Abstract
Bioassay-guided fractionation of the organic extract of Ambrosia tenuifolia Sprengel (Asteraceae) led to the isolation of two bioactive sesquiterpene lactones with significant trypanocidal and leishmanicidal activities. By spectroscopic methods (1H- and 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance, distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer, correlated spectroscopy, heteronuclear multiple-quantum coherence, electron impact-mass spectrometry, and infrared spectroscopy), these compounds were identified as psilostachyin and peruvin. Both compounds showed a marked in vitro trypanocidal activity against Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes with 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of less than 2 μg/ml. Psilostachyin exerted a significant in vitro activity against the trypomastigote forms of T. cruzi (IC50, 0.76 μg/ml) and was selected for in vivo testing. Psilostachyin-treated mice had a survival of 100% and lower parasitemia values than control mice. Both compounds were also tested on Leishmania sp. promastigotes: psilostachyin (IC50, 0.12 μg/ml) and peruvin (IC50, 0.39 μg/ml) exerted significant leishmanicidal activities. This is the first time that the trypanocidal and leishmanicidal activities of these compounds have been reported. The selectivity index (SI) was employed to evaluate the cytotoxic effect of lactones on T lymphocytes. Although the SIs of both compounds were high for T. cruzi epimastigotes, psilostachyin was more selective against trypomastigotes (SI, 33.8) while peruvin showed no specificity for this parasite. Both compounds presented high selectivity for Leishmania spp. The results shown herein suggest that psilostachyin and peruvin could be considered potential candidates for the development of new antiprotozoal agents against Chagas' disease and leishmaniasis.
Trypanosomiasis and leishmaniasis are widespread protozoal diseases that affect mostly poor and marginal populations in Latin America, Africa, and Asia and have been neglected by the pharmaceutical industry and governments. Under normal circumstances (efficient epidemiological surveillance programs and sanitary education) the control of these diseases could be achieved. Nevertheless, the implementation of an adequate health care system to palliate the necessities of the affected populations is hindered by the lack of financial and human resources (5, 10), political instability in these countries, and often questionable government prioritization (4, 19). Chagas' disease is caused by Trypanosoma cruzi (Trypanosomatidae), a parasite responsible for progressive damage to organs, mainly the heart, esophagus, and lower intestine. Leishmania spp. belong to the same family and cause several clinical forms of leishmaniasis. In Latin America, cutaneous, mucocutaneous, and mucosal forms of leishmaniasis are the most frequent forms of the disease. In Argentina, the causative parasite of the disease is mainly Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis, though other species have also been reported (12, 16), and the localized cutaneous form is the most frequent.
The chemotherapy for these diseases is not satisfactory due to the partial effectiveness and the toxicity associated with long-term treatments. Current treatments for Chagas' disease employ benznidazole or nifurtimox, two drugs that have been in use for over 40 years. As for pentavalent antimony drugs, Leishmania has developed resistance, requiring that physicians use other toxic drugs, such as amphotericin B, pentamidine, paromomycin, or allopurinol (18). Taking into consideration that there exist in Argentina patients coinfected with both T. cruzi and Leishmania spp. (7, 12) and, in Brazil, there are people coinfected with T. cruzi and two different species of Leishmania (17), research and development of new drugs effective in the treatment of both kinetoplastid infections is a real need and requires new strategies for drug development (34). Over the last century, natural products have provided molecules with drug-like properties and high structural diversity. Recently, the Tropical Diseases Program of the World Health Organization, working with the Drug Discovery Research Program, have considered the investigation of medicinal plants traditionally used to treat parasitic infections as an essential and high-priority field of study (6).
We have previously reported the in vitro trypanocidal activities of 32 extracts belonging to 12 different plant species. These Argentine species were mainly selected on the basis of their ethnomedical evidence of use for conditions related to parasitic infections. Among them, the organic extract of Ambrosia tenuifolia showed trypanocidal activity with 81.1 ± 0.8% (mean ± standard error of the mean [SEM]) growth inhibition of parasites when used at 100 μg/ml (29). Biossay-guided fractionation of this extract led to the isolation and identification of the flavonoid hispidulin, which has significant trypanocidal and leishmanicidal activities (30). The present investigation was undertaken in order to isolate and identify other bioactive compounds that may account for the trypanocidal activity of this species. Two sesquiterpene lactones were isolated by bioassay-guided fractionation and tested in in vitro assays on two different developmental stages of T. cruzi (epimastigotes and trypomastigotes). According to the results obtained, one of the lactones was selected for testing in vivo in a murine model of T. cruzi infection. Additionally, the in vitro leishmanicidal activity and the antiparasitic selectivity were evaluated for the purified compounds.
