Abstract
Pathogenic yersiniae utilize a type III secretion system to inject antihost factors, called Yops, directly into the cytosol of eukaryotic cells. The Yops are injected via a needle-like structure, comprising the YscF protein, on the bacterial surface. While the needle is being assembled, Yops cannot be secreted. YscP and YscU switch the substrate specificity of the secretion system to enable Yop export once the needle attains its proper length. Here, we demonstrate that the inner rod protein YscI plays a critical role in substrate specificity switching. We show that YscI is secreted by the type III secretion system and that YscI secretion by a yscP mutant is abnormally elevated. Furthermore, we show that mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of YscU reduce YscI secretion by the yscP null strain. We also demonstrate that mutants expressing one of three forms of YscI (those with mutations Q84A, L87A, and L96A) secrete substantial amounts of Yops yet exhibit severe defects in needle formation. In the absence of YscP, mutants with the same changes in YscI assemble needles but are unable to secrete Yops. Together, these results suggest that the formation of the inner rod, not the needle, is critical for substrate specificity switching and that YscP and YscU exert their effects on substrate export by controlling the secretion of YscI.
There are three Yersinia species pathogenic for humans: Yersinia pestis, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and Y. enterocolitica. Y. pestis is the causative agent of plague, while infection with the enteric pathogen Y. pseudotuberculosis or Y. enterocolitica generally results in self-limited mesenteric lymphadenitis (8, 44). Despite causing diseases with very different clinical outcomes, pathogenic yersiniae share a common 70-kb virulence plasmid (referred to as pCD, pIB, or pYV) (10). The principle virulence determinant encoded by the 70-kb plasmid is a type III secretion system (T3SS) (11). Pathogenic yersiniae use the T3SS to inject effector proteins called Yops (Yersinia outer proteins) into eukaryotic cells to inhibit phagocytosis (17, 46) and suppress host immune responses (24, 40, 53).
Many of the components of the Yersinia T3SS are conserved in the T3SSs of other gram-negative pathogens (15, 22). In addition, nine components of the export apparatus responsible for assembling bacterial flagella are conserved (30). In addition to showing sequence homology to flagella, the T3SSs of gram-negative pathogens share structural features with flagella. For example, the T3SS encoded by Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1) resembles the flagellar basal body (25, 26). The T3SS of Shigella flexneri exhibits a similar structure (6, 54). The surface appendages of the T3SSs of gram-negative pathogens differ from the hook and filament of the flagellum in that they generally consist of hollow needle-like structures that likely serve as conduits for effector proteins destined for the eukaryotic cell cytosol (6, 21, 25, 54).
Virulence-associated T3SSs and flagella are also similar in that the lengths of their surface appendages are regulated. For example, the length of the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium flagellar hook is 55 nm (20). The needle structures of the SPI1, Shigella, and Yersinia T3SSs range from 45 to 80 nm in length (6, 21, 25, 26, 54). The regulation of needle length is critical, as Mota et al. demonstrated that the Yersinia needle structure must attain a minimal length in order for Yops to be delivered into eukaryotic cells (38).
As first described for the flagellar system, the type III secretion machinery regulates the lengths of these surface structures by imposing a hierarchy in substrate export. A previous study found that null mutations in fliK result in a polyhook phenotype in which hooks sometimes reach several microns in length (42). Unlike normal flagella, these mutant structures do not assemble a filament onto the end of the hook. This study led to the notion that FliK is responsible for switching the substrate specificity of the flagellar export apparatus once the hook reaches its normal length. Such a substrate specificity switching defect has also been observed in the T3SSs of gram-negative pathogens. In an invJ mutant, the SPI1 T3SS assembles abnormally elongated needle structures on the cell surface (27) but does not secrete effector proteins (9). Similarly, Shigella spa32 (54, 55) and Yersinia yscP (23) mutants assemble elongated needles but secrete only low levels of effector proteins (31, 43, 49, 55). Although FliK, InvJ, Spa32, and YscP do not show significant amino acid similarity, Agrain et al. used hydrophobic cluster analyses to show that the C termini of these proteins consist of a globular domain, termed T3S4 (type III secretion and substrate specificity switch) (1). Mutations within this domain of the FliK (37, 57) and YscP (1) proteins abolish substrate specificity switching of the flagellar and Yersinia T3SSs, respectively.
FliK (36), InvJ (9), Spa32 (31, 55), and YscP (43, 49) are all secreted proteins, which raises the possibility that they physically measure hook or needle length. By introducing deletions or insertions into the central region of YscP, Journet et al. were able to change the lengths of the needle structures of the Yersinia T3SS (23). Specifically, shorter versions of YscP made shorter needles, while elongated versions of YscP made longer needles, thereby suggesting that YscP functions as a molecular ruler. Analogous models to explain the function of FliK in regulating hook length have been put forth (37). However, Marlovits et al. challenged the molecular ruler hypothesis by demonstrating that InvJ is required for the formation of an inner rod structure (32), comprising the PrgJ protein (33), of the SPI1 T3SS. This finding suggests that the formation of the inner rod, not the maturation of the needle structure, is the critical event that triggers substrate specificity switching.
The export apparatus component involved in regulating substrate specificity was first identified in the flagellar system. Specifically, it was shown previously that mutations in flhB, which encodes one of the inner membrane proteins that is part of the flagellar export apparatus (30), can partially suppress the phenotype of a fliK mutant (20, 28, 57). The presence of these suppressor mutations results in a polyhook-filament phenotype in which a flagellar filament is now assembled onto the end of an elongated hook. Although FlhB is an inner membrane protein, all of the mutations suppressing the fliK mutant phenotype map to the cytoplasmic domain. The Yersinia T3SS operates in a similar fashion, as Edqvist et al. showed that the phenotype of a yscP mutant can be partially suppressed by mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of YscU (13). Specifically, mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of YscU conferred greater levels of Yop secretion on the yscP mutant while reducing the export of the needle component YscF.
In the present study, we examined the roles of YscP, YscU, and the inner rod protein YscI in switching the substrate specificity of the virulence plasmid-encoded T3SS of Y. pseudotuberculosis. We showed that YscI was secreted by the T3SS and that YscP and YscU regulated the secretion of YscI. Specifically, YscI was secreted in abnormally large amounts by a yscP mutant. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of YscU, previously shown to suppress the yscP mutant phenotype (13), reduced the amount of YscI secretion by the yscP mutant. Furthermore, using site-directed mutagenesis, we demonstrated that bacteria expressing one of three YscI mutant forms (those with mutations Q84A, L87A, and L96A) were able to undergo substrate specificity switching yet were defective in needle assembly. When these same YscI mutant proteins were expressed in a yscP mutant background, the mutants assembled needles but did not secrete late substrates. This finding suggests that the formation of the inner rod, not the formation of the needle, is critical for substrate specificity switching and that YscP and YscU regulate the substrate specificity of the Yersinia T3SS by modulating the secretion of YscI.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Media and growth conditions.
Escherichia coli strains were grown in Luria-Bertani broth. Yersinia strains were grown in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth supplemented with either 2.5 mM CaCl2 (BHI plus calcium) or 5 mM EGTA and 20 mM MgCl2 (BHI minus calcium); Triton X-100 was present in all media at 0.1% to prevent secreted proteins from adhering to the bacteria. Kanamycin at 50 μg/ml was added to select for the virulence plasmid; ampicillin at 100 μg/ml was added to maintain ColE1 ori plasmids expressing YscI, YscP, and YscU; chloramphenicol at 34 μg/ml was added to maintain a compatible p15a ori YscP-expressing plasmid. Strains and plasmids are listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Description | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| E. coli | ||
| S17-1λpir | Recipient for suicide plasmids | 48 |
| BL21(DE3) | Host for protein expression experiments | 51 |
| E. cloni | Recipient for cloning experiments | Lucigen |
| TOP10 | Recipient for cloning experiments | Invitrogen |
| Y. pseudotuberculosis | ||
| SAL1 | YPIII(pIB102), wild-type parental strain | 7 |
| SAL2 | yscP mutant | This study |
| SAL3 | yscP yscU double mutant | This study |
| SAL4 | yscI mutant | This study |
| SAL5 | yscS mutant | 5 |
| SAL6 | yscI yscP double mutant | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pSE380 | High-copy-no. expression vector | Invitrogen |
| pSW71 | Vector for YscI expression from pSE380 | This study |
| pSW71-P77A | P77A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-L80A | L80A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-M83A | M83A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-Q84A | Q84A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-W85A | W85A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-L87A | L87A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-R89D | R89D mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-I90A | I90A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-T91A | T91A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-Q93A | Q93A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-E94K | E94K mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-E95K | E95K mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-L96A | L96A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-I97A | I97A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-A98V | A98V mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-K99E | K99E mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-T100A | T100A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-G102A | G102A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-Q106A | Q106A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-N107A | N107A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-E109K | E109K mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-T110A | T110A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-L111A | L111A mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pSW71-K113E | K113E mutation in pSW71 | This study |
| pBAD18 | Arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter | 18 |
| pBAD33 | PBAD promoter; p15a ori | 18 |
| pSL327 | yscP gene in pBAD18 | This study |
| pJJ8 | yscU gene in pBAD18 | This study |
| pJJ10 | yscP gene in pBAD33 | This study |
| pSW30 | yscU(Y287G) gene in pBAD18 | This study |
| pSW31 | yscU(Y317D) gene in pBAD18 | This study |
| pGEX-GP-1 | GST fusion vector; parent vector | GE Healthcare |
| pSL303 | GST-YscF overexpression vector | This study |
| pSL310 | GST-YscI overexpression vector | This study |
| pDM4 | Suicide vector | 35 |
| pSL217 | yscP deletion in pDM4 | This study |
| pJJ1 | yscI deletion in pDM4 | This study |
| pJJ2 | yscU deletion in pDM4 | This study |
DNA methods.
