Abstract
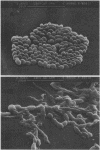
The mechanism of anticandidal action of novel synthetic dipeptides containing N3-(4-methoxyfumaroyl)-L-2,3-diaminopropanoic acid (FMDP) residues was shown to be consistent with the "warhead delivery" concept. FMDP dipeptides were shown to be transported into Candida albicans cells by the di-tripeptide permease and subsequently hydrolyzed by intracellular peptidases, especially aminopeptidase. The anticandidal activity of the particular FMDP dipeptide was influenced by the rate of its transport and, to a lower extent, by the intracellular cleavage rate. A high transport rate accompanied by a high cleavage rate resulted in the high anticandidal activity of L-norvalyl-FMDP. The strong growth-inhibitory effect of this compound was the consequence of inhibition of the enzyme glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase by the released FMDP. The action of L-norvalyl-FMDP on exponentially growing C. albicans cells resulted in a sharp decrease of incorporation of 14C label from [14C]glucose into chitin, mannoprotein, and glucan. This effect, as well as the growth-inhibitory effect, was fully reversed by exogenous N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase was proved to be the only essential target for FMDP dipeptides. Scanning electron microscopy of C. albicans cells treated with L-norvalyl-FMDP revealed highly distorted, wrinkled, and collapsed forms. Cells formed long, bulbous chains, and partial lysis occurred.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Ames G. F., Young J. D., Tsuchiya D., Lecocq J. Illicit transport: the oligopeptide permease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):456–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andruszkiewicz R., Chmara H., Milewski S., Borowski E. Synthesis and biological properties of N3-(4-methoxyfumaroyl)-L-2,3-diaminopropanoic acid dipeptides, a novel group of antimicrobial agents. J Med Chem. 1987 Oct;30(10):1715–1719. doi: 10.1021/jm00393a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andruszkiewicz R., Chmara H., Milewski S., Borowski E. Synthesis of N3-fumaramoyl-L-2,3-diaminopropanoic acid analogues, the irreversible inhibitors of glucosamine synthetase. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1986 May;27(5):449–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1986.tb01041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hall M. J., Hassall C. H., Holmes S. W., Lambert R. W., Lloyd W. J., Ringrose P. S. Phosphonopeptide antibacterial agents related to alafosfalin: design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Dec;18(6):897–905. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton F. R., Hassall C. H., Lambert R. W. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of antibacterial phosphonopeptides incorporating (1-aminoethyl)phosphonic acid and (aminomethyl)phosphonic acid. J Med Chem. 1986 Jan;29(1):29–40. doi: 10.1021/jm00151a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. M., Covert N. L., Shenbagamurthi P., Steinfeld A. S., Naider F. Polyoxin D inhibits growth of zoopathogenic fungi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):926–929. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzola J. J., Mehta R. J., Nisbet L. J., Valenta J. R. The effect of aculeacin A and papulacandin B on morphology and cell wall ultrastructure in Candida albicans. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jun;30(6):857–863. doi: 10.1139/m84-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulo A. N., Bradley S. F., Kauffman C. A. Susceptibility of yeast-like fungi to a new antifungal agent, LY 121019. Mycoses. 1988 Jun;31(6):330–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.1988.tb04426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chmara H., Andruszkiewicz R., Borowski E. Inactivation of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium LT2 by fumaroyl diaminopropanoic acid derivatives, a novel group of glutamine analogs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 28;870(2):357–366. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi E., Shibata D., Matoba T. Modified colorimetric ninhydrin methods for peptidase assay. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickel T. E., Gilvarg C. Transport of impermeant substances in E. coli by way of oligopeptide permease. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 7;241(110):161–163. doi: 10.1038/newbio241161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galardy R. E., Craig L. C., Jamieson J. D., Printz M. P. Photoaffinity labeling of peptide hormone binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3510–3518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal P., Sullivan P. A., Shepherd M. G. Metabolism of [14C]glucose by regenerating spheroplasts of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Feb;130(2):325–335. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenig M., Vandamme E., Abraham E. P. The mode of action of bacilysin and anticapsin and biