Abstract
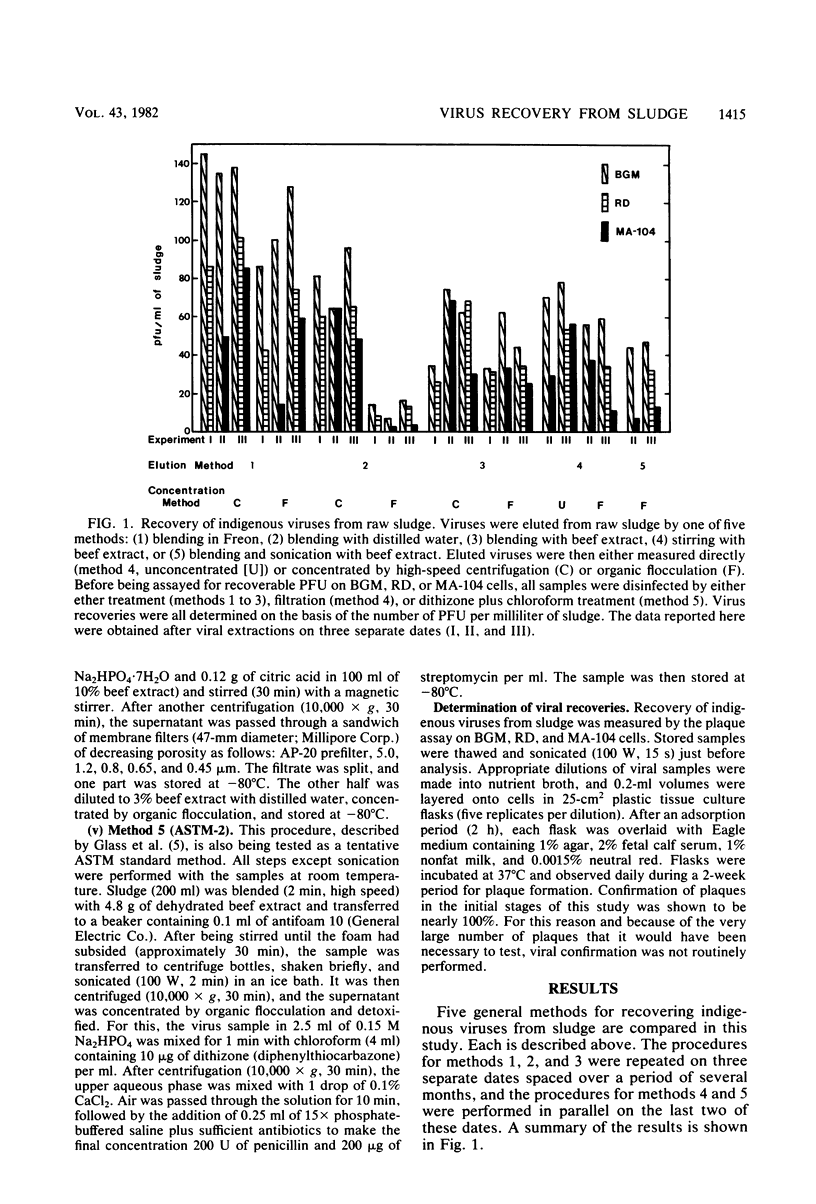
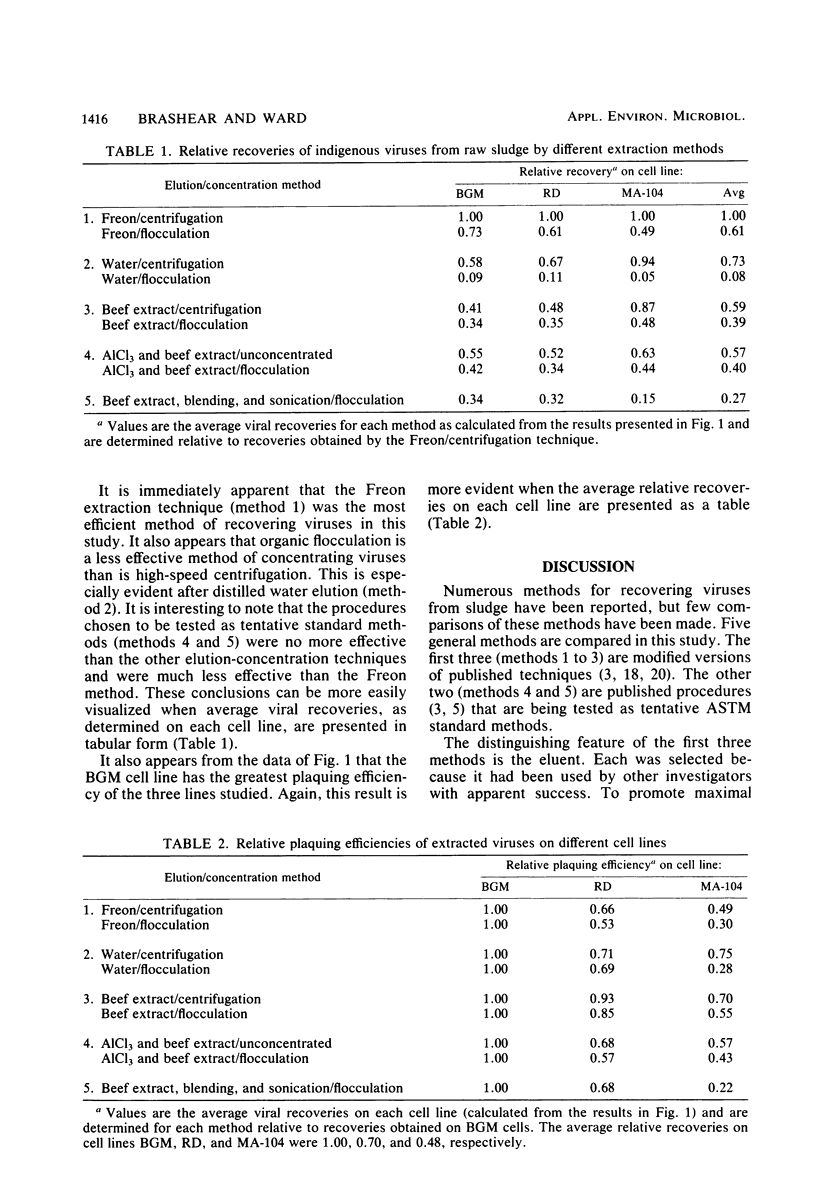
Five general methods for recovering indigenous viruses from raw wastewater sludge were compared. Each method included elution, concentration, and disinfection steps. The elution method, found to consistently yield the greatest viral recovery, was a two-phase technique that involved blending sludge with Freon. Other methods, including two being tested as American Society for Testing Materials tentative standard methods, were less effective. Viral recoveries were generally greater (sometimes much greater) if samples were concentrated by high-speed centrifugation rather than by organic flocculation with 3% beef extract. Three cell lines were used to measure viral recoveries by the plaque assay. The efficiency of recovery was greatest on BGM cells, followed by RD and MA-104 cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg G., Dahling D. R. Method for recovering viruses from river water solids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):850–853. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.850-853.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman D., Berg G., Safferman R. S. A method for recovering viruses from sludges. J Virol Methods. 1981 Dec;3(5):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Scheuerman P. R., Bitton G. Urea-lysine method for recovery of enteroviruses from sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):455–458. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.455-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass J. S., Van Sluis R. J., Yanko W. A. Practical method for detecting poliovirus in anaerobic digester sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):983–985. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.983-985.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst C. J., Farrah S. R., Gerba C. P., Melnick J. L. Development of quantitative methods for the detection of enteroviruses in sewage sludges during activation and following land disposal. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.81-89.