Routine preparations were performed according to the methods of Sambrook et al. (47). Enzymes were obtained from New England Biologicals, except where noted. The sequencing of plasmids was performed by the Biopolymer Core Facility at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
Construction of the yscP null strain.
Overlapping PCR (2) with the primer pairs Lloyd249/Lloyd250 and Lloyd251/Lloyd252 (primers are listed in Table 2) was used to amplify genomic DNA of the wild-type Y. pseudotuberculosis strain YPIII(pIB102) (SAL1) and join sequences flanking the yscP gene. The resulting PCR product was digested with SphI and XbaI and cloned into the corresponding sites of the sucrose-selectable suicide plasmid pDM4 (35) to yield pSL217. E. coli strain S17-1λpir (48) was transformed with pSL217, and pSL217 was conjugated into SAL1 (7) by the plating of bacteria onto cefsulodin-irgasan-novobiocin Yersinia-selective agar containing 34 μg of chloramphenicol/ml. Exconjugants were restreaked onto Luria-Bertani plates containing 5% sucrose to eliminate bacteria still carrying pSL217. Sucrose-resistant colonies were subjected to PCR amplification with the Lloyd249/Lloyd252 primer pair to confirm the presence of the deletion. The resulting yscP null strain, SAL2, lacks codons 7 to 449 of the yscP gene.
TABLE 2.
Oligonucleotides used in this study
| Activity and plasmid (target or product) | Oligonucleotide or oligonucleotide paira | Sequenceb (restriction endonuclease) |
|---|---|---|
| Deletion mutant construction | ||
| pSL217 (yscP) | Lloyd249 and Lloyd250 | 5′-GCC GCA TGC GCT TGC AGG CAG CTC ATC GAC-3′ (SphI) |
| 5′-AGC CTC CCA CTC AGT GGT GAT TTT TAT TCA TTA GGC G-3′ | ||
| Lloyd251 and Lloyd252 | 5′-AAA ATC ACC ACT GAG TGG GAG GCT GAA GAA TGA G-3′ | |
| 5′-GGC TCT AGA GCT GAG GTT AGC CAG AAG GAG-3′ (XbaI) | ||
| pJJ1 (yscI) | Lloyd325 and Lloyd326 | 5′-GCC TCT AGA GTG AAT CCG CTG AAA AGA CAC-3′ (XbaI) |
| 5′-CGA CAA GGT TTC AGC TAT TTC TAT GTT CGG CAT-3′ | ||
| Lloyd327 and Lloyd328 | 5′-ATA GAA ATA GCT GAA ACC TTG TCG AAG GGG GGG-3′ | |
| 5′-GGC CTC GAG GCC CGT AAT TTC AGA TAA AG-3′ (XhoI) | ||
| pJJ2 (yscU) | Lloyd316 and Lloyd317 | 5′-GCC CTC GAG CTC AAT CCT GGA CTT GAT AGT C-3′ (XhoI) |
| 5′-TTC GGA ATG TTG TTG CTC TGT CTT TTC TCC TCC GCT T-3′ | ||
| Lloyd318 and Lloyd333 | 5′-AAG ACA GAG CAA CAA CAT TCC GAA ATG TTA TAA TAG GC-3′ | |
| 5′-GCT CAC GAG CTC GCA CAG GAG AAA TAC AAT TAC C-3′ (SacI) | ||
| Antibody production | ||
| pSL303 (GST-YscF) | Lloyd222 and Lloyd244 | 5′-GCC GAA TTC ATG AGT AAC TTC TCT GGA TTT AC-3′ (EcoRI) |
| 5′-GGC CTC GAG TAA TGG AAC CTC TAT TAA GGG-3′ (XhoI) | ||
| pSL310 (GST-YscI) | Lloyd224 and Lloyd225 | 5′-GCC GAA TCC ATG CCG AAC ATA GAA ATA GCT C-3′ (EcoRI) |
| 5′-GGC CTC GAG TCA CCC CCC CTT CGA CAA GGT-3′ (XbaI) | ||
| Complementation | ||
| pSL322 (YscP) | Lloyd344 and Lloyd252 | 5′-GCC GCC GTC GAC GCT TGC AGG CAG CTC ATC GAC-3′ (SalI) |
| 5′-GGC TCT AGA GCT GAG GTT AGC CAG AAG GAG-3′ (XbaI) | ||
| pSW71 (YscI) | Lloyd325 and Lloyd328 | |
| pJJ3 (YscU) | Lloyd330 and Lloyd333 | 5′-GC TGA TCT AGA TAT TAA TCG CCG CTG TAT TGG C-3′ (XbaI) |
| 5′-GCT CAC GAG CTC GCA CAG GAG AAA TAC AAT TAC C-3′ (SacI) | ||
| Site-directed mutagenesis | ||
| pSW30 (YscU Y287G mutant form) | Lloyd544 and Lloyd545 | 5′-GTA ACA TTC AAA GGT ACC GAT GCC CAA G-3′ |
| 5′-CTT GGG CAT CGG TAC CTT TGA ATG TTA C-3′ | ||
| pSW31 (YscU Y317D mutant form) | Lloyd548 and Lloyd549 | 5′-GCC CGT GCT CTT GAT TGG GAT GCG CTC G-3′ |
| 5′-CGA GCG CAT CCC AAT CAA GAG CAC GGG C-3′ | ||
| pSW71-P77A | Lloyd359 | 5′-CAF TTG ATA ATG CCA ACG ACC TG-3′ |
| pSW71-L80A | Lloyd360 | 5′-AAT CCC AAC GAC GCG ATG CTA ATG C-3′ |
| pSW71-M83A | Lloyd361 | 5′-CGA CCT GAT GCT AGC GCA ATG GTC AC-3′ |
| pSW71-Q84A | Lloyd362 | 5′-CCT GAT GCT AAT GGC ATG GTC ACT TAT CC-3′ |
| pSW71-W85A | Lloyd363 | 5′-GAT GCT AAT GCA AGC GTC ACT TAT CCG-3′ |
| pSW71-L87A | Lloyd364 | 5′-ATG CAA TGG TCA GCT ATC CGT ATA AC-3′ |
| pSW71-R89D | Lloyd365 | 5′-TGG TCA CTT ATC GAT ATA ACA ATC CAA G-3′ |
| pSW71-I90A | Lloyd366 | 5′-GTC ACT TAT CCG TGC AAC AAT CCA AGA AG-3′ |
| pSW71-T91A | Lloyd367 | 5′-CTT ATC CGT ATA GCA ATC CAA GAA GAA C-3′ |
| pSW71-Q93A | Lloyd368 | 5′-CGT ATA ACA ATC GCA GAA GAA CTT ATC G-3′ |
| pSW71-E94K | Lloyd369 | 5′-ATA ACA ATC CAA AAA GAA CTT ATC GCC-3′ |
| pSW71-E95K | Lloyd370 | 5′-ACA ATC CAA GAA AAA CTT ATC GCC AAG-3′ |
| pSW71-L96A | Lloyd371 | 5′-ATC CAA GAA GAA GCT ATC GCC AAG ACT G-3′ |
| pSW71-I97A | Lloyd372 | 5′-CCA AGA AGA ACT TGC CGC CAA GAC TGC CG-3′ |
| pSW71-A98V | Lloyd373 | 5′-GAA CTT ATC GTC AAG ACT GCC GG-3′ |
| pSW71-K99E | Lloyd374 | 5′-GAA CTT ATC GCC GAG ACT GCC GGG-3′ |
| pSW71-T100A | Lloyd375 | 5′-TAT CGC CAA GGC TGC CGG GCG-3′ |
| pSW71-G102A | Lloyd376 | 5′-AAG ACT GCC GCG CGA ATG AGC-3′ |
| pSW71-Q106A | Lloyd377 | 5′-GGG CGA ATG AGC GCA AAT GTT GAA ACC-3′ |
| pSW71-N107A | Lloyd378 | 5′-CGA ATG AGC CAA GCT GTT GAA ACC TTG-3′ |
| pSW71-E109K | Lloyd379 | 5′-GCC AAA ATG TTA AAA CCT TGT CG-3′ |
| pSW71-T110A | Lloyd380 | 5′-AAT GTT GAA GCC TTG TCG GAA GG-3′ |
| pSW71-L111A | Lloyd381 | 5′-AAT GTT GAA ACC GCG TCG AAG GGG GG-3′ |
| pSW71-K113E | Lloyd382 | 5′-ACC TTG TCG GAG GGG GGG TG-3′ |
For oligonucleotide pairs, sequences are listed respectively.