Sesquiterpene lactones are terpenoid compounds with a wide variety of chemical structures and are characteristic of the Asteraceae family. A remarkable array of pharmacological activities, such as antitumorigenic, cytotoxic, antibacterial, antifungal, insecticidal, cardiotonic, antiulcer, and antiprotozoal properties, have already been reported for these terpenoids (23, 24, 25). Their antiprotozoal potential has attracted renewed interest with the development of the antimalarial drug artemisinin, isolated from the Chinese medicinal herb Artemisia annua, which has high clinical relevance. In addition, other series of sesquiterpene lactones with antiprotozoal activity have been described (13, 14, 27, 32).
The species under study, Ambrosia tenuifolia Sprengel (Asteraceae), is an Argentine medicinal plant which grows in the north and central regions of Argentina, southern Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay (33) and is commonly known as ajenjo del campo, altamisa, saltamisa, or artemisia. The decoction product of the aerial parts is traditionally used as a carminative, antihelminthic, and febrifugue. The decoction product of the powdered seeds and leaves is administered to eliminate intestinal worms (26).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Parasites.
Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes (RA strain) were grown in biphasic medium as previously described (8). Leishmania mexicana promastigotes (MNYC/BZ/62/M strain) were grown on liver infusion tryptose medium. Both cultures were routinely maintained by weekly passages at 26 and 28°C, respectively. T. cruzi bloodstream trypomastigotes were obtained from infected CF1 mice by cardiac puncture, at the peak of parasitemia on day 15 postinfection. Trypomastigotes were routinely maintained by infecting 21-day-old CF1 mice (weighing 23.8 ± 2.6 g).
Animals.
Inbred male CF1 and C3H/HeN mice were nursed at the Departamento de Microbiología, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Buenos Aires. Inbred female BALB/c mice were purchased from the Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria (INTA). Animals were kept according to practices described in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Research Council (21).
Plant material.
The aerial parts of A. tenuifolia were collected in Punta Lara in the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina, in 2004. Plant material was identified by G. Giberti, and a voucher specimen (BAF 649) was deposited at the Herbarium of the Museo de Farmacobotánica, Facultad de Farmacia y Bioquímica, Universidad de Buenos Aires.
Extraction and isolation of pure compounds.
The aerial parts of A. tenuifolia (1,000 g) were air dried, ground to powder, and extracted with dichloromethane-methanol (1:1). This organic extract was fractionated into five fractions (F1AT to F5AT) as previously described (30). Pure compound 1 was obtained from fraction F4AT as colorless crystals. Further purification of the mother liquor of F4AT, carried out by gel filtration on a Sephadex LH-20 column, eluted with n-hexane-ethyl acetate (100:0 to 0:100) and methanol, yielded 120 subfractions of 10 ml each (F4AT1 to F 4AT120). Pure compound 2 was obtained as an amorphous white powder from fraction F4AT(85-92) eluted with n-hexane-ethyl acetate (3:7).
Structure elucidation.
The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data, 1H-NMR (500 MHz) and 13C-NMR (500 MHz), were recorded on a Varian Inova 500 in CDCl3 at room temperature. Distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer, correlated spectroscopy, and heteronuclear multiple-quantum coherence experiments were run. Mass spectrometry (electron impact) analysis was performed with an Agilent 5973, and infrared spectroscopy (IR) was performed with a Bruker FT-IR IFS25 spectrophotometer.
In vitro assays for trypanocidal activity.
Growth inhibition of T. cruzi epimastigotes was evaluated by a [3H]thymidine uptake assay for fractions F1AT to F5AT and compounds 1 and 2, as previously described (30). Parasites were adjusted to a cell density of 1.5 × 106/ml and cultured in the presence of 0.01 to 100 μg/ml of each fraction or pure compound for 72 or 120 h. Benznidazole (5 to 20 μM; Roche) was used as positive control. The percentage of inhibition was calculated as 100 − {[(cpm of treated parasites)/(cpm of untreated parasites)] × 100}.
