Abstract
The nephrotic syndrome has emerged over several centuries as the consequence of continued profuse proteinuria, arising in turn from a variety of lesions affecting the glomerulus which impair glomerular ability to retain plasma proteins, in particular, albumin. As a syndrome, it has its own complications and requires its own management irrespective of the underlying lesions. Dissection of these by renal biopsy and by clinical investigation reveals a variety of systemic diseases which affect the kidney, but a majority of primary immune-based diseases appear unique to the glomerulus. Whether the lesion called by Müller and Munk ‘nephrosis’, and now called minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis is one disease or many, is the subject of intense debate at the moment, as is the relationship between two types of lesion. Only a better understanding of their pathogenesis, and of how the glomerulus normally retains plasma protein, will solve this knotty problem.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARNEIL G. C. 164 children with nephrosis. Lancet. 1961 Nov 18;2(7212):1103–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)91026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. H., Schapel G. J., Edwards K. D. Increased incidence of coronary heart disease associated with combined elevation of serum triglyceride and cholesterol concentrations in the nephrotic syndrome in man. Med J Aust. 1974 Jul 27;2(4):119–122. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb93641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrassy K., Ritz E., Bommer J. Hypercoagulability in the Nephrotic syndrome. Klin Wochenschr. 1980 Oct 1;58(19):1029–1036. doi: 10.1007/BF01476873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARCLAY G. P., CAMERON H. M., LOUGHRIDGE L. W. Amyloid disease of the kidney and renal vein thrombosis. Q J Med. 1960 Jan;29:137–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAINEY J. D., BREWER D. B., HARDWICKE J., SOOTHILL J. F. The nephrotic syndrome. Diagnosis by renal biopsy and biochemical and immunological analyses related to the response to steroid therapy. Q J Med. 1960 Apr;29:235–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlyne G. M., Mallick N. P. Ischaemic heart-disease as a complication of nephrotic syndrome. Lancet. 1969 Aug 23;2(7617):399–400. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90110-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. S. Coagulation and thromboembolic complications in the nephrotic syndrome. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1984;13:75–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain M. J., Pringle A., Wrong O. M. Oliguric renal failure in the nephrotic syndrome. Q J Med. 1966 Apr;35(138):215–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curt G. A., Kaldany A., Whitley L. G., Crosson A. W., Rolla A., Merino M. J., D'Elia J. A. Reversible rapidly progressive renal failure with nephrotic syndrome due to fenoprofen calcium. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jan;92(1):72–73. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-1-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
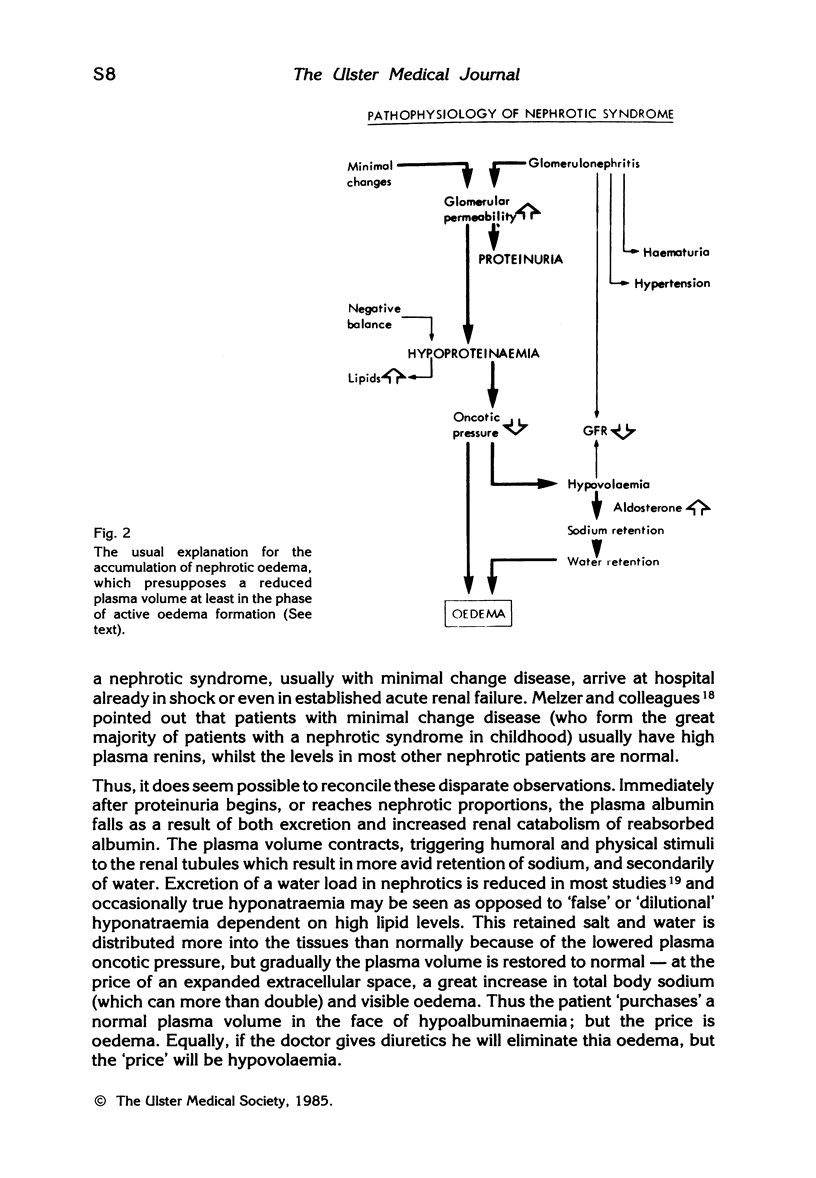