Restriction sites used for subcloning are italicized. Complementary sequences for primer pairs used in overlapping PCR are underlined. Nucleotides altered via site-directed mutagenesis are in bold.
Construction of the yscP yscU double null strain.
Overlapping PCR (2) with the primer pairs Lloyd316/Lloyd317 and Lloyd318/Lloyd333 was used to amplify and join sequences flanking the yscU gene. The resulting PCR product was digested with SacI and XhoI and cloned into pDM4 (35) to yield pJJ2. pJJ2 was conjugated into the yscP null strain SAL2 as described above. The resulting yscP yscU double null strain, SAL3, lacks codons 9 to 348 of the yscU gene.
Construction of the yscI null strain.
Overlapping PCR (2) with the primer pairs Lloyd325/Lloyd326 and Lloyd327/Lloyd328 was used to amplify and join sequences flanking the yscI gene. The resulting PCR product was digested with XbaI and XhoI and cloned into pDM4 (35) to yield pJJ1. pJJ1 was conjugated into the wild-type strain SAL1 as described above. The resulting yscI null strain, SAL4, lacks codons 8 to 108 of the yscI gene.
Construction of the yscI yscP double null strain.
pJJ1 was conjugated into the yscP null strain SAL2 as described above. The resulting yscI yscP double null strain was designated SAL6.
Preparation of YscF antibody.
YPIII(pIB102) genomic DNA was PCR amplified using the primer pair Lloyd222 and Lloyd244. The resulting PCR product, which comprised the yscF gene, was digested with EcoRI and XhoI and cloned into the corresponding sites of pGEX-6P-1 to yield pSL303. E. coli strain BL21(DE3) (19, 51) was transformed with pSL303, which expresses a glutathione S-transferase (GST)-YscF fusion protein, and inclusion bodies were isolated, washed, and solubilized in 8 M urea, largely as described previously (29). Solubilized GST-YscF was isolated via preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Gel slices were excised and used to raise a polyclonal antiserum in rabbits (Lampire Biologicals). The antiserum was used without further purification.
Preparation of YscI antibody.
YPIII(pIB102) genomic DNA was PCR amplified with the Lloyd224/Lloyd225 primer pair. The resulting PCR product, encompassing the yscI gene, was digested with EcoRI and XhoI and cloned into pGEX-6P-1 to yield pSL310. The resulting GST-YscI fusion protein was isolated from inclusion bodies and used to raise a polyclonal antiserum in rabbits (Lampire Biologicals). The resulting antiserum was affinity purified against membrane-immobilized GST-YscI according to standard protocols (19).
Construction of YscI complementation plasmids.
Primer pair Lloyd325/Lloyd328 was used to amplify the yscI gene, as well as a total of approximately 400 bp of upstream and downstream sequences. The resulting PCR product was digested with XbaI and XhoI and cloned into the high-copy-number plasmid pSE380 (Invitrogen) to yield pSW71. The expression of YscI is under the control of the IPTG (isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside)-inducible trc promoter and utilizes the native yscI Shine-Dalgarno site.
Sequence alignment analysis of YscI.
Pallen et al. first demonstrated that YscI is homologous to the SPI1 T3SS inner rod component PrgJ and other members of this protein family (41). They also determined that inner rod proteins show significant homology to proteins that constitute the needle structures of T3SSs. Using PSI-BLAST searches (4), we confirmed the results of Pallen et al. and identified 24 amino acid residues in the C terminus of YscI that are identical to residues in homologous proteins from the T3SSs of Aeromonas hydrophila (AscI), Photorhabdus luminescens (LscI), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PscI), and Vibrio parahaemolyticus (VscI). The residues are P77, L80, M83, Q84, W85, L87, R89, I90, T91, Q93, E94, E95, L96, I97, A98, K99, T100, G102, Q106, N107, E109, T110, L111, and K113. The sequences of the aforementioned proteins were also aligned with those of the inner rod proteins recombinant Orf8 (E. coli), MxiI (Shigella flexneri), and PrgJ (Salmonella serovar Typhimurium). In addition, alignments included sequences of the needle proteins YscF (Y. pseudotuberculosis), MxiH (Shigella flexneri), PrgI (Salmonella serovar Typhimurium), and BsaL (Burkholderia pseudomallei). Alignments were performed using the Clustal server (www.ch.embnet.org/software/ClustalW.html), and the results were printed using the Boxshade server (www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html).
Site-directed mutagenesis of yscI.
Variants with site-directed mutations were constructed using the GeneEditor site-directed mutagenesis kit according to the instructions of the manufacturer (Promega). Plasmid pSW71 served as template DNA. The oligonucleotide primers used are shown in Table S1 in the supplemental material.
Construction of YscP complementation plasmids.
Primer pair Lloyd252/Lloyd344 was used to amplify the yscP gene, as well as approximately 400 bp of upstream and 400 bp of downstream sequences. The resulting PCR product was digested with SalI and XbaI and cloned into the high-copy-number plasmid pSE380 (Invitrogen) to yield pSL322. The expression of YscP was under the control of the IPTG-inducible trc promoter and utilized the native yscP Shine-Dalgarno site. pSL322 was introduced into the yscP null strain, SAL2, by electroporation; however, complementation was poor. Therefore, pSL322 was digested with EcoRI and XbaI and the yscP-expressing insert was cloned into the corresponding sites of pBAD18 (18). The resulting plasmid, pSL327, expresses YscP from the arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter and utilizes the native yscP Shine-Dalgarno site. For experiments in which both YscI and YscP were expressed in trans in the yscI yscP double null strain, a compatible YscP plasmid was constructed by digesting pSL327 with EcoRI and XbaI. The yscP-expressing insert was cloned into the corresponding sites of plasmid pBAD33 (18), which utilizes the origin of replication from pACYC184, to yield pJJ10.
Construction of mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of YscU.
Primer pair Lloyd330/Lloyd333 was used to amplify the yscU gene, as well as approximately 400 bp of upstream and 400 bp downstream sequences, by PCR. The resulting PCR product was digested with XbaI and SacI and cloned into pSE380 to yield pJJ3. The ability of pJJ3 to trans-complement a yscU null strain was poor. Therefore, pJJ3 was digested with XbaI and HinDIII and the yscU-expressing insert was cloned into pBAD18 to yield pJJ8. The YscU Y287G (pSW30) and YscU Y317D (pSW31) mutations were created with the QuikChange II site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene) using pJJ8 as a template and the primer pairs Lloyd545/Lloyd545 and Lloyd548/Lloyd549, respectively.
Type III secretion assay.
Overnight cultures of Yersinia strains were grown in BHI medium at 26°C. Cultures were diluted to an optical density at 600 nm of 0.2 in 10 ml of either BHI-plus-calcium medium or BHI-minus-calcium medium as appropriate and were grown for 1 h at 26°C and 3 h at 37°C. Cultures were centrifuged at 3,000 × g for 15 min. Supernatants containing secreted proteins were passed through a 0.45-μm-pore-size filter and precipitated with 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA). TCA precipitates were centrifuged at 3,000 × g for 15 min. The pellets were resuspended in 200 μl of 2% SDS and precipitated with acetone at −20°C for 30 min. Samples were centrifuged at 15,000 × g for 10 min, and the pellets were air dried and resuspended in 100 μl of 8 M urea and an equal amount of 2× sample buffer. Sample volumes were adjusted according to optical density measurements of bacterial cultures. Equal amounts of culture supernatant and cell pellet fractions were separated by SDS-12% PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue or transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Proteins were detected with polyclonal antisera or a mouse monoclonal antibody against the cytoplasmic protein GroEL (Calbiochem) as a control for cell lysis.
Immunoblotting.
Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and electroblotted onto a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Millipore) by using a semidry transfer apparatus (Bio-Rad). Membranes were blocked for 30 min with Tris-buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween 20 (TBS-T) and 5% nonfat dry milk. Membranes were probed with antisera in 10 ml of blocking buffer for 1 h and washed three times with TBS-T. The membranes were then incubated for 1 h with either anti-rabbit or anti-mouse secondary antibodies (GE Healthcare Life Sciences) in 10 ml of blocking buffer and washed three times with TBS-T. Proteins were detected using the ECL Plus enhanced chemiluminescence detection kit according to the instructions of the manufacturer (GE Healthcare Life Sciences).
Surface localization of YscF.