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenelson E., Fattal B., Hostovesky T. Organic flocculation: an efficient second-step concentration method for the detection of viruses in tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):638–639. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.638-639.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Hedström C. E. The use of an aqueous polymer phase system for enterovirus isolations from sewage. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Sep;84(2):287–291. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancorbo O. C., Scheuerman P. R., Farrah S. R., Bitton G. Effect of sludge type on poliovirus association with and recovery from sludge solids. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Mar;27(3):279–287. doi: 10.1139/m81-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattar S. A., Westwood J. C. Comparison of four eluents in the recovery of indigenous viruses from raw sludge. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Oct;22(10):1586–1589. doi: 10.1139/m76-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattar S. A., Westwood J. C. Recovery of viruses from field samples of raw, digested, and lagoon-dried sludges. Bull World Health Organ. 1979;57(1):105–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyan T. P. Persistence of enteroviruses in sewage sludge. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(4):431–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk C. A., Moore B. E., Sagik B. P., Sorber C. A. Recovery of indigenous viruses from wastewater sludges, using a bentonite concentration procedure. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):423–425. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.423-425.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Inactivation of poliovirus in digested sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):921–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.921-930.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Lewis A. L., Mountain C. W. Demonstration of solids-associated virus in wastewater and sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):354–358. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.354-358.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


