Abstract
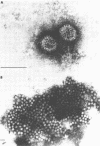
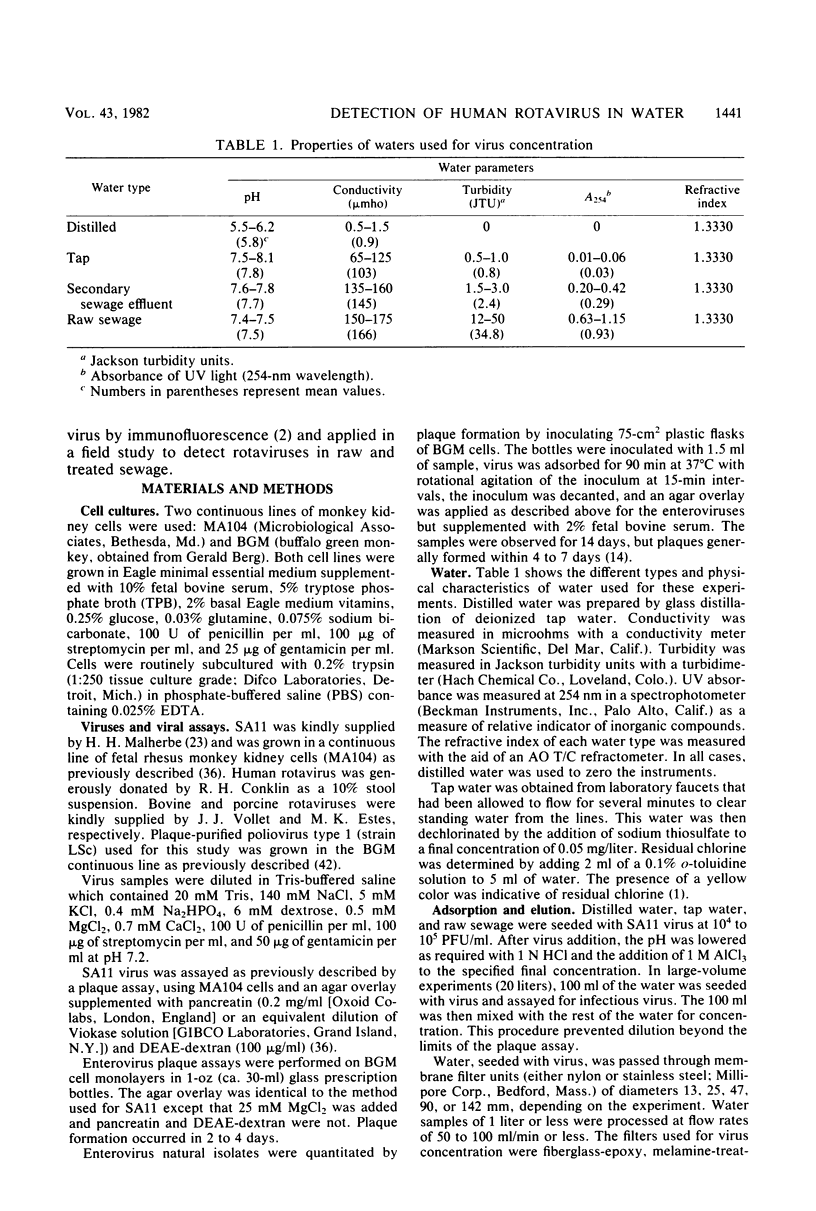
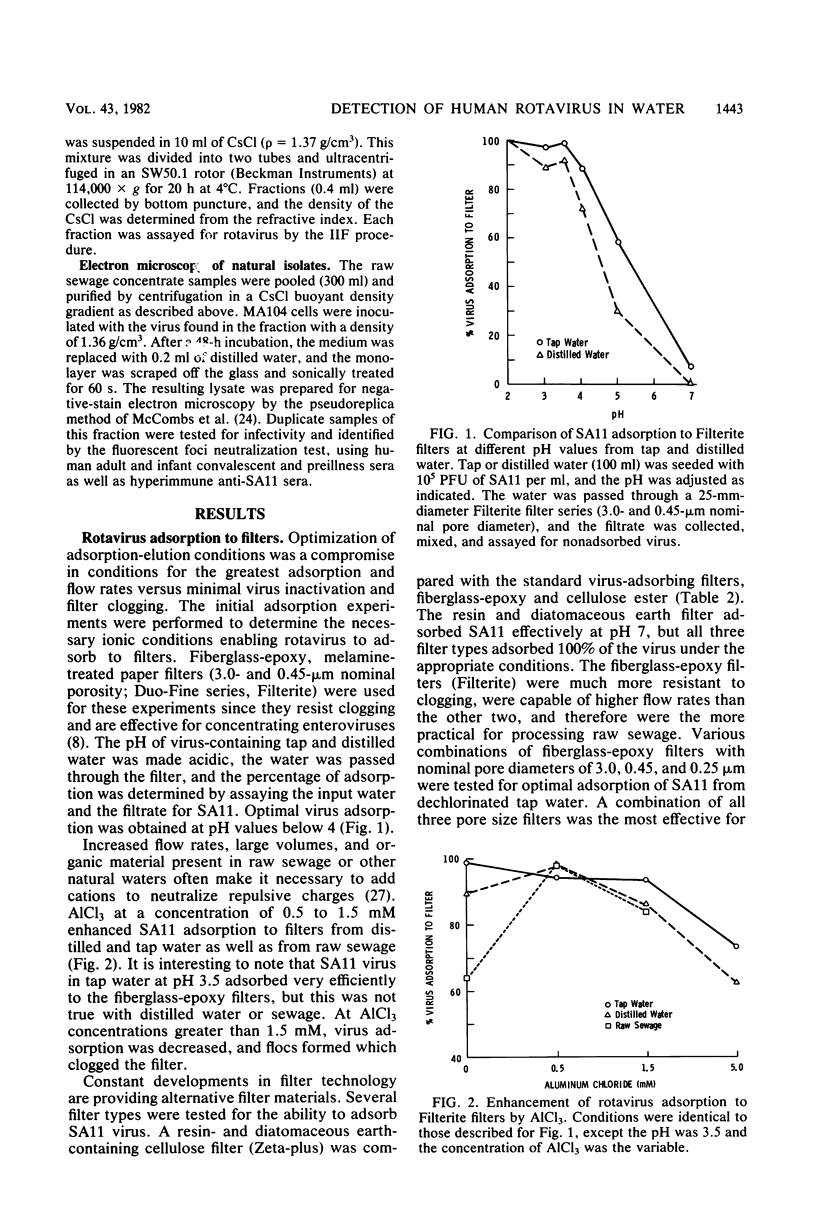
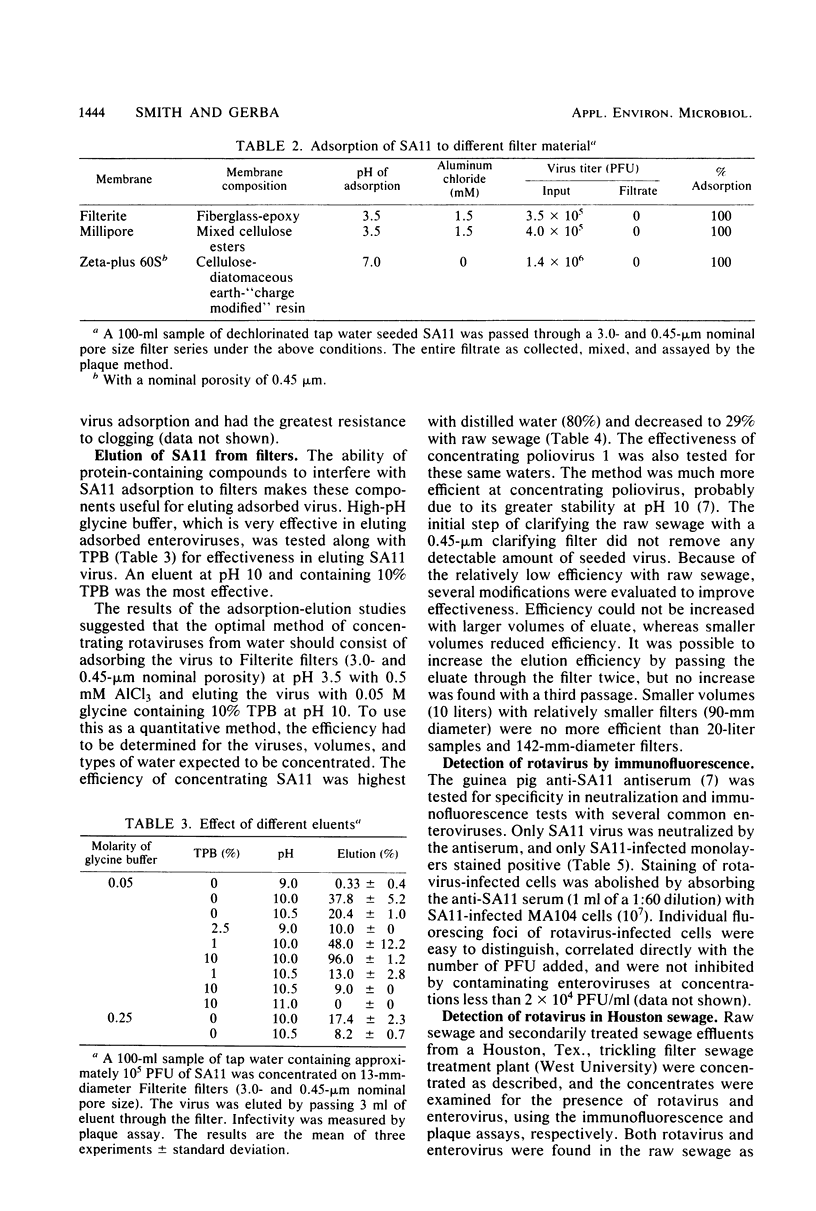
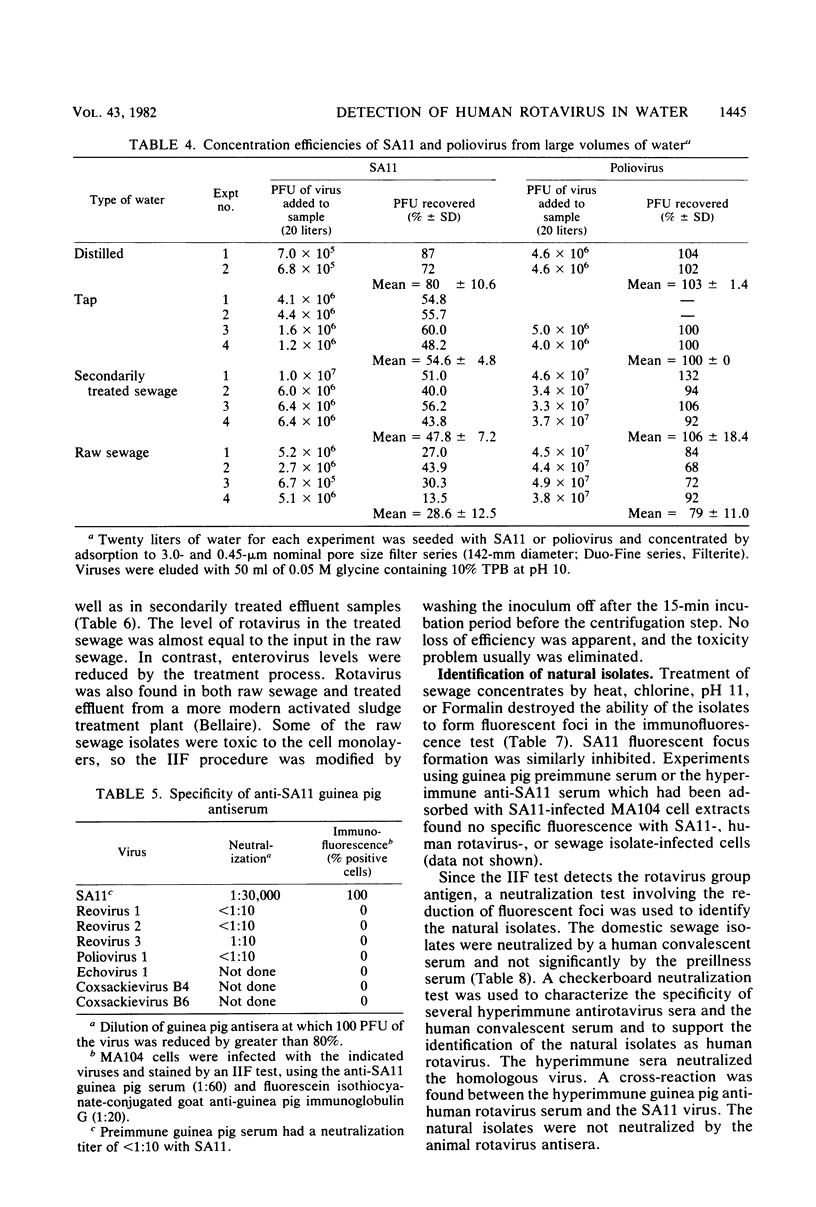
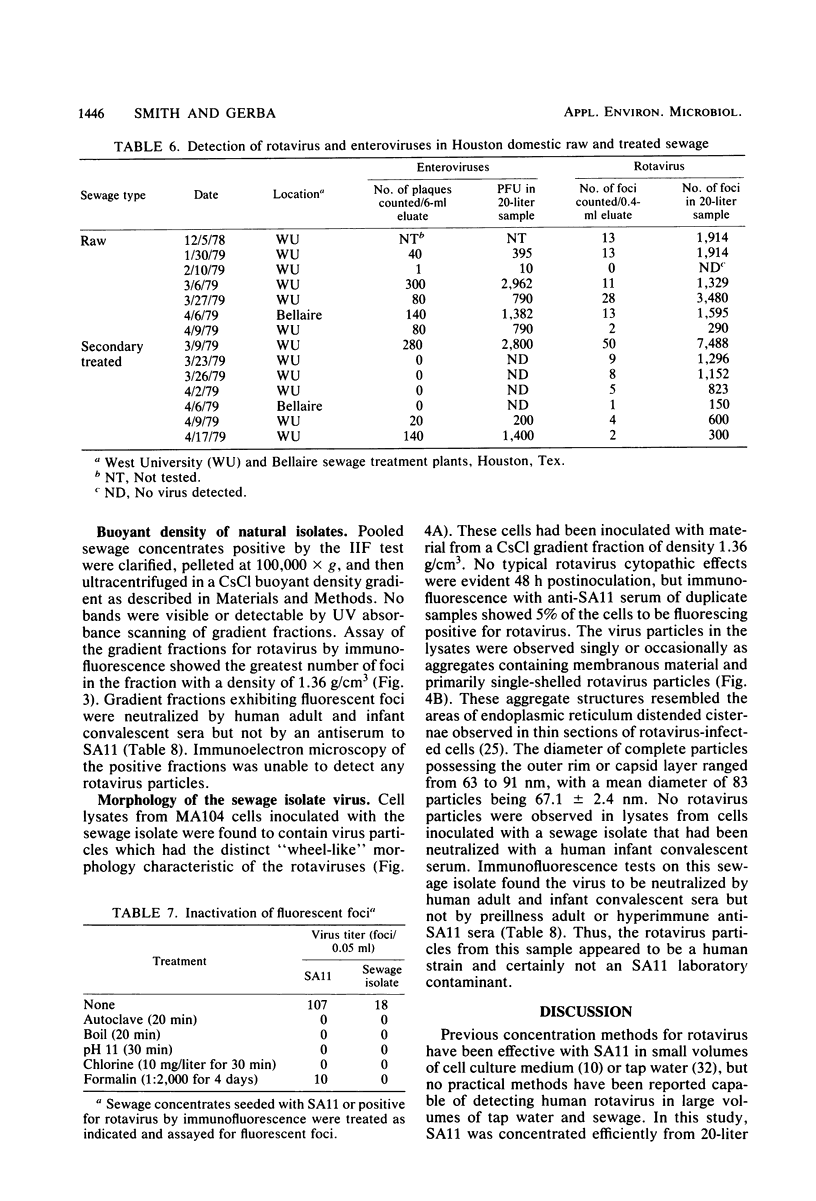
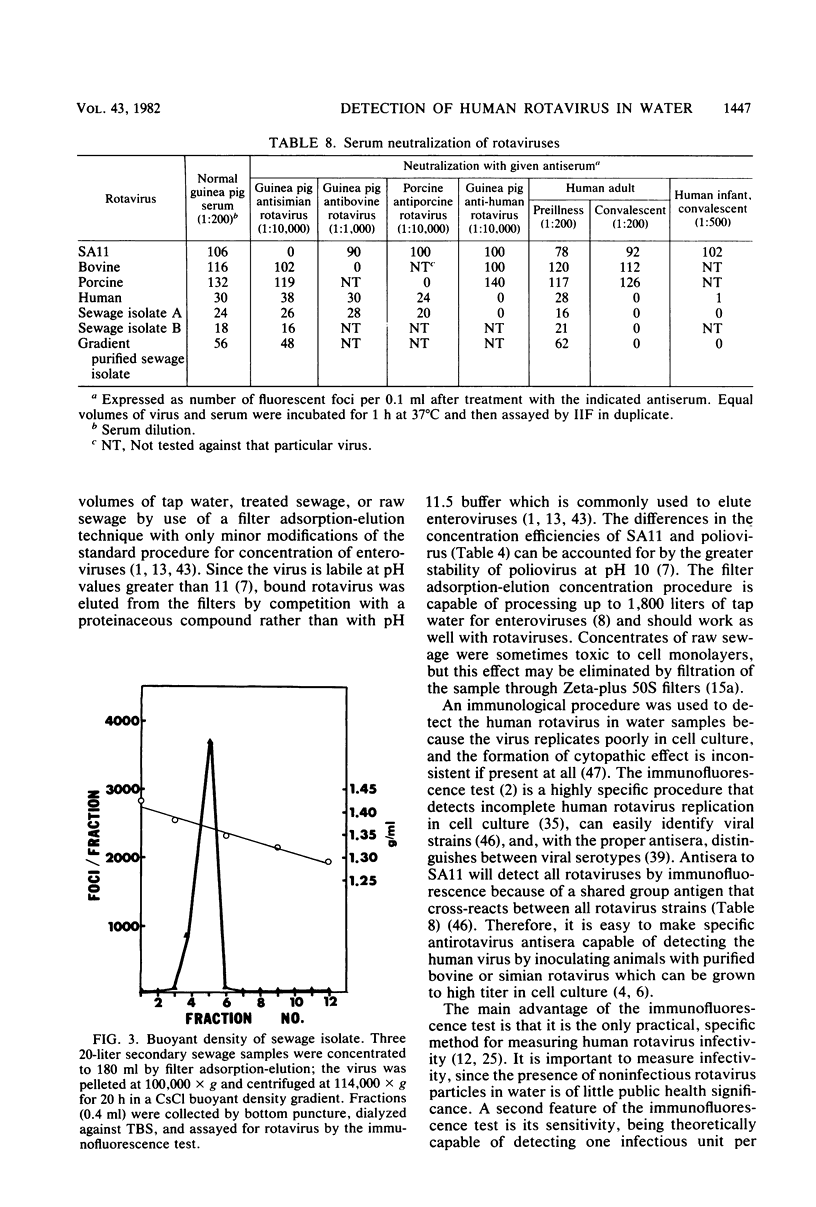
The simian rotavirus SA11 was used to develop a simple, reliable, and efficient method to concentrate rotavirus from tap water, treated sewage, and raw sewage by absorption to and elution from Filterite fiberglass-epoxy filters. SA11 adsorbed optimally to Filterite filters from water containing 0.5 mM AlCl3 at pH 3.5. Filter-bound virus was eluted with 0.05 M glycine-NaOH supplemented with 10% tryptose phosphate broth at pH 10. SA11 was quantitated by plaque assay, whereas human rotavirus was detected by immunofluorescence. The method was applied to detect rotavirus in raw and treated sewage at two Houston, Tex., sewage treatment plants. The sewage isolates were identified as rotavirus, probably a human strain, based on several criteria. The sewage isolates were detectable by an immunofluorescence test, using anti-SA11 serum which would detect the simian, human bovine, and porcine rotaviruses. No reaction was noted by immunofluorescence with the reoviruses or several common enteroviruses. The sewage isolates were neutralized by convalescent sera from a human adult and infant who had been infected by rotavirus as well as by a hyperimmune serum prepared in guinea pigs against purified human rotavirus. Preimmune or preillness sera did not react with the isolates by neutralization or immunofluorescence. The natural isolates were sensitive to pH 11 and other inactivating agents, similar to SA11. The buoyant density of the sewage isolates in CsCl