Experiments were performed largely as described by Edqvist et al. (13). Briefly, overnight cultures of Yersinia strains were grown at 26°C in BHI medium. Cultures were diluted to an optical density at 600 nm of 0.2 in 10 ml of BHI-plus-calcium medium containing 0.1% Triton X-100 and grown for 1 h at 26°C, followed by 2 h of growth at 37°C. Whole cultures were sheared by five passages through a 22-gauge hypodermic needle. (We [13] and others [39, 52] have used this approach previously to break off the T3SS needle structures from the bacterial surface, thereby providing a better estimate of the amount of the needle component exported by the T3SS.) Culture supernatants were isolated as described above and precipitated with TCA. Sample volumes were adjusted based on optical density measurements of bacterial cultures. Equal amounts of culture supernatant and cell pellet fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gels (16% acrylamide). YscF was detected using a polyclonal antiserum.
Cross-linking of YscF.
Experiments were performed largely as described by Torruellas et al. (56). Briefly, overnight cultures of Yersinia strains were grown at 26°C in BHI medium. Cultures were diluted to an optical density at 600 nm of 0.2 in 10 ml of BHI medium and grown for 1 h at 26°C, followed by 2 h of growth at 37°C. One-milliliter culture aliquots were washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and resuspended in 500 μl of PBS. An equal amount of PBS containing 5 mM bis(sulfosuccinimidyl)suberate (BS3) was then added, and the suspensions were incubated for 30 min at 37°C. Excess cross-linker was then quenched via the addition of 50 μl of 1 M Tris-Cl, pH 8.0, for 15 min. Bacteria were then centrifuged (12,000 × g for 5 min), and the bacterial pellet was resuspended in 20 μl of water. An equal volume of 2× sample buffer was added, and the samples were boiled for 2 min. Samples were run on SDS-PAGE gels (12 or 16% acrylamide). YscF was detected by Western blotting using a polyclonal antiserum. As shown previously (12, 56), the formation of YscF multimers was dependent upon the presence of BS3 (data not shown).
RESULTS
YscI is secreted by the T3SS.
PrgJ constitutes the inner rod of the SPI1 T3SS (32, 33) and is secreted by the T3SS (52). A recent report by Pallen et al. showed that PrgJ is a member of a family of proteins that are found in other T3SSs and that YscI is the Yersinia PrgJ homolog (41). Therefore, we sought to determine whether YscI is secreted by the Yersinia T3SS. Wild-type (SAL1) and yscS (SAL5) and yscI (SAL4) mutant strains were grown under Yop-inducing conditions, and secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions were isolated (Fig. 1). The results show that YscI was found in both the secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions of the wild-type strain. YscI expression in the yscS strain (5) that lacks a functional T3SS was not observed. An analogous result for PrgJ was observed by Sukhan et al. (52), who showed that PrgJ is not expressed in an invA mutant that lacks a functional T3SS. The fact that no bands were observed for the yscI mutant confirms that our polyclonal antiserum was indeed specific for YscI. Based on these results, we conclude that YscI is a secreted substrate of the Yersinia T3SS.
FIG. 1.
YscI is a secreted substrate of the T3SS. Wild-type (WT) and yscS and yscI mutant strains were grown at 37°C in BHI-minus-calcium medium. Secreted supernatant (SN) and cell pellet (P) fractions were separated by centrifugation, and proteins in the supernatant were TCA precipitated. Equal percentages of the two fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gels, and YscI was detected by Western blotting with a polyclonal antiserum.
YscP and YscU regulate YscI secretion.
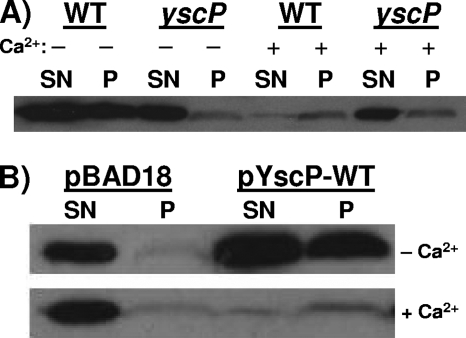
Previous work on the SPI1 T3SS demonstrated that InvJ is required for the assembly of the inner rod component PrgJ (32). In an invJ mutant, increased amounts of PrgJ are instead secreted into the culture supernatant (52). Based on this work, we sought to determine whether YscP (the Yersinia InvJ homolog) regulates the secretion of YscI. Wild-type and yscP null strains were grown at 37°C in either the absence or the presence of calcium, and secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions were isolated. In the absence of calcium, the wild-type strain, but not the yscP mutant (43), induces the low-calcium response (LCR); the induction of the LCR results in the up-regulation of the expression of the T3SS (14, 16, 45, 50). In the presence of calcium, neither strain induces the LCR. The results show that both the wild-type and yscP strains secreted large amounts of YscI in calcium-deficient medium, although YscI was more abundant in the wild-type strain due to the induction of the LCR (Fig. 2A). However, when YscI secretion in the presence of calcium was examined, we observed that the yscP mutant secreted substantially greater amounts of YscI into the culture supernatant than did the wild-type strain. Trans-complementation of the yscP null strain with a plasmid expressing native YscP (pSL327) and with a vector control (pBAD18) yielded the same phenotype (Fig. 2B). That is, in calcium-containing medium, YscI secretion in the absence of YscP was substantially elevated but the amounts of YscI secretion by the two strains were comparable when the strains were grown in calcium-deficient medium, with YscI being more abundant in the strain expressing YscP due to the induction of the LCR. We conclude that YscP does in fact regulate the secretion of YscI and that YscI is an early substrate of the T3SS.
FIG. 2.
YscP regulates YscI secretion. (A) Wild-type (WT) strain SAL1 and yscP mutant strain SAL2 were grown in either BHI-minus-calcium medium (−; LCR-inducing conditions) or BHI-plus-calcium medium (+; LCR-inhibiting conditions). Secreted supernatant (SN) and cell pellet (P) fractions were separated by centrifugation, and proteins in the supernatant were TCA precipitated. Equal percentages of the two fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gels, and YscI was detected by Western blotting using a polyclonal antiserum. (B) The yscP mutant SAL2 was trans-complemented with a vector control (pBAD18) or a plasmid expressing YscP (pYscP-WT). Bacteria were grown as described above, and the amounts of YscI in secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions were determined as previously described.
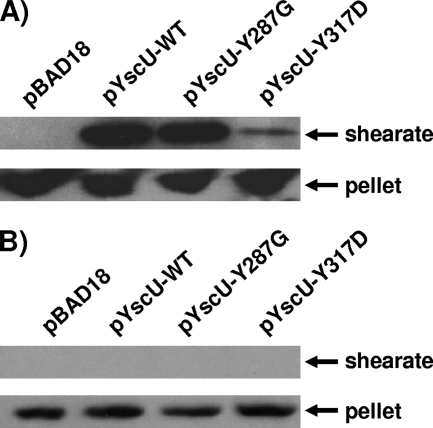
In a previous study, we demonstrated that certain mutations in the YscU cytoplasmic domain can partly suppress a yscP null phenotype by reducing the amount of surface-located YscF and increasing the amounts of secreted Yops (13). Thus, we sought to determine the effects of some of these YscU mutations on the export of YscI. Either native YscU (pJJ8) or the YscU Y287G (pSW30) or YscU Y317D (pSW31) mutant form was expressed in trans under the control of the arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter in a yscP yscU double null strain. To confirm that these mutant proteins could reduce YscF export in the absence of YscP, bacteria were grown at 37°C in the presence of calcium and subjected to shearing to release T3SS needle structures (Fig. 3A). The results show that the YscU Y287G mutation slightly reduced the amount of surface-located YscF relative to that in a control strain expressing native YscU. In contrast, the YscU Y317D mutation dramatically reduced the amount of surface-located YscF. As expected, YscF was not observed in the sheared fraction when a vector control (pBAD18) was utilized due to the fact that YscU is required for T3SS function (5). As an additional control for cell lysis, Western blotting was used to detect the cytoplasmic protein GroEL in sheared and cell pellet fractions. The results show that GroEL localized exclusively to the cell pellet fractions, thus demonstrating that the presence of YscF in the sheared fractions was not due to cell lysis (Fig. 3B). These results confirm that mutations in the YscU cytoplasmic domain can suppress the yscP null phenotype and that, as noted previously (13), the YscU Y317D mutation is a particularly strong suppressor.
FIG. 3.
Mutations in yscU reduce YscF export by a yscP mutant. (A) Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of YscU were introduced in trans into the yscP yscU double null strain SAL3. Bacteria were grown at 37°C in BHI-plus-calcium medium, and YscU expression was induced with 0.2% arabinose. Cultures were sheared to remove T3SS needle structures. Sheared and cell pellet fractions were separated by centrifugation, and proteins in the sheared fraction (shearate) were precipitated with TCA. Equal percentages of sheared and cell pellet fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gels. YscF was detected by Western blotting with a polyclonal antiserum. pBAD18, vector control; pYscU-WT, plasmid expressing wild-type YscU; pYscU-Y287G, plasmid expressing YscU with the Y287G mutation; pYscU-Y317D, plasmid expressing YscU with the Y317D mutation. (B) The same fractions described above were probed with a monoclonal antibody against the cytoplasmic protein GroEL.
