can induce EAAT2 expression. Although GLAST and GLT-1 are mainly expressed in glial cells, excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1) (rodent homolog of human EAAT3) is predominantly expressed in neurons (4). In the CA1 region of the hippocampus, a neuronal transporter (EAAC1) regulates glutamate concentration and activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (43). A recent report also suggested that N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-dependent regulation of EAAC1 may modulate excitatory signaling during synaptic plasticity and excitotoxicity (44). However, CEF did not induce EAAC1 expression (20). These data argue that CEF can specifically modulate expression of EAAT2, and not EAAT1 or EAAT3.
NF-κB is a transcription factor that plays a decisive role in regulating a diverse array of genes involved in immune responses, cell growth and survival, and differentiation (27, 45). As shown in Fig. 3A, NF-κB inhibitors attenuate the CEF-mediated EAAT2 induction, indicating that activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway regulates this induction (Fig. 3A). In the central nervous system, NF-κB is ubiquitously expressed in neurons and glia where it participates in pathological events associated with neurodegeneration in addition to regulating physiological processes (45, 46). Moreover, NF-κB has been regarded as a compensatory factor that might elevate expression of anti-oxidant or anti-apoptotic genes in the brain rather than participating in the toxicity of glutamate or tumor necrosis factor (45, 46). Recent reports also established that the EAAT2 promoter has four NF-κB binding sites that are important for positive and negative regulation of EAAT2 expression (19, 26, 47). Interestingly, however, we found that only one NF-κB binding site at the -272 position of the EAAT2 promoter is responsible for the CEF-mediated EAAT2 promoter activation (Fig. 3, B and C). Our previous experiments indicated that EAAT2 promoter is differentially regulated depending on extracellular signals and NF-κB can activate or repress EAAT2 transcription through distinct signaling pathways in combination with other transcription factors, such as N-Myc (26). Accordingly, these results suggest that each NF-κB binding site in the EAAT2 promoter is responsible for activation/repression of different signaling pathways through NF-κB interaction with other regulatory factors. We demonstrate that CEF also activates the canonical NF-κB signaling pathway inducing p65 nuclear translocation through the proteasomal degradation of IκBα, which promotes CEF-mediated EAAT2 promoter activation (Fig. 4) and induction of glutamate uptake in PHFA (Fig. 5). In total, our data indicate that CEF is a potent modulator of glutamate transport through NF-κB-mediated EAAT2 transcriptional activation. In addition, recent reports indicate that CEF induces ischemic tolerance in focal cerebral ischemia and attenuates hyperthermia caused by morphine and neurotoxicity and neuronal cell death by HIV proteins through activation of EAAT2 expression, further indicating that CEF might be a useful clinical alternative to treat various brain diseases (48–50).
Although the number of patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases continues to increase, few if any effective treatment options are available. Taken together, these results suggest that CEF, or rationally designed and pharmacologically enhanced drugs that act in a similar manner as this antibiotic, might serve as a therapeutic drug for ameliorating and potentially preventing a wide spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases caused by glutamate excitotoxicity.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant P01 NS31492 (to D. J. V. and P. B. F.). This work was also supported by the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation (SWCRF) (to P. B. F.). The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
Footnotes
The abbreviations used are: EAAT, excitatory amino acid transporter; CEF, ceftriaxone; PHFA, primary human fetal astrocyte; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; GLAST, glutamate/aspartate transporter; GLT-1, glutamate transporter-1; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; quinazoline, 6-amino-4-(4-phenoxyphenylethylamino)quinazoline; EAAC1, excitatory amino acid carrier 1; siRNA, small interference RNA.
References
- 1.Fonnum, F. (1984) J. Neurochem. 42 1-11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Headley, P. M., and Grillner, S. (1990) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 11 205-211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anderson, C. M., and Swanson, R. A. (2000) Glia 32 1-14 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rothstein, J. D., Martin, L., Levey, A. I., Dykes-Hoberg, M., Jin, L., Wu, D., Nash, N., and Kuncl, R. W. (1994) Neuron 13 713-725 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Plaitakis, A., and Caroscio, J. T. (1987) Ann. Neurol. 22 575-579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Couratier, P., Hugon, J., Sindou, P., Vallat, J. M., and Dumas, M. (1993) Lancet 341 265-268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rothstein, J. D., Martin, L. J., and Kuncl, R. W. (1992) N. Engl. J. Med. 326 1464-1468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rothstein, J. D., Van Kammen, M., Levey, A. I., Martin, L. J., and Kuncl, R. W. (1995) Ann. Neurol. 38 73-84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Trotti, D., Aoki, M., Pasinelli, P., Berger, U. V., Danbolt, N. C., Brown, R. H., Jr., and Hediger, M. A. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276 576-582 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li, S., Mallory, M., Alford, M., Tanaka, S., and Masliah, E. (1997) J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 56 901-911 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tanaka, K., Watase, K., Manabe, T., Yamada, K., Watanabe, M., Takahashi, K., Iwama, H., Nishikawa, T., Ichihara, N., Kikuchi, T., Okuyama, S., Kawashima, N., Hori, S., Takimoto, M., and Wada, K. (1997) Science 276 1699-1702 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Torp, R., Lekieffre, D., Levy, L. M., Haug, F. M., Danbolt, N. C., Meldrum, B. S., and Ottersen, O. P. (1995) Exp. Brain Res. 103 51-58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Martin, L. J., Brambrink, A. M., Lehmann, C., Portera-Cailliau, C., Koehler, R., Rothstein, J., and Traystman, R. J. (1997) Ann. Neurol. 