Abstract
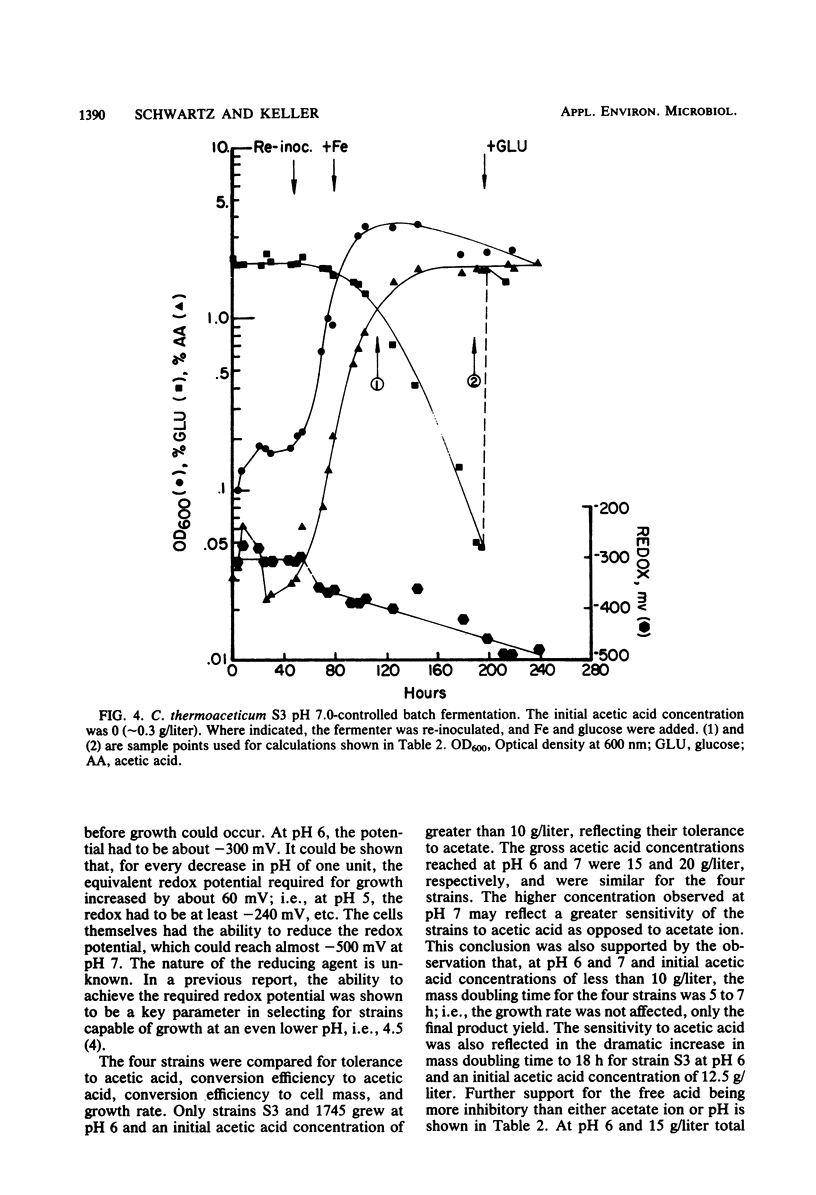
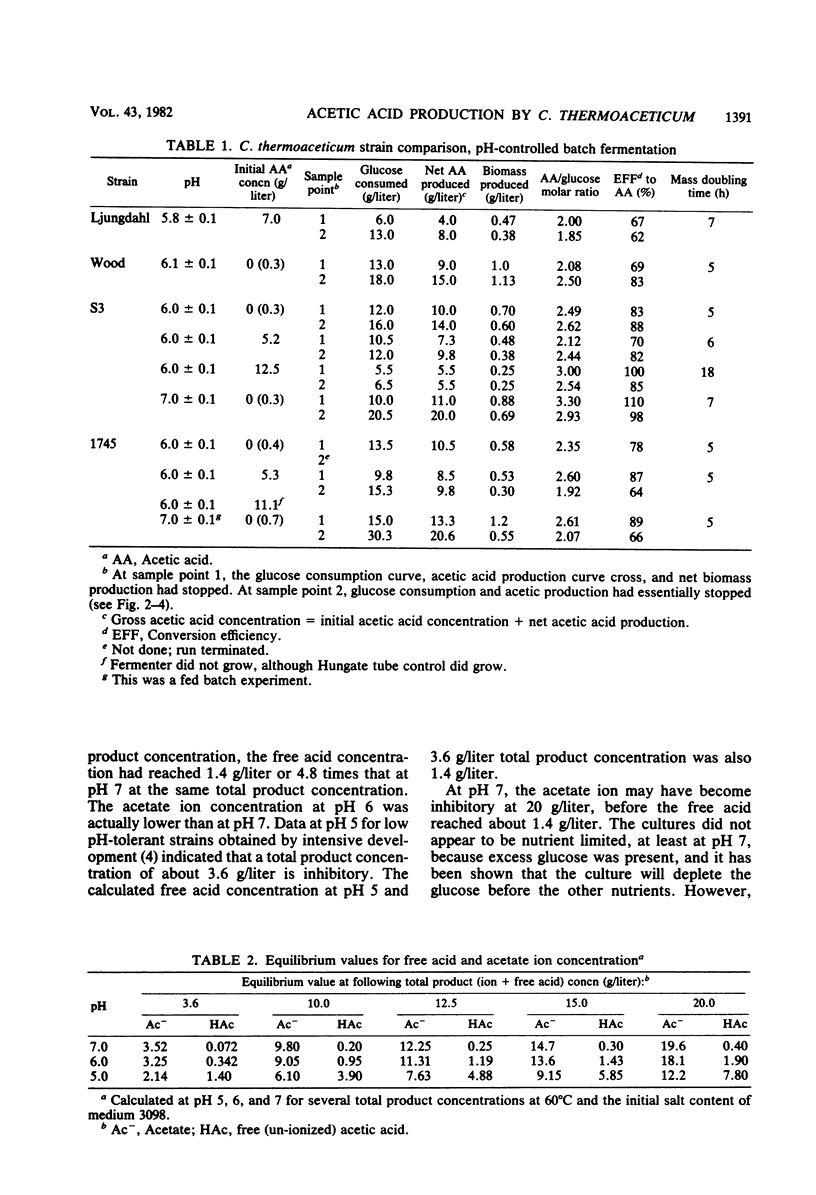
Four strains of the homofermentative, obligately anaerobic thermophile Clostridium thermoaceticum were compared in pH-controlled batch fermentation for their tolerance to acetic acid, efficiency of converting glucose to acetic acid and cell mass, and growth rate. At pH 6 (and pH 7) and initial acetic acid concentrations of less than 10 g/liter, the four strains had mass doubling times of 5 to 7 h and conversion efficiencies to acetic acid and cell mass of about 90% (70 to 110%) and 10%, respectively. At pH 6 and initial acetic acid concentrations of greater than 10 g/liter, only two of the strains grew, the mass doubling time increased to 18 h, and the conversion efficiencies to acetic acid and cell mass remained unchanged. Both of these strains had been selected for their ability to grow in the presence of acetate at neutral pH. The highest acetic acid concentrations reached were about 15 and 20 g/liter at pH 6 and 7, respectively. C. thermoaceticum is apparently more sensitive to free acetic acid than to either acetate ion or pH. It was also shown that, at pH 6 and 7, the redox potential must be at least as low as −300 and −360 mV, respectively, for growth to occur.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreesen J. R., Schaupp A., Neurauter C., Brown A., Ljungdahl L. G. Fermentation of glucose, fructose, and xylose by Clostridium thermoaceticum: effect of metals on growth yield, enzymes, and the synthesis of acetate from CO 2 . J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):743–751. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.743-751.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine F. E., Peterson W. H., McCoy E., Johnson M. J., Ritter G. J. A New Type of Glucose Fermentation by Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1942 Jun;43(6):701–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.6.701-715.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L. G. Total synthesis of acetate from CO2 by heterotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:515–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. D., Keller F. A. Isolation of a Strain of Clostridium thermoaceticum Capable of Growth and Acetic Acid Production at pH 4.5. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.117-123.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]