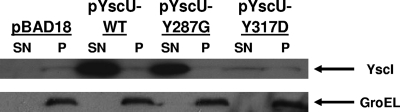
Next, we sought to determine the effects of the aforementioned YscU mutations on the export of YscI. Bacteria were grown in calcium-containing medium at 37°C, and secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions were isolated. The results show that the YscU Y287G mutation slightly reduced YscI secretion but that YscI secretion was dramatically reduced by the YscU Y317D mutation (Fig. 4). Once again, Western blotting to detect GroEL showed that the presence of YscI in secreted supernatant fractions was not due to cell lysis. These results suggest that the ability of the YscU Y317D mutation to suppress a yscP mutant phenotype may be due to its ability to down-regulate the secretion of YscI.
FIG. 4.
Mutations in yscU reduce YscI export by a yscP mutant. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of YscU were introduced in trans into the yscP yscU double null strain SAL3. Bacteria were grown at 37°C in BHI-plus-calcium medium, and YscU expression was induced with 0.2% arabinose. Secreted supernatant (SN) and cell pellet (P) fractions were separated by centrifugation, and proteins in the supernatant were TCA precipitated. Equal percentages of secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gels. YscI was detected by Western blotting with a polyclonal antiserum (upper panel); the cytoplasmic protein GroEL was detected with a monoclonal antibody (lower panel). pBAD18, vector control; pYscU-WT, plasmid expressing wild-type YscU; pYscU-Y287G, plasmid expressing YscU with the Y287G mutation; pYscU-Y317D, plasmid expressing YscU with the Y317D mutation.
Conserved residues in the C terminus of YscI are critical for T3SS function.
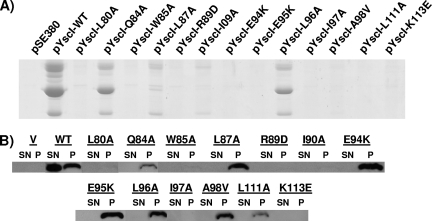
Sequence alignments revealed that 24 amino acid residues in the YscI C terminus are identical to residues found in the C termini of homologous proteins present in the T3SSs that are most closely related to the Yersinia T3SS (34) (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). To determine whether these conserved residues are critical for the function of the Yersinia T3SS, the YscI gene was cloned into the IPTG-inducible expression vector pSE380. Site-directed mutagenesis was then used to alter these residues individually, and the abilities of the resulting YscI mutant proteins to trans-complement a yscI null strain were assessed. Bacteria were grown under Yop-inducing conditions in the presence of 20 μM IPTG, and cultures were separated into secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions. Coomassie staining revealed that the P77A, M83A, T91A, Q93A, K99E, T100A, G102A, Q106A, N107A, E109K, and T110A mutant proteins all restored a wild-type level of Yop secretion to the yscI null strain (data not shown). Bacteria expressing any of the other mutant proteins exhibited reduced Yop secretion relative to that of a control strain expressing native YscI (Fig. 5A). Western blotting of secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions revealed that YscI expression in the mutant expressing the L80A mutant protein (referred to as the L80A mutant) and in the W85A, R89D, I90A, I97A, and K113E mutants was virtually undetectable (Fig. 5B). For the Q84A, L87A, E94K, E95K, L96A, A98V, and L111A mutants, YscI was observed only in cell pellet fractions. Interestingly, no YscI was observed in culture supernatants from the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants despite the fact that these mutants secreted significant amounts of Yops.
FIG. 5.
Conserved residues in the C terminus of YscI are critical for T3SS function. (A) Yop secretion by YscI mutants. Mutations in yscI were introduced in trans into the yscI null strain SAL4. Bacteria were grown in Yop-inducing medium (BHI minus calcium), and YscI expression was induced with 20 μM IPTG. Secreted supernatant fractions were isolated by centrifugation, precipitated with TCA, and run on SDS-PAGE gels. Yops were visualized by staining with Coomassie blue. Higher induction levels did not result in greater Yop secretion (data not shown). pSE380, vector control; pYscI-WT, plasmid expressing wild-type YscI; pYscI-L80A to pYscI-K113E, plasmids expressing YscI proteins with the indicated mutations. (B) YscI expression and secretion. The aforementioned strains were grown as described above. Secreted supernatant (SN) and cell pellet (P) fractions were separated by centrifugation, and proteins in the supernatant were TCA precipitated. Equal percentages of the two fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gels, and YscI was detected by Western blotting using a polyclonal antiserum. Proteins are indicated by the corresponding mutations. V, vector control; WT, wild type.
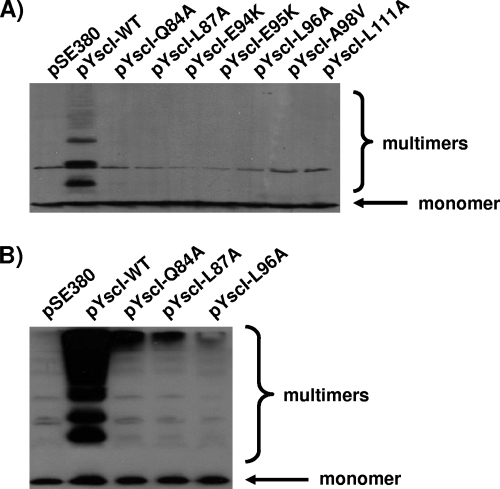
Therefore, these mutants (as well as the E94K, E95K, A98V, and L111A mutants) were analyzed to determine whether they could assemble T3SS needle structures. First, bacteria were grown at 37°C in the presence of calcium to inhibit the induction of the LCR by the strain expressing native YscI in trans. Surface-located YscF was then cross-linked with the cell-impermeable, amine-specific cross-linker BS3. Previous studies have shown that such treatment cross-links the needle component YscF into a ladder of high-molecular-weight multimers (12, 56). Our results confirm this conclusion, as the control strain expressing native YscI exhibited cross-linked products (Fig. 6A). In contrast, the Q84A, L87A, E94K, E95K, L96A, A98V, and L111A mutants exhibited very little, if any, cross-linked YscF, thus demonstrating that these mutants were defective in needle assembly. This result was surprising given that the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants secreted Yops. Therefore, the abilities of these mutants to form needles were reexamined following growth at 37°C in the absence of calcium in order to fully induce the T3SS. Despite the growth of the aforementioned mutants under LCR-inducing conditions, only small amounts of high-molecular-weight cross-linked products were observed (Fig. 6B). We conclude that needle assembly by these mutants was defective but not completely abolished. Note that the additional bands observed in the samples from these mutants were also observed for the vector control (pSE380) strain, which did not express a functional T3SS. These bands were due to cross-reactivity with our polyclonal antiserum and were routinely observed upon long exposure.
FIG. 6.
YscI mutants exhibit defects in needle assembly. (A) Either wild-type YscI or the indicated YscI mutant forms were expressed in trans in the yscI null strain SAL4. Bacteria were grown in BHI-plus-calcium medium, and surface proteins were cross-linked via the addition of 2.5 mM BS3. Samples were run on SDS-PAGE gels, and the needle component YscF was detected by Western blotting using a polyclonal antiserum. pSE380, vector control; pYscI-WT, plasmid expressing wild-type YscI; pYscI-Q84A to pYscI-L111A, plasmids expressing YscI proteins with the indicated mutations. (B) Either wild-type YscI or the indicated YscI mutant forms were expressed in trans in the yscI null strain SAL4. Bacteria were grown in BHI-minus-calcium medium, and YscF was cross-linked and detected as described above.
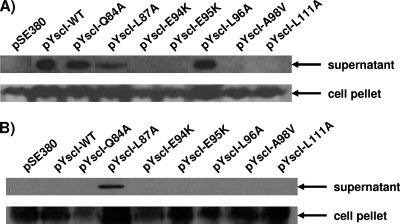
The aforementioned defects in needle assembly could be due to a defect in the export of the needle subunit YscF or a failure of exported YscF to undergo needle assembly. To test these possibilities, the Q84A, L87A, E94K, E95K, L96A, A98V, and L111A mutants were grown in calcium-deficient medium at 37°C to induce the T3SS and the secreted supernatant fractions were analyzed for the presence of free YscF. The results demonstrate that the E94K, E95K, A98V, and L111A mutants did not secrete YscF (Fig. 7A). In contrast, YscF was observed in the culture supernatants isolated from the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants. Western blotting for the cytoplasmic protein GroEL confirmed that the presence of YscF in culture supernatants was not due to cell lysis (Fig. 7B), except in the case of the L87A mutant. Low levels of cell lysis were reproducibly observed for this mutant. In this particular case, we cannot unambiguously conclude that the L87A mutant secreted YscF. Note, however, that in later experiments we did observe needle formation by this mutant (see Fig. 9). For the Q84A and L96A mutants, we can conclude that the defect in needle formation was likely due to the failure of exported YscF to undergo assembly.
