Abstract
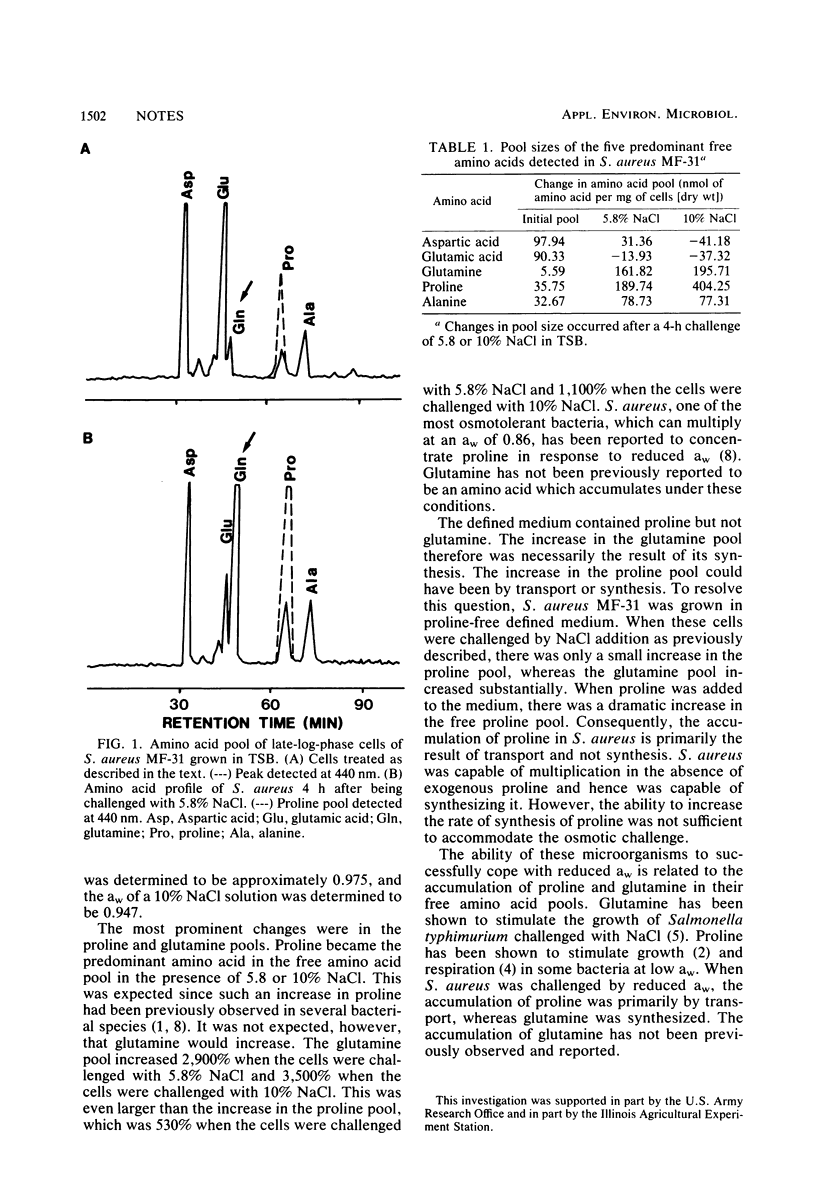
Proline and glutamine were found to be the predominant free amino acids in Staphylococcus aureus MF-31 challenged by 5.8 or 10% NaCl in the growth medium. The accumulation of glutamine was the result of its synthesis, whereas the accumulation of proline was by transport.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. THE COMPOSITION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN RELATION TO THE WATER ACTIVITY OF THE GROWTH MEDIUM. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:205–213. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian J. H., Waltho J. A. Water relations of Salmonella oranienburg; stimulation of respiration by amino acids. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):345–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. Proline over-production results in enhanced osmotolerance in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):82–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00422771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Measures J. C. Water relations in single cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Mar 29;278(959):151–166. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1977.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koujima I., Hayashi H., Tomochika K., Okabe A., Kanemasa Y. Adaptational change in proline and water content of Staphylococcus aureus after alteration of environmental salt concentration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Mar;35(3):467–470. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.3.467-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran J. W. Branched-chain amino acid transport in Streptococcus agalactiae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):25–31. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.25-31.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Neveln D. S. Transformation analysis of three linkage groups in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):201–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.201-211.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