- Dorhout Mees E. J., Geers A. B., Koomans H. A. Blood volume and sodium retention in the nephrotic syndrome: a controversial pathophysiological concept. Nephron. 1984;36(4):201–211. doi: 10.1159/000183155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorhout E. J., Roos J. C., Boer P., Yoe O. H., Simatupang T. A. Observations on edema formation in the nephrotic syndrome in adults with minimal lesions. Am J Med. 1979 Sep;67(3):378–384. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90782-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Fraley D. S., Stachura I., Feldman H. A., Gandy D. R., Bourke E. Fenoprofen nephropathy: lipoid nephrosis and interstitial nephritis. A possible T-lymphocyte disorder. Am J Med. 1982 Jan;72(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geers A. B., Koomans H. A., Roos J. C., Boer P., Dorhout Mees E. J. Functional relationships in the nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1984 Sep;26(3):324–330. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington J. T., Kassirer J. P. Renal vein thrombosis. Annu Rev Med. 1982;33:255–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.33.020182.001351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
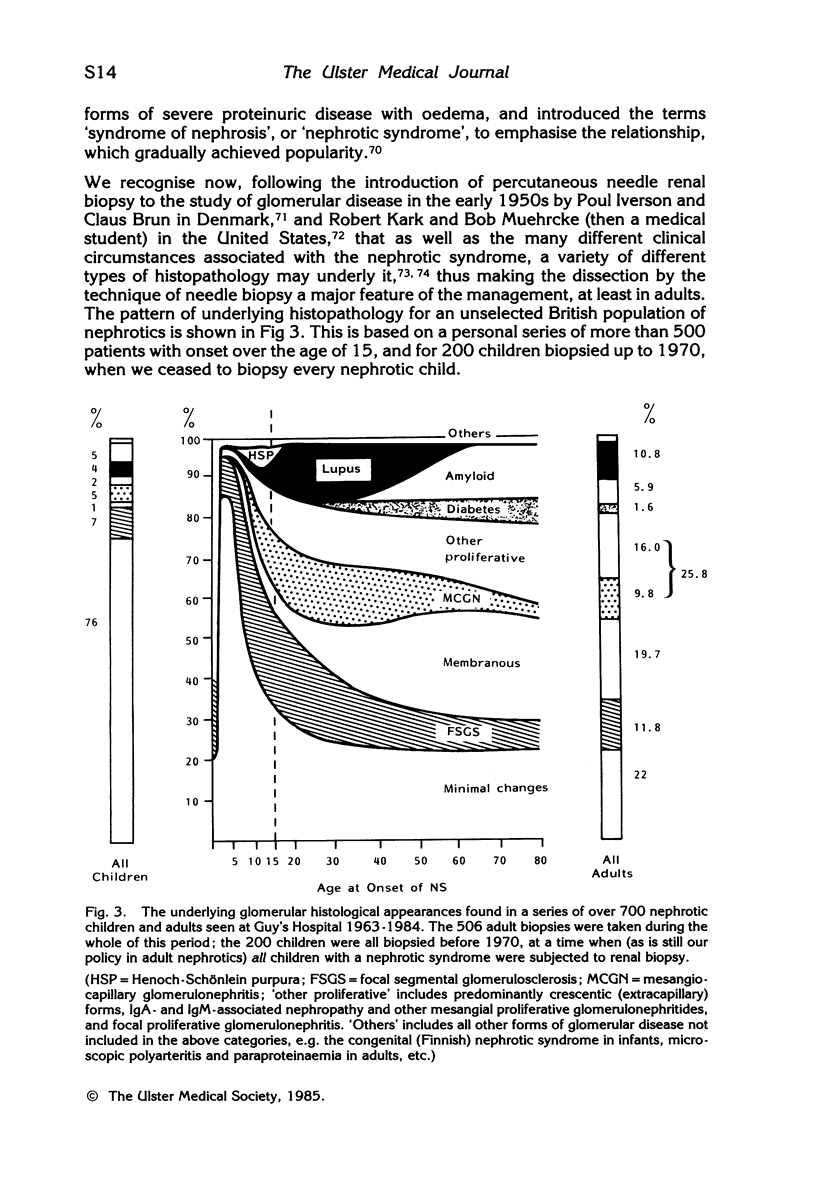
- Hlatky M. A. Is renal biopsy necessary in adults with nephrotic syndrome. Lancet. 1982 Dec 4;2(8310):1264–1268. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbasciati E., Ponticelli C., Case N., Altieri P., Bolasco F., Mihatsch M. J., Zollinger H. U. Acute renal failure in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Nephron. 1981;28(4):186–191. doi: 10.1159/000182173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES D. B. Nephrotic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1957 Mar-Apr;33(2):313–329. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARK R. M., PIRANI C. L., POLLAK V. E., MUEHRCKE R. C., BLAINEY J. D. The nephrotic syndrome in adults: a common disorder with many causes. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Oct;49(4):751–754. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-49-4-751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallen R. J., Brynes R. K., Aronson A. J., Lichtig C., Spargo B. H. Premature coronary atherosclerosis in a 5-year-old with corticosteroid-refractory nephrotic syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1977 Sep;131(9):976–980. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1977.02120220042006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassirer J. P. Is renal biopsy necessary for optimal management of the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome? Kidney Int. 1983 Oct;24(4):561–575. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Ingelfinger J. R., Grupe W. E. Peritonitis in childhood nephrotic syndrome: 1970-1980. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Aug;136(8):732–736. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970440076023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann U., Steurer J., Bollinger A., Pouliadis G., Briner J., Siegenthaler W. Inzidenz und klinische Bedeutung von Thrombosen und thromboembolischen Komplikationen bei Patienten mit nephrotischem Syndrom. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1981 Jul 7;111(27-28):1034–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder G. C., Lundsgaard C., Van Slyke D. D., Stillman E. CHANGES IN THE VOLUME OF PLASMA AND ABSOLUTE AMOUNT OF PLASMA PROTEINS IN NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1924 May 31;39(6):921–929. doi: 10.1084/jem.39.6.