FIG. 7.
YscF secretion by YscI mutants. (A) Either wild-type (WT) YscI or the indicated YscI mutants were expressed in trans in the yscI null strain SAL4. Bacteria were grown in Yop-inducing medium (BHI minus calcium), and YscI expression was induced with 20 μM IPTG. Secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions were separated by centrifugation. Secreted proteins were precipitated with TCA, and equal percentages of the two fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gel. YscF was detected by Western blotting with a polyclonal antiserum. pSE380, vector control; pYscI-WT, plasmid expressing wild-type YscI; pYscI-Q84A to pYscI-L111A, plasmids expressing YscI proteins with the indicated mutations. (B) The same fractions described above were probed with a monoclonal antibody against the cytoplasmic protein GroEL.
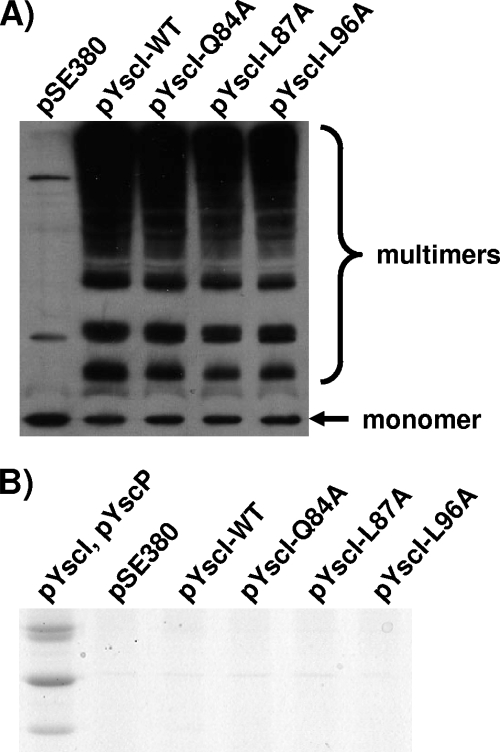
FIG. 9.
The YscI Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutant forms assemble needles in the absence of YscP. (A) Either wild-type YscI or the indicated YscI mutant forms were expressed in trans in the yscI yscP double null strain SAL6. Bacteria were grown in BHI-minus-calcium medium, and YscI expression was induced with 20 μM IPTG. Surface proteins were cross-linked via the addition of 2.5 mM BS3. Samples were run on SDS-PAGE gels, and the needle component YscF was detected by Western blotting using a polyclonal antiserum. pSE380, vector control; pYscI-WT, plasmid expressing wild-type YscI; pYscI-Q84A to pYscI-L96A, plasmids expressing YscI proteins with the indicated mutations. (B) The aforementioned strains were grown in Yop-inducing medium (BHI minus calcium), and YscI expression was induced with 20 μM IPTG. In addition, a control strain expressing YscI and YscP from two compatible plasmids (pYscI and pYscP) was utilized; YscI expression was induced as described above, and YscP expression was induced with 0.2% arabinose. Secreted supernatant fractions were isolated by centrifugation, precipitated with TCA, and run on SDS-PAGE gels. Yops were visualized by staining with Coomassie blue.
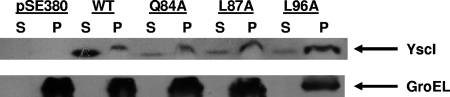
The Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants secrete YscI in the absence of YscP.
The failure to detect YscI in secreted supernatant fractions of the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants was surprising given the fact that these mutants secreted significant amounts of both Yops (Fig. 5) and the needle component YscF (Fig. 7). To determine whether the localization of YscI to the cell pellet fraction in these mutants was dependent upon YscP, plasmids expressing the corresponding mutant proteins were introduced into the yscI yscP double null strain SAL6 by electroporation. Bacteria were grown at 37°C in calcium-deficient medium, and secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions were isolated. In the absence of YscP, a small amount of YscI was now observed in the culture supernatant fraction from each mutant (Fig. 8). To ensure that the small amounts of YscI present in the culture supernatant fractions were not due to cell lysis, culture supernatant and cell pellet fractions were analyzed for the presence of the cytoplasmic protein GroEL. GroEL was detected in cell pellet but not secreted supernatant fractions, thus demonstrating that the presence of YscI in supernatant fractions was not due to cell lysis. We conclude that these mutant forms of YscI are inherently secretable and that their localization to the cell pellet fraction is dependent upon YscP.
FIG. 8.
YscP regulates the secretion of the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutant forms of YscI. Either wild-type (WT) YscI or the indicated YscI mutant forms (indicated by the corresponding mutations) were expressed in trans in the yscI yscP double null strain SAL6. Bacteria were grown in Yop-inducing medium (BHI minus calcium), and YscI expression was induced with 20 μM IPTG. Secreted supernatant (S) and cell pellet (P) fractions were separated by centrifugation. Secreted proteins were precipitated with TCA, and equal percentages of the two fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gels. YscI was detected by Western blotting with a polyclonal antiserum (upper panel); GroEL was detected using a monoclonal antibody (lower panel). pSE380, vector control.
The Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants assemble needles in the absence of YscP.
Given the results demonstrating that YscP does in fact regulate the secretion of YscI in the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants, we sought to determine whether YscP had an effect on needle assembly by these mutants. Therefore, the corresponding mutant proteins were expressed in trans in the yscI yscP double null strain SAL6 and needle assembly was assessed by cross-linking with BS3. The results demonstrate that, in the absence of YscP, the bacteria expressing the YscI Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutant proteins exhibited a degree of needle assembly similar to that observed for the control strain expressing native YscI (Fig. 9A). Note that these results represent much greater levels of needle assembly than those observed for strains expressing YscP together with the same mutant proteins (Fig. 6). To determine whether these mutants could undergo substrate specificity switching, bacteria were grown at 37°C in calcium-deficient medium and secreted supernatant fractions were isolated. Coomassie staining of the supernatant fractions revealed that Yops (late substrates) were in fact not secreted by these mutants. Thus, the mutant proteins behaved identically to native YscI and did not suppress the phenotype of the yscP mutant. To demonstrate the levels of Yop secretion expected for a wild-type strain, the yscI yscP mutant was trans-complemented with two compatible plasmids expressing YscI (pSW71) and YscP (pJJ10). As expected, an abundance of secreted Yops was observed. We conclude that the YscI Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutant proteins do not restore substrate specificity switching in the absence of YscP. Taken together, these results show that needle assembly is not sufficient to trigger a switch in the substrate specificity of the T3SS.
DISCUSSION
T3SSs are complex macromolecular organelles whose assembly requires the ordered export of their components. For virulence-associated T3SSs, this means that type III effectors destined for the eukaryotic cell cytosol must not be exported while the secretion system is being assembled. Regulating the substrate specificity of the secretion apparatus prevents such unwanted export. In Yersinia, YscP and YscU have been shown to play a role in substrate specificity switching. A yscP mutant assembles elongated needle structures on the bacterial cell surface (23) but secretes only small amounts of Yop effectors (43, 49). Similar phenotypes corresponding to mutations in the YscP homologs InvJ (SPI1 T3SS) (27), Spa32 (Shigella T3SS) (31, 55), and FliK (flagella) (20, 28, 57) have been reported previously. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of YscU can partially suppress a yscP mutant phenotype, as evidenced by decreased export of YscF (the needle component) and increased Yop secretion (13). Similarly, mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of FlhB (the flagellar YscU homolog) can partially suppress a fliK mutant phenotype (20, 28, 57).
Despite these results, the exact nature of the switching event is poorly understood. A previous study proposed that YscP functions as a molecular ruler that switches the substrate specificity of the secretion apparatus once the length of the needle structure matches the length of the extended YscP polypeptide (23). In support of this hypothesis, it was shown that the deletion of the central region of YscP results in shorter needles and that the insertion of additional sequences generates longer needles. However, recent work on the SPI1 T3SS has challenged this hypothesis. Specifically, the investigators showed that an invJ mutant, which is defective for substrate specificity switching (9, 27), does not assemble the inner rod structure of the T3SS secreton (32) and secretes excess amounts of the inner rod component PrgJ into cell culture supernatant fractions (52). This finding suggests that inner rod formation is critical for substrate specificity switching.
Based on these results, we sought to determine whether YscI, the inner rod component of the Yersinia T3SS (41), plays a direct role in substrate specificity switching. A previous study demonstrated that YscI is required for the secretion of Yop effectors by the T3SS (3). In this work, we have demonstrated that YscI is secreted by the T3SS. Specifically, YscI was found in both the secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions of a wild-type strain but was not expressed in a yscS mutant that lacked a functional T3SS. Analogous results for the SPI1 T3SS were obtained by Sukhan et al., who demonstrated that PrgJ expression in the absence of a functional T3SS is undetectable (52).