gradients was 1.36 g/cm3, which is the value usually reported for complete, infectious rotavirus particles. The double-shelled particle diameter was 67.1 +/- 2.4 nm. Finally, electron micrographs of cell lysates inoculated with the sewage isolate showed particles displaying characteristic rotavirus morphology.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banatvala J. E., Totterdell B., Chrystie I. L., Woode G. N. In-vitro detection of human rotaviruses. Lancet. 1975 Oct 25;2(7939):821–821. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)80057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar R., Conklin R. H., Vollet J. J., Pickering L. K., DuPont H. L., Walters D. L., Kohl S. Rotavirus in travelers' diarrhea: study of an adult student population in Mexico. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):324–327. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. M., Barnett B. B., Spendlove R. S. Production of high-titer bovine rotavirus with trypsin. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Mar;9(3):413–417. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.3.413-417.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Gerba C. P., Smith E. M. Simian rotavirus SA11 replication in cell cultures. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):810–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.810-815.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Smith E. M., Gerba C. P. Rotavirus stability and inactivation. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):403–409. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of viruses from large volumes of tap water using pleated membrane filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):221–226. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.221-226.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Goyal S. M., Gerba C. P., Conklin R. H., Smith E. M. Comparison between adsorption of poliovirus and rotavirus by aluminum hydroxide and activated sludge flocs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):360–363. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.360-363.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Goyal S. M., Gerba C. P., Conklin R. H., Wallis C., Melnick J. L., DuPont H. L. A simple method for concentration of enteroviruses and rotaviruses from cell culture harvests using membrane filters. Intervirology. 1978;9(1):56–59. doi: 10.1159/000148921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel M., Spence L., Babiuk L. A., Petro R., Bloch S. Hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition studies with a strain of Nebraska calf diarrhea virus (bovine rotavirus). Intervirology. 1978;9(2):95–105. doi: 10.1159/000148927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Farrah S. R., Goyal S. M., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses from large volumes of tap water, treated sewage, and seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):540–548. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.540-548.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley C. E., Gunn R. A., Hughes J. M., Lippy E. C., Craun G. F. From the Center for Disease Control. Outbreaks of waterborne diseases in the United States, 1978. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):794–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejkal T. W., Gerba C. P., Rao V. C. Reduction of cytotoxicity in virus concentrates from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):731–733. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.731-733.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst C. J., Gerba C. P. Stability of simian rotavirus in fresh and estuarine water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.1-5.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenelson E. A rapid method for quantitative assay of poliovirus from water with the aid of the fluorescent antibody technique. Arch Virol. 1976;50(3):197–206. doi: 10.1007/BF01320573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedmi S., Katzenelson E. A rapid quantitative fluorescent antibody assay of polioviruses using tragacanth gum. Arch Virol. 1978;56(4):337–340. doi: 10.1007/BF01315284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. W., Brandt C. D., Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Arrobio J. O., Rodriguez W. J., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent infection. Occurrence in adult contacts of pediatric patients with gastroenteritis. JAMA. 1977 Aug 1;238(5):404–407. doi: 10.1001/jama.238.5.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwert E., Höher P. G., Primavesi C. A. Intratypische Differenzierung von Poliomyelitis-Virusstämmen aus Abwasser: Schlussfolgerungen für die Impfpraxis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;215(1):16–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Blomberg J., Berg G., Eriksson A., Madsen L. Epidemic acute diarrhoea in adults associated with infantile gastroenteritis virus. Lancet. 1978 Nov 11;2(8098):1056–1057. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92389-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe H. H., Strickland-Cholmley M. Simian virus SA11 and the related O agent. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):235–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01240518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty M. S. Rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman O. H., Laine M. J. Rotavirus epidemic in adults. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 2;296(22):1298–1299. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706022962220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morens D. M., Zweighaft R. M., Vernon T. M., Gary G. W., Eslien J. J., Wood B. T., Holman R. C., Dolin R. A waterborne outbreak of gastroenteritis with secondary person-to-person spread. Association with a viral agent. Lancet. 1979 May 5;1(8123):964–966. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91734-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. B., Circo R., Evans A. S. Strategic viral surveillance of sewage during and following an oral poliovirus vaccine campaign. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Nov;86(3):641–652. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Wimberly I., Benyesh-Melnick M. Prevalence of antibodies to EB virus and other herpesviruses. JAMA. 1969 Jun 2;208(9):1675–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIORDAN J. T. The 1961 Middletown Oral Poliovirus Vaccine Program. IX. Isolation of enteroviruses from sewage before and after vaccine administration. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Apr;34:512–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramia S., Sattar S. A. Concentration of seeded simian rotavirus SA-11 from potable waters by using talc-celite layers and hydroextraction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):493–499. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.493-499.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoub B. D., Kalica A. R., Greenberg H. B., Bertran D. M., Sereno M. M., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enhancement of antigen incorporation and infectivity of cell cultures by human rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):488–492. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.488-492.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Gerba C. P. A plaque assay for the simian rotavirus SAII. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):513–519. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Glass J. S. Poliovirus concentration from tap water with electropositive adsorbent filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):201–210. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.201-210.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarabcák M., Kratochvil I., Milosovicová A. Study of the effect of vaccination with live poliomyelitis vaccine on the circulation of enteroviruses in the population. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1971;15(3):258–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H. Serotypes of human rotavirus. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):39–39. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Bryden A. S., Flewett T. H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A. Serological relationships between rotaviruses from different species as studied by complement fixation and neutralization. Arch Virol. 1977;53(4):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01315627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Henderson M., Melnick J. L. Enterovirus concentration on cellulose membranes. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):476–480. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.476-480.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L., Gerba C. P. Concentration of viruses from water by membrane chromatography. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:413–437. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenman W. M., Hinde D., Feltham S., Gurwith M. Rotavirus infection in adults. Results of a prospective family study. N Engl J Med. 1979 Aug 9;301(6):303–306. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197908093010604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilterdink J. B., Weiland H. T., Verlinde J. D. A longitudinal study on the significance of examination of sewage for the presence of poliovirus in the population. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;32(1):82–90. doi: 10.1007/BF01241523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Jones J. M., Flewett T. H., Davies H. A., Davis H. A., White G. B. Morphological and antigenic relationships between viruses (rotaviruses) from acute gastroenteritis of children, calves, piglets, mice, and foals. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.804-810.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Gill V. W., Sereno M. M., Kalica A. R., VanKirk D. H., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Letter: Probable in-vitro cultivation of human reovirus-like agent of infantile diarroea. Lancet. 1976 Jan 10;1(7950):98–99. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bonsdorff C. H., Hovi T., Mäkelä P., Mörttinen A. Rotavirus infections in adults in association with acute gastroenteritis. J Med Virol. 1978;2(1):21–28. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]