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein J., Schacht R. G., Baldwin D. S. Renal failure in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Am J Med. 1981 Feb;70(2):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90754-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUEHRCKE R. C., KARK R. M., PIRANI C. L. Technique of percutaneous renal biopsy in the prone position. J Urol. 1955 Sep;74(3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)67279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallick N. P., Short C. D. The nephrotic syndrome and ischaemic heart disease. Nephron. 1981;27(2):54–57. doi: 10.1159/000182024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinley E., Lowe G. D., Boulton-Jones M., Forbes C. D., Prentice C. R. Blood viscosity and haemostasis in the nephrotic syndrome. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Jun 28;49(3):155–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. H., Forsgren A., Björkstén B., Kim Y., Quie P. G., Michael A. F. Decreased serum factor B concentration associated with decreased opsonization of Escherichia coli in the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Res. 1977 Aug;11(8):910–916. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197708000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer J. I., Keim H. J., Laragh J. H., Sealey J. E., Jan K. M., Chien S. Nephrotic syndrome: vasoconstriction and hypervolemic types indicated by renin-sodium profiling. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):688–696. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne P., Francis R. B., Meiselman H. J. Red blood cell aggregation in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1983 Mar;23(3):519–525. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G., Mecca G., Marchesi D., Livio M., de Gaetano G., Donati M. B., Silver M. J. Platelet hyperaggregability and the nephrotic syndrome. Thromb Res. 1979;16(3-4):345–354. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trompeter R. S., Lloyd B. W., Hicks J., White R. H., Cameron J. S. Long-term outcome for children with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91387-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usberti M., Federico S., Meccariello S., Cianciaruso B., Balletta M., Pecoraro C., Sacca L., Ungaro B., Pisanti N., Andreucci V. E. Role of plasma vasopressin in the impairment of water excretion in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1984 Feb;25(2):422–429. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagoner R. D., Stanson A. W., Holley K. E., Winter C. S. Renal vein thrombosis in idiopathic membranous glomerulopathy and nephrotic syndrome: incidence and significance. Kidney Int. 1983 Feb;23(2):368–374. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wass V. J., Jarrett R. J., Chilvers C., Cameron J. S. Does the nephrotic syndrome increase the risk of cardiovascular disease? Lancet. 1979 Sep 29;2(8144):664–667. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wass V., Cameron J. S. Cardiovascular disease and the nephrotic syndrome: the other side of the coin. Nephron. 1981;27(2):58–61. doi: 10.1159/000182025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R. O., Nester B. Histological reassessment of three kidneys originally described by Richard Bright in 1827-36. Br Med J. 1972 Jun 24;2(5816):761–763. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5816.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAUCHI H., HOPPER J., Jr HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK AND HYPOTENSION AS A COMPLICATION IN THE NEPHROTIC SYNDROME. REPORT OF TEN CASES. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Feb;60:242–254. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-60-2-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