Sukhan et al. previously observed that a Salmonella invJ mutant secretes large amounts of PrgJ into the culture supernatant but that no PrgJ is observed in cellular fractions enriched with the SPI1 T3SS secreton (52). Our results show that the Yersinia T3SS behaves in a similar fashion, as we observed a substantially elevated amount of YscI in the culture supernatant fraction from a yscP mutant compared to that in the fraction from a wild-type strain grown under LCR-inhibiting conditions. To date, the Yersinia T3SS secreton has yet to be isolated in a purified form. Therefore, we cannot conclude that the increased secretion of YscI into culture supernatants reflects the fact that YscI is not incorporated into an inner rod structure, although this is our favored hypothesis. Ultimately, the purification of the Yersinia T3SS secreton will be needed to address this question.
Previous work by Edqvist et al. (13) demonstrated that mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of the inner membrane protein YscU can partially suppress the phenotype of a yscP mutant, as evidenced by the fact that these suppressor mutations reduce the amount of surface-located YscF in the yscP strain. Here, we have confirmed these results. In addition, we examined the effects of two of these YscU mutations (Y287G and Y317D) on YscI export by the yscP mutant. The results paralleled the effects on YscF export observed earlier, that is, the Y287G mutation slightly reduced the amount of YscI exported by the yscP mutant, while the Y317D mutation dramatically reduced YscI export. These results confirm that YscP and YscU coordinately regulate the export of early substrates (both YscF and YscI) and that the Y317D mutation is a particularly strong suppressor of the yscP mutant phenotype. However, these results did not enable us to determine whether YscF or YscI export is truly critical for substrate specificity switching.
Therefore, to determine whether YscI plays a direct role in substrate specificity switching, we performed an extensive mutational analysis of conserved amino acid residues in the C terminus of YscI. Using this approach, we generated seven mutants (the Q84A, L87A, E94K, E95K, L96A, A98V, and L111A mutants) that exhibited mild to severe defects in Yop secretion (late substrate export) without abolishing YscI expression. Unlike native YscI, which was found in both secreted supernatant and cell pellet fractions, YscI from the aforementioned mutants localized exclusively to the cell pellet fractions. This pattern was particularly striking for the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants, which secreted significant amounts of Yops. The fact that YscI is required for Yop secretion suggests that YscI in these mutants does in fact assemble into an inner rod structure. The absence of YscI in secreted supernatant fractions may reflect the fact that the corresponding mutant forms of YscI have a greater propensity to assemble into the inner rod structure than does native YscI.
The cross-linking of surface-located proteins with the cell-impermeable cross-linker BS3 revealed that the Q84A, L87A, E94K, E95K, L96A, A98V, and L111A mutants exhibited severe defects in the assembly of the T3SS needle structure. This result is quite significant for the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants due to the fact that they underwent a substantial degree of substrate specificity switching (as evidenced by the fact that they secreted Yops). This finding suggests that needle assembly is not a prerequisite for substrate specificity switching.
The analysis of secreted supernatant fractions revealed that the E94K, E95K, A98V, and L111A mutants were unable to export the needle component YscF, thus explaining their defect in needle assembly. In contrast, the Q84A and L96A mutants (and, possibly, the L87A mutant) exported significant amounts of YscF yet exhibited severe defects in needle assembly. Therefore, we posit that in these mutants, YscI assembled into the inner rod structure but adopted a conformation that impaired the assembly of YscF into the needle-like structure that sits atop the inner rod. A role for the inner rod as an anchoring point for the needle structure is not without precedent, as Marlovits et al. (32) demonstrated that the elongated needle structures formed by a Salmonella invJ mutant, which is defective for inner rod assembly, are more labile (that is, more easily broken off) than the needle structures formed by a wild-type strain.
Based on the aforementioned hypotheses (namely, that YscI assembly into an inner rod structure is dependent upon YscP and that the YscI Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutant proteins form an inner rod structure that impairs needle assembly), we examined the phenotypes of bacteria expressing the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutant proteins in a yscP null background. The results demonstrated that in the absence of YscP, the mutant forms of YscI were now secreted into culture supernatant fractions. This finding suggests that, in the absence of YscP, these YscI mutant proteins no longer formed the inner rod structure of the T3SS. Consistent with this view is the fact that needle formation by these mutant proteins was now similar to that observed for native YscI. Despite the restoration of needle assembly in the yscP background, the Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutants did not undergo substrate specificity switching, as evidenced by their failure to secrete Yops. Together, these results suggest that the inner rod protein YscI, not the needle protein YscF, is critical for substrate specificity switching. In conjunction with the aforementioned roles that YscP and YscU play in coordinately regulating YscI export, we suggest that YscP and YscU switch the substrate specificity of the secretion apparatus by regulating the export of YscI and the assembly of YscI into the inner rod structure of the T3SS. Clearly, future studies will be needed to understand the precise roles of YscI, YscP, and YscU in this process.
Thus, our results are consistent with the view of Marlovits et al. (32) that the formation of the inner rod structure of T3SSs governs substrate specificity switching. Of course, one must reconcile this view with the hypothesis put forth by Journet et al. (23), which posits that YscP acts as a molecular ruler that physically measures the length of the T3SS needle structure and switches the substrate specificity of the export apparatus when the length of the needle equals the length of the extended YscP polypeptide. Recall that in the experiments by Journet et al., deletions within the central region of the YscP polypeptide resulted in shorter needles and insertions of additional amino acid residues generated longer needles. Thus, the physical length of the YscP polypeptide seemingly governs the length of the T3SS needle structure. We must point out that, in addition to the length of the YscP polypeptide, a second variable was implicitly changed in these experiments, namely, the time needed to synthesize YscP. A shorter YscP polypeptide will be synthesized more quickly and accumulate at a greater rate than a longer YscP polypeptide. Therefore, these experiments did not distinguish between molecular ruler and molecular stopwatch mechanisms. If YscP is required for inner rod formation (as we propose), then a truncated version of YscP should increase the rate of inner rod formation due to a higher rate of accumulation. This effect would result in the substrate specificity switch's occurring more quickly by reducing the time permitted for needle assembly and would, therefore, result in shorter needles. The results of Marlovits et al. (32) support this view, as they have demonstrated that the timing of inner rod assembly is critical for substrate specificity switching. Specifically, they demonstrated that the overexpression of the SPI1 T3SS inner rod component PrgJ results in shorter needles (presumably due to faster inner rod assembly) and that the overexpression of the needle component PrgI results in longer needles (presumably because PrgI outcompetes PrgJ for access to the secretion apparatus and thereby delays inner rod formation). Further characterization of the role of YscP homologs will ultimately be required to further our understanding of substrate specificity switching.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Hans Wolf-Watz for some strains and plasmids and Jim Nataro and anonymous reviewers for comments on the manuscript.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 18 April 2008.