The trypanocidal effects of compounds 1 and 2 were also tested on bloodstream trypomastigotes according to a standard WHO protocol with minor modifications (11). Briefly, mouse blood containing trypomastigotes was diluted in complete liver infusion tryptose medium to adjust the parasite concentration to 1.5 × 106/ml. Parasites were seeded (150 μl/well) in duplicate in a 96-well microplate, and 2 μl of each compound/well (1 to 100 μg/ml, final concentration) or control was added. Plates were incubated for 24 h, and the remaining live parasites were counted in a Neubauer chamber as previously described (30).
In vitro assay for leishmanicidal activity.
Growth inhibition of L. mexicana promastigotes was evaluated for compounds 1 and 2 by a [3H]thymidine uptake assay as described above. Amphotericin B (0.27, 0.4, 0.8, and 1.6 μM; ICN) was used as a positive control.
Cytotoxicity assay.
T-lymphocyte suspensions from BALB/c mice (weighing 22 ± 2 g) were employed for the determination of cell viability by the trypan blue dye exclusion method in the absence and presence of increasing concentrations of the pure compounds (0.1, 1, 10, and 50 μg/ml) during 3 or 24 h, as previously described (1, 30). The selectivity index (SI) was calculated as the 50% cytotoxic concentration on murine T lymphocytes (24 h) divided by the 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of the compound for T. cruzi trypomastigotes.
In vivo trypanocidal activity assay.
Groups of five C3H/HeN mice (6 to 8 weeks old; 27.2 ± 0.9 g) maintained under standard conditions were infected with 5 × 103 bloodstream T. cruzi trypomastigotes by the intraperitoneal route. Five days after infection, the presence of circulating parasites was confirmed by the microhematocrit method. Mice were treated daily with compound 1 or benznidazole (1 mg/kg of body weight/day) for five consecutive days (days 5 to 10 postinfection), by the intraperitoneal route. Drugs were resuspended in 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2), and this vehicle was employed also as a negative control. Levels of parasitemia were monitored every 2 days in 5 μl of blood diluted 1:5 in lysis buffer (0.75% NH4Cl, 0.2% Tris, pH 7.2) by counting parasites in a Neubauer chamber. The number of deaths was recorded daily.
RESULTS
Bioassay-guided fractionation and structure elucidation.
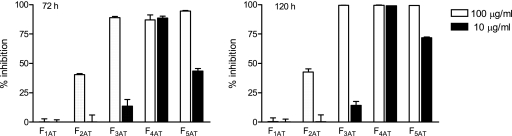
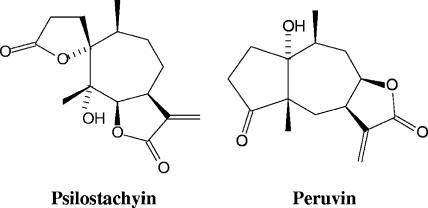
Fractionation of the A. tenuifolia organic extract by chromatographic techniques yielded five fractions (F1AT to F5AT), which were then assayed for their in vitro activity against T. cruzi epimastigotes. Fraction F4AT showed the strongest trypanocidal activity at the lower concentration tested (88.5 ± 1.7%; IC50, 2.49 μg/ml, 72 h) (Fig. 1) and was selected for further fractionation. Two sesquiterpene lactones were isolated from the active fraction F4T and identified by comparison of their spectral data (1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, electron impact-mass spectrometry, and IR) with published values (3, 22) as follows: psilostachyin (compound 1), (2′R,3aS,6s,8s,8aR)-octahydro-8-hydroxy-6,8-dimethyl-3-methylene-spiro[7H-cyclohepta[b]furan-7,2′(5′H)-furan]-2,5′(3H)-dione; peruvin (compound 2), (3aR,4aS,7aR,8S,9aR)-decahydro-7a-hydroxy-4a,8-dimethyl-3-methyleneazulene [6,5-b]-furan-2,5-dione (Fig. 2).
FIG. 1.
Growth inhibition of T. cruzi epimastigotes by fractions F1AT to F5AT. Epimastigotes were cultured in triplicate in the presence of 10 or 100 μg/ml of each fraction. Cultures were done in 96-well plates with 1.5 × 106 parasites/ml during 72 or 120 h with the addition of [3H]thymidine for the last 16 h. Bars represent means ± SEMs.