42 335-348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pappas, T. C., Alagarsamy, S., Pollard, R. B., and Nokta, M. (1998) J. Neurovirol. 4 69-79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang, Z., Pekarskaya, O., Bencheikh, M., Chao, W., Gelbard, H. A., Ghorpade, A., Rothstein, J. D., and Volsky, D. J. (2003) Virology 312 60-73 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Blei, A. T., and Larsen, F. S. (1999) J. Hepatol. 31 771-776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chan, H., and Butterworth, R. F. (1999) Neurochem. Res. 24 1397-1401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Trotti, D., Rolfs, A., Danbolt, N. C., Brown, R. H., Jr., and Hediger, M. A. (1999) Nat. Neurosci. 2 427-433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Su, Z. Z., Leszczyniecka, M., Kang, D. C., Sarkar, D., Chao, W., Volsky, D. J., and Fisher, P. B. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100 1955-1960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rothstein, J. D., Patel, S., Regan, M. R., Haenggeli, C., Huang, Y. H., Bergles, D. E., Jin, L., Dykes Hoberg, M., Vidensky, S., Chung, D. S., Toan, S. V., Bruijn, L. I., Su, Z. Z., Gupta, P., and Fisher, P. B. (2005) Nature 433 73-77 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goodman, L. S., Hardman, J. G., Limbird, L. E., and Gilman, A. G. (2001) Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, McGraw Hill Medical Publishing, New York
- 22.Rothstein, J. D., Jin, L., Dykes-Hoberg, M., and Kuncl, R. W. (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90 6591-6595 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee, S. G., Su, Z. Z., Emdad, L., Sarkar, D., and Fisher, P. B. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103 17390-17395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lee, S. G., Su, Z. Z., Emdad, L., Sarkar, D., Franke, T. F., and Fisher, P. B. (2008) Oncogene 27 1114-1121 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Emdad, L., Sarkar, D., Su, Z. Z., Randolph, A., Boukerche, H., Valerie, K., and Fisher, P. B. (2006) Cancer Res. 66 1509-1516 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sitcheran, R., Gupta, P., Fisher, P. B., and Baldwin, A. S. (2005) EMBO J. 24 510-520 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Karin, M. (2006) Nature 441 431-436 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schlag, B. D., Vondrasek, J. R., Munir, M., Kalandadze, A., Zelenaia, O. A., Rothstein, J. D., and Robinson, M. B. (1998) Mol. Pharmacol. 53 355-369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lipton, S. A., and Rosenberg, P. A. (1994) N. Engl. J. Med. 330 613-622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mathern, G. W., Mendoza, D., Lozada, A., Pretorius, J. K., Dehnes, Y., Danbolt, N. C., Nelson, N., Leite, J. P., Chimelli, L., Born, D. E., Sakamoto, A. C., Assirati, J. A., Fried, I., Peacock, W. J., Ojemann, G. A., and Adelson, P. D. (1999) Neurology 52 453-472 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bruijn, L. I., Becher, M. W., Lee, M. K., Anderson, K. L., Jenkins, N. A., Copeland, N. G., Sisodia, S. S., Rothstein, J. D., Borchelt, D. R., Price, D. L., and Cleveland, D. W. (1997) Neuron 18 327-338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lin, C. L., Bristol, L. A., Jin, L., Dykes-Hoberg, M., Crawford, T., Clawson, L., and Rothstein, J. D. (1998) Neuron 20 589-602 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kaul, M., Garden, G. A., and Lipton, S. A. (2001) Nature 410 988-994 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.McDonald, J. W., Althomsons, S. P., Hyrc, K. L., Choi, D. W., and Goldberg, M. P. (1998) Nat. Med. 4 291-297 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Meldrum, B. S. (2000) J. Nutri. 130 (Suppl.) S1007-S1015 [Google Scholar]
- 36.Smith, T., Groom, A., Zhu, B., and Turski, L. (2000) Nat. Med. 6 62-66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nicholls, D., and Attwell, D. (1990) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 11 462-468 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Robinson, M. B. (1998) Neurochem. Int. 33 479-491 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Boston-Howes, W., Gibb, S. L., Williams, E. O., Pasinelli, P., Brown, R. H., Jr., and Trotti, D. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281 14076-14084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chandrasekar, P. H., Rolston, K. V., Smith, B. R., and LeFrock, J. L. (1984) J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 14 427-430 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nau, R., Prange, H. W., Muth, P., Mahr, G., Menck, S., Kolenda, H., and Sorgel, F. (1993) Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37 1518-1524 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tian, G., Lai, L., Guo, H., Lin, Y., Butchbach, M. E., Chang, Y., and Lin, C. L. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282 1727-1737 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Diamond, J. S. (2001) J. Neurosci. 21 8328-8338 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Waxman, E. A., Baconguis, I., Lynch, D. R., and Robinson, M. B. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282 17594-17607 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Massa, P. T., Aleyasin, H., Park, D. S., Mao, X., and Barger, S. W. (2006) J. Neurochem. 97 607-618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.O'Neill, L. A., and Kaltschmidt, C. (1997) Trends Neurosci. 20 252-258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zelenaia, O., Schlag, B. D., Gochenauer, G. E., Ganel, R., Song, W., Beesley, J. S., Grinspan, J. B., Rothstein, J. D., and Robinson, M. B. (2000) Mol. Pharmacol. 57 667-678 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chu, K., Lee, S. T., Sinn, D. I., Ko, S. Y., Kim, E. H., Kim, J. M., Kim, S. J., Park, D. K., Jung, K. H., Song, E. C., Lee, S. K., Kim, M., and Roh, J. K. (2007) Stroke 38 177-182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rawls, S. M., Tallarida, R., Robinson, W., and Amin, M. (2007) Br. J. Pharmacol. 151 1095-1102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rumbaugh, J. A., Li, G., Rothstein, J., and Nath, A. (2007) J. Neurovirol. 13 168-172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]