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://jb.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1.Agrain, C., I. Callebaut, L. Journet, I. Sorg, C. Paroz, L. J. Mota, and G. R. Cornelis. 2005. Characterization of a type III secretion substrate specificity switch (T3S4) domain in YscP from Yersinia enterocolitica. Mol. Microbiol. 5654-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ali, S. A., and A. Steinkasserer. 1995. PCR-ligation-PCR mutagenesis: a protocol for creating gene fusions and mutations. BioTechniques 18746-750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Allaoui, A., R. Schulte, and G. R. Cornelis. 1995. Mutational analysis of the Yersinia enterocolitica virC operon: characterization of yscE, F, G, I, J, K required for Yop secretion and yscH encoding YopR. Mol. Microbiol. 18343-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Altschul, S. F., T. L. Madden, A. A. Schaffer, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, W. Miller, and D. J. Lipman. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 253389-3402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bergman, T., K. Erickson, E. Galyov, C. Persson, and H. Wolf-Watz. 1994. The lcrB (yscN/U) gene cluster of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is involved in Yop secretion and shows high homology to the spa gene clusters of Shigella flexneri and Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1762619-2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Blocker, A., N. Jouihri, E. Larquet, P. Gounon, F. Ebel, C. Parsot, P. Sansonetti, and A. Allaoui. 2001. Structure and composition of the Shigella flexneri “needle complex,” a part of its type III secreton. Mol. Microbiol. 39652-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bolin, I., and H. Wolf-Watz. 1984. Molecular cloning of the temperature-inducible outer membrane protein 1 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 4372-78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bottone, E. J. 1997. Yersinia enterocolitica: the charisma continues. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 10257-276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Collazo, C. M., and J. E. Galan. 1996. Requirement for exported proteins in secretion through the invasion-associated type III system of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 643524-3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cornelis, G. R., A. Boland, A. P. Boyd, C. Geuijen, M. Iriarte, C. Neyt, M. P. Sory, and I. Stainier. 1998. The virulence plasmid of Yersinia, an antihost genome. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 621315-1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cornelis, G. R., and H. Wolf-Watz. 1997. The Yersinia Yop virulon: a bacterial system for subverting eukaryotic cells. Mol. Microbiol. 23861-867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Davis, A. J., and J. Mecsas. 2007. Mutations in the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis type III secretion system needle protein, YscF, that specifically abrogate effector translocation into host cells. J. Bacteriol. 18983-97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Edqvist, P. J., J. Olsson, M. Lavander, L. Sundberg, A. Forsberg, H. Wolf-Watz, and S. A. Lloyd. 2003. YscP and YscU regulate substrate specificity of the Yersinia type III secretion system. J. Bacteriol. 1852259-2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fields, K. A., G. V. Plano, and S. C. Straley. 1994. A low-Ca2+ response (LCR) secretion (ysc) locus lies within the lcrB region of the LCR plasmid in Yersinia pestis. J. Bacteriol. 176569-579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Galan, J. E., and H. Wolf-Watz. 2006. Protein delivery into eukaryotic cells by type III secretion machines. Nature 444567-573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Goguen, J. D., J. Yother, and S. C. Straley. 1984. Genetic analysis of the low calcium response in Yersinia pestis Mu d1(Ap lac) insertion mutants. J. Bacteriol. 160842-848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Grosdent, N., I. Maridonneau-Parini, M. P. Sory, and G. R. Cornelis. 2002. Role of Yops and adhesins in resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica to phagocytosis. Infect. Immun. 704165-4176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guzman, L. M., D. Belin, M. J. Carson, and J. Beckwith. 1995. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol. 1774121-4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Harlow, E., and D. Lane. 1988. Antibodies: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
- 20.Hirano, T., S. Yamaguchi, K. Oosawa, and S. Aizawa. 1994. Roles of FliK and FlhB in determination of flagellar hook length in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1765439-5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hoiczyk, E., and G. Blobel. 2001. Polymerization of a single protein of the pathogen Yersinia enterocolitica into needles punctures eukaryotic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 984669-4674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hueck, C. J. 1998. Type III protein secretion systems in bacterial pathogens of animals and plants. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62379-433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Journet, L., C. Agrain, P. Broz, and G. R. Cornelis. 2003. The needle length of bacterial injectisomes is determined by a molecular ruler. Science 3021757-1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kerschen, E. J., D. A. Cohen, A. M. Kaplan, and S. C. Straley. 2004. The plague virulence protein YopM targets the innate immune response by causing a global depletion of NK cells. Infect. Immun. 724589-4602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kimbrough, T. G., and S. I. Miller. 2000. Contribution of Salmonella typhimurium type III secretion components to needle complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 9711008-11013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kubori, T., Y. Matsushima, D. Nakamura, J. Uralil, M. Lara-Tejero, A. Sukhan, J. E. Galan, and S. I. Aizawa. 1998. Supramolecular structure of the Salmonella typhimurium type III protein secretion system. Science 280602-605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kubori, T., A. Sukhan, S. I. Aizawa, and J. E. Galan. 2000. Molecular characterization and assembly of the needle complex of the Salmonella typhimurium type III protein secretion system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 9710225-10230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kutsukake, K., T. Minamino, and T. Yokoseki. 1994. Isolation and characterization of FliK-independent flagellation mutants from Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1767625-7629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lavander, M., L. Sundberg, P. J. Edqvist, S. A. Lloyd, H. Wolf-Watz, and A. Forsberg. 2002. Proteolytic cleavage of the FlhB homologue YscU of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is essential for bacterial survival but not for type III secretion. J. Bacteriol. 1844500-4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Macnab, R. M. 2004. Type III flagellar protein export and flagellar assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1694207-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Magdalena, J., A. Hachani, M. Chamekh, N. Jouihri, P. Gounon, A. Blocker, and A. Allaoui. 2002. Spa32 regulates a switch in substrate specificity of the type III secreton of Shigella flexneri from needle components to Ipa proteins. J. Bacteriol. 1843433-3441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Marlovits, T. C., T. Kubori, M. Lara-Tejero, D. Thomas, V. M. Unger, and J. E. Galan. 2006. Assembly of the inner rod determines needle length in the type III secretion injectisome. Nature 441637-640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Marlovits, T. C., T. Kubori, A. Sukhan, D. R. Thomas, J. E. Galan, and V. M. Unger. 2004. Structural insights into the assembly of the type III secretion needle complex. Science 3061040-1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Medini, D., A. Covacci, and C. Donati. 2006. Protein homology network families reveal step-wise diversification of type III and type IV secretion systems. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2e173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Milton, D. L., R. O'Toole, P. Horstedt, and H. Wolf-Watz. 1996. Flagellin A is essential for the virulence of Vibrio anguillarum. J. Bacteriol. 1781310-1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Minamino, T., B. Gonzalez-Pedrajo, K. Yamaguchi, S. I. Aizawa, and R. M. Macnab. 1999. FliK, the protein responsible for flagellar hook length control in Salmonella, is exported during hook assembly. Mol. Microbiol. 34295-304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Moriya, N., T. Minamino, K. T. Hughes, R. M. Macnab, and K. Namba. 2006. The type III flagellar export specificity switch is dependent on FliK ruler and a molecular clock. J. Mol. Biol. 359466-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mota, L. J., L. Journet, I. Sorg, C. Agrain, and G. R. Cornelis. 2005. Bacterial injectisomes: needle length does matter. Science 3071278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mueller, C. A., P. Broz, S. A. Muller, P. Ringler, F. Erne-Brand, I. Sorg, M. Kuhn, A. Engel, and G. R. Cornelis. 2005. The V-antigen of Yersinia forms a distinct structure at the tip of injectisome needles. Science 310674-676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mukherjee, S., G. Keitany, Y. Li, Y. Wang, H. L. Ball, E. J. Goldsmith, and K. Orth. 2006. Yersinia YopJ acetylates and inhibits kinase activation by blocking phosphorylation. Science 3121211-1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pallen, M. J., S. A. Beatson, and C. M. Bailey. 2005. Bioinformatics analysis of the locus for enterocyte effacement provides novel insights into type-III secretion. BMC Microbiol. 59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Patterson-Delafield, J., R. J. Martinez, B. A. Stocker, and S. Yamaguchi. 1973. A new fla gene in Salmonella typhimurium—flaR—and its mutant phenotype—superhooks. Arch. Mikrobiol. 90107-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Payne, P. L., and S. C. Straley. 1999. YscP of Yersinia pestis is a secreted component of the Yop secretion system. J. Bacteriol. 1812852-2862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Perry, R. D., and J. D. Fetherston. 1997. Yersinia pestis—etiologic agent of plague. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1035-66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Plano, G. V., and S. C. Straley. 1995. Mutations in yscC, yscD, and yscG prevent high-level expression and secretion of V antigen and Yops in Yersinia pestis. J. Bacteriol. 1773843-3854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rosqvist, R., I. Bolin, and H. Wolf-Watz. 1988. Inhibition of phagocytosis in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: a virulence plasmid-encoded ability involving the Yop2b protein. Infect. Immun. 562139-2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sambrook, J., E. F. Fritsch, and T. Maniatis. 1989. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
- 48.Simon, R., U. Priefer, and A. Puhler. 1983. A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram negative bacteria. Biotechnology 1787-796. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stainier, I., S. Bleves, C. Josenhans, L. Karmani, C. Kerbourch, I. Lambermont, S. Totemeyer, A. Boyd, and G. R. Cornelis. 2000. YscP, a Yersinia protein required for Yop secretion that is surface exposed, and released in low Ca2+. Mol. Microbiol. 371005-1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Straley, S. C., and W. S. Bowmer. 1986. Virulence genes regulated at the transcriptional level by Ca2+ in Yersinia pestis include structural genes for outer membrane proteins. Infect. Immun. 51445-454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Studier, F. W., and B. A. Moffatt. 1986. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J. Mol. Biol. 189113-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sukhan, A., T. Kubori, and J. E. Galan. 2003. Synthesis and localization of the Salmonella SPI-1 type III secretion needle complex proteins PrgI and PrgJ. J. Bacteriol. 1853480-3483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sweet, C. R., J. Conlon, D. T. Golenbock, J. Goguen, and N. Silverman. 2007. YopJ targets TRAF proteins to inhibit TLR-mediated NF-κB, MAPK and IRF3 signal transduction. Cell. Microbiol. 92700-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tamano, K., S. Aizawa, E. Katayama, T. Nonaka, S. Imajoh-Ohmi, A. Kuwae, S. Nagai, and C. Sasakawa. 2000. Supramolecular structure of the Shigella type III secretion machinery: the needle part is changeable in length and essential for delivery of effectors. EMBO J. 193876-3887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tamano, K., E. Katayama, T. Toyotome, and C. Sasakawa. 2002. Shigella Spa32 is an essential secretory protein for functional type III secretion machinery and uniformity of its needle length. J. Bacteriol. 1841244-1252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Torruellas, J., M. W. Jackson, J. W. Pennock, and G. V. Plano. 2005. The Yersinia pestis type III secretion needle plays a role in the regulation of Yop secretion. Mol. Microbiol. 571719-1733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Williams, A. W., S. Yamaguchi, F. Togashi, S. I. Aizawa, I. Kawagishi, and R. M. Macnab. 1996. Mutations in fliK and flhB affecting flagellar hook and filament assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1782960-2970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.