FIG. 2.
Chemical structures of the sesquiterpene lactones psilostachyin and peruvin isolated from A. tenuifolia.
In vitro trypanocidal activity.
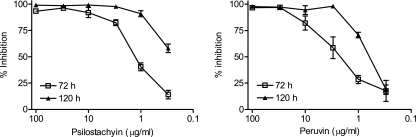
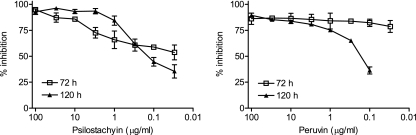
The results for the in vitro assay with T. cruzi epimastigotes are shown in Fig. 3. Although IC50 values of both compounds were similar for the noninfective form of T. cruzi (psilostachyin, 1.22 μg/ml; peruvin, 1.65 μg/ml; 72 h), psilostachyin was more active on the trypomastigote forms (0.76 μg/ml versus 52.8 μg/ml) (Fig. 4).
FIG. 3.
Growth inhibition of T. cruzi epimastigotes by psilostachyin and peruvin. Epimastigotes were cultured in triplicate in the presence of 0.3 to 100 μg/ml of each compound. Cultures were done in 96-well plates with 1.5 × 106 parasites/ml during 72 or 120 h with the addition of [3H]thymidine for the last 16 h. Symbols represent means ± SEMs.
FIG. 4.
Trypanocidal activities against T. cruzi trypomastigotes by psilostachyin and peruvin. Bloodstream trypomastigotes were cultured in duplicate in the presence of 1 to 100 μg/ml of each compound. Cultures were done in 96-well plates with 1.5 × 106 parasites/ml during 24 h, and the remaining live parasites were counted in a Neubauer chamber. Symbols represent means ± SEMs.
In vitro leishmanicidal activity.
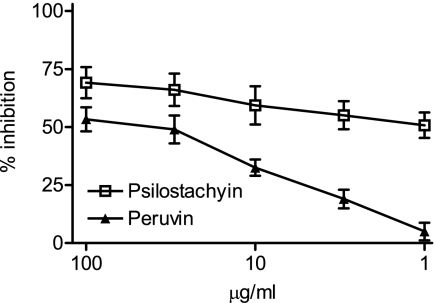
The inhibitory activity of psilostachyin and peruvin on Leishmania sp. promastigotes is shown in Fig. 5. After 120 h the IC50 values were 0.12 and 0.39 μg/ml for psilostachyin and peruvin, respectively.
FIG. 5.
Growth inhibition of Leishmania sp. promastigotes by psilostachyin and peruvin. Promastigotes were cultured in triplicate in the presence of 0.01 to 100 μg/ml of each compound. Cultures were done in 96-well plates with 1.5 × 106 parasites/ml during 72 or 120 h with the addition of [3H]thymidine for the last 16 h. Symbols represent means ± SEMs.
Cytotoxicity assay.
The results of the cytotoxic activity of the purified compounds on murine T lymphocytes are shown in Fig. 6. When lymphoid cell suspensions were treated with psilostachyin and peruvin, the 50% cytotoxic concentrations were 25.7 ± 2.5 and 35.0 ± 2.5, respectively. The SI was used to compare the toxicity for mammalian cells and the activity against the parasites. The SIs for T. cruzi trypomastigotes were 33.8 for psilostachyin and 0.7 for peruvin.
FIG. 6.
Effects of psilostachyin and peruvin on T-lymphocyte viability. Cultures were done in 96-well plates with 2 × 106 lymphocytes/ml during 3 or 24 h in the presence of different concentrations (0.1 to 50 μg/ml) of one of the compounds. Cell viability was determined by the trypan blue exclusion method and is expressed as viability. Bars represent the means ± SEMs of three experiments carried out in duplicate.
In vivo trypanocidal activity.
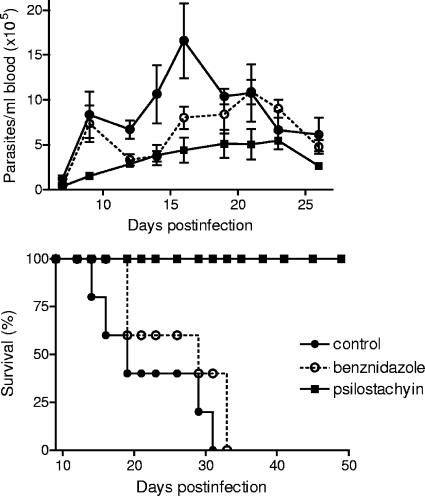
Mice infected with T. cruzi trypomastigotes and injected with PBS had high levels of parasitemia leading to death between days 14 and 33 postinfection (Fig. 7). In contrast, although psilostachyin was administered for only 5 days (at 5 to 10 days postinfection), 100% of psilostachyin-treated mice survived acute infection and displayed the lowest parasitemia. Thus, at the peak of parasitemia in untreated mice (day 16), psilostachyin-treated mice presented a significant reduction in circulating parasites ([5.8 ± 1.8] × 105 versus [15 ± 5.0] × 105 parasites/ml; P < 0.05 by analysis of variance). In addition, a 1.5-fold reduction of parasitemia in psilostachyin-treated mice throughout the acute phase of infection was observed (psilostachyin, 7.0 × 106 parasites/ml, versus control, 17.4 × 106 parasites/ml in the acute phase). The reduced number of parasites was crucial for animal survival, since all animals treated with PBS (control) or benznidazole died before entering the nonparasitemic phase of the disease.
FIG. 7.
Parasitemia levels and survival curve during the acute infection period in C3H mice infected with 5 × 103 bloodstream trypomastigotes of T. cruzi. Mice were treated with psilostachyin or benznidazole from day 5 to 10 of infection. Parasitemia was determined by counting the number of trypomastigotes in 5 μl of fresh blood collected from the tail every other day (means ± SEMs). Mortality was recorded every day. The results presented are representative of three independent experiments.
DISCUSSION
By means of a bioassay-guided fractionation of the organic extract of A. tenuifolia, a fraction that we called F4AT was obtained. This fraction presented the greatest in vitro inhibitory activity against T. cruzi epimastigotes (Fig. 1). Two active sesquiterpene lactones were isolated from this fraction and identified by spectroscopic methods as psilostachyin and peruvin (Fig. 2). Both pure compounds showed a marked in vitro trypanocidal activity against T. cruzi epimastigotes, with IC50 values less than 2 μg/ml (Fig. 3). Psilostachyin was selected for in vivo testing in a murine model, since it showed the highest activity against the infective forms of T. cruzi (IC50, 0.76 μg/ml) (Fig. 4). In this assay, psilostachyin (1 mg/kg/day) induced a significant decrease in parasitemia compared to untreated mice and 100% survival until day 100 postinfection, when the animals were sacrificed. On the other hand, control mice succumbed to death before the end of the acute phase of the infection (Fig. 7). It is noteworthy that mice treated with psilostachyin presented lower parasitemia values than those treated with beznidazole, and more importantly, intraperitoneal administration of benznidazole did not prevent mice from dying, as psilostachyin did.
However, it must be borne in mind that we used a nontraditional route for drug administration. We chose the intraperitoneal route because small amounts of a new test compound have the best chance to show activity when it is administered abdominally (31).
These promising findings of antiparasitic activity against T. cruzi prompted us to test both compounds against another related parasite, Leishmania sp. The discovery of a drug useful for the treatment of both kinetoplastid infections could be an important solution, especially in Argentina, where endemic areas overlap and sometimes differential diagnoses between them are not possible by conventional serological techniques. Significant activity of both compounds against Leishmania promastigotes was also seen, with IC50 values of 0.12 μg/ml and 0.39 μg/ml for psilostachyin and peruvin, respectively (Fig. 5).
As selectivity is a relevant characteristic for defining lead molecules (31), the cytotoxicities of the purified compounds for mammalian cells (murine T lymphocytes) were evaluated and compared to their antiparasitic activities. The SI for psilostachyin was 33.8 for T. cruzi trypomastigotes, showing a good selectivity for this infective form, whereas no selectivity was observed for peruvin (SI, 0.7).
Psilostachyin and peruvin have been previously isolated from A. tenuifolia (22) and from other species of Ambrosia (15, 20). Psilostachyin has demonstrated molluscicidal activity (35), inhibition of nitrite accumulation in cell cultures, and inhibition of the G2 DNA damage checkpoint (9, 28). Peruvin inhibits the aromatase enzyme activity in human placental microsomes (2). This is the first time that the trypanocidal and leishmanicidal activities of these compounds have been reported.
In conclusion, the results for psilostachyin and peruvin suggest that these compounds could be considered lead molecules and may be potential candidates for novel therapeutics for the treatment of Chagas' disease and leishmaniasis. Further investigations will involve evaluation of underlying mechanisms and the effects of these compounds on the morphology and ultrastructure of the parasites.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from PICT 2002 05-11240 and 05-12217 (Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica), PIP 5641 (Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas), and UBACYT B101.
We thank Berta Franke de Cazzulo for providing Leishmania parasites and Guillermo Nuñez for critical review of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 28 April 2008.
REFERENCES
- 1.Anesini, C., A. Genaro, G. Cremaschi, L. Sterin Borda, C. Cazaux, and E. Borda. 1996. Immunomodulatory action of Larrea divaricata Cav. Fitoterapia 4:329-333. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blanco, J. G., R. R. Gil, C. I. Alvarez Patrito, S. Genti-Raimondi, and A. Flury. 1997. A novel activity for a group of sesquiterpene lactones: inhibition of aromatase. FEBS Lett. 409:396-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Borges-del-Castillo, J., M. T. Manresa-Ferrero, F. Rodríguez-Luis, P. Vázquez-Bueno, and P. Joseph-Nathan. 1981. 13C NMR study of psilostachyinolides from some Ambrosia species. Org. Mag. Res. 17:232-234. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Broder, S., S. L. Hoffman, and P. J. Hotez. 2002. Cures for the third world's problems. EMBO Rep. 3:806-812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bundred, P. E., and C. Levitt. 2000. Medical migration: who are the real losers? Lancet 356:245-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chan-Bacab, M. J., and L. M. Peña-Rodriguez. 2001. Plant natural products with leishmanicidal activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 18:674-688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chiaramonte, M. G., F. M. Frank, G. M. Furer, N. J. Taranto, R. A. Margni, and E. L. Malchiodi. 1999. Polymerase chain reaction reveals Trypanosoma cruzi infection suspected by serology in cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis patients. Acta Trop. 72:295-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chiari, E., and E. P. Camargo. 1984. Culturing and cloning of T. cruzi, p. 23-26. In C. M. Morel (ed.), Genes and antigens of parasites, Fundação Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- 9.Dirsch, V. M., H. Stuppner, E. P. Ellmerer-Muller, and A. M. Vollmar. 2000. Structural requirements of sesquiterpene lactones to inhibit LPS-induced nitric oxide synthesis in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8:2747-2753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dussault, G., and C. A. Dubois. 2003. Human resources for health policies: a critical component in health policies. Hum. Resour. Health. 1:1-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Esteva, M. A., A. M. Ruiz, and A. M. Stoka. 2002. Trypanosoma cruzi: methoprene is a potent agent to sterilize blood infected with trypomastigotes. Exp. Parasitol. 100:248-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Frank, F. M., M. M. Fernandez, N. J. Taranto, S. P. Cajal, R. A. Margni, E. Castro, V. Thomaz-Soccol, and E. L. Malchiodi. 2003. Characterization of human infection by Leishmania spp. in the northwest of Argentina: immune response, double infection with Trypanosoma cruzi and species of Leishmania involved. Parasitology 126:31-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Grael, C. F. F., S. Albuquerque, and J. L. C. Lopes. 2005. Chemical constituents of Lychnophora pohlii and trypanocidal activity of crude plant extracts and of isolated compounds. Fitoterapia 76:73-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kayser, O., A. F. Kiderlen, and S. L. Croft. 2003. Natural products as antiparasitic drugs. Parasitol. Res. 90:55-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mabry, T. J., H. E. Miller, H. B. Kagan, and W. Renold. 1966. The structure of psilostachyin, a new sesquiterpene dilactone from Ambrosia psilostachya. Tetrahedron 22:1139-1146. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Marco, J. D., P. A. Barroso, M. Calvopina, H. Kumazawa, M. Furuya, M. Korenaga, S. P. Cajal, M. C. Mora, M. M. Rea, C. E. Borda, M. A. Basombrio, N. J. Taranto, and Y. Hashiguchi. 2005. Species assignation of Leishmania from human and canine American tegumentary leishmaniasis cases by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis in North Argentina. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 72:606-611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mendes, D. G., L. Lauria-Pires, N. Nitz, S. P. Lozzi, R. J. Nascimento, P. S. Monteiro, M. M. Rebelo, C. Rosa Ade, J. M. Santana, and A. R. Teixeira. 2007. Exposure to mixed asymptomatic infections with Trypanosoma cruzi, Leishmania braziliensis and Leishmania chagasi in the human population of the greater Amazon. Trop. Med. Int. Health 12:629-636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mishra, J., A. Saxena, and S. Singh. 2007. Chemotherapy of leishmaniasis: past, present and future. Curr. Med. Chem. 14:1153-1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Morel, C. 2003. Neglected diseases: under-funded research and inadequate health interventions. EMBO Rep. 4:35-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nathan, P. J., and J. Romo. 1966. Isolation and structure of peruvin. Tetrahedron 22:1723-1738. [Google Scholar]
- 21.National Research Council. 1996. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy Press, Washington, DC.
- 22.Oberti, J., G. Silva, V. Sosa, P. Kulanthaivel, and W. Herz. 1986. Ambrosanolides and secoambrosanolides from Ambrosia tenuifolia. Phytochemistry 25:1355-1358. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Picman, A. K. 1986. Biological activities of sesquiterpene lactones. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 14:255-281. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Robles, M., M. Aregullin, J. West, and E. Rodriguez. 1995. Recent studies on the zoopharmacognosy, pharmacology and neurotoxicology of sesquiterpene lactones. Planta Med. 61:199-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rodriguez, E. G., N. H. Towers, and J. C. Mitchell. 1976. Biological activities of sesquiterpene lactones. Phytochemistry 15:1573-1580. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schmeda Hirschmann, G., F. Bohlmann, and J. Jakupovic. 1986. The constituents of Ambrosia tenuifolia and Pectis odorata. Rev. Latinoam. Quim. 17:200-202. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schmidt, T. J., R. Brun, G. Willuhn, and S. A. Khalid. 2002. Anti-trypanosomal activity of helenalin and some structurally related sesquiterpene lactones. Planta Med. 68:750-751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sturgeon, C. M., K. Craig, C. Brown, N. T. Rundle, R. J. Andersen, and M. Roberge. 2005. Modulation of the G2 cell cycle checkpoint by sesquiterpene lactones psilostachyins A and C isolated from the common ragweed Ambrosia artemisiifolia. Planta Med. 71:938-943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sülsen, V., C. Güida, J. Coussio, C. Paveto, L. Muschietti, and V. Martino. 2006. In vitro evaluation of trypanocidal activity in plants used in Argentine traditional medicine. Parasitol. Res. 98:370-374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sülsen, V., S. Cazorla, F. Frank, F. Redko, C. Anesini, J. Coussio, E. Malchiodi, V. Martino, and L. Muschietti. 2007. Trypanocidal and leishmanicidal activities of flavonoids from argentine medicinal plants. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 77:654-659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tasdemir, D., M. Kaiser, R. Brun, V. Yardley, T. Schmidt, F. Tosun, and P. Rüedi. 2006. Antitrypanosomal and antileishmanial activities of flavonoids and their analogues: in vitro, in vivo, structure-activity relationship, and quantitative structure-activity relationship studies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:1352-1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tiuman, T. S., T. Ueda-Nakamura, D. A. García Cortez, B. P. Dias Filho, J. A. Morgado-Díaz, W. de Souza, and C. V. Nakamura. 2005. Antileishamnial activity of parthenolide, a sesquiterpene lactone isoltaed from Tanacetum parthenium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49:176-182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Toursarkissian, M. 1980. Plantas medicinales de la Argentina, p. 26. Hemisferio Sur S.A., Buenos Aires, Argentina.
- 34.Troullier, P., P. Olliaro, E. Torreele, J. Orbinski, R. Laing, and N. Ford. 2002. Drug development for neglected diseases: a deficient market and a public health policy failure. Lancet 359:2188-2194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang, P. H., J. Xu, and M. Y. Wu. 1993. Chemical constituents of ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.). Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 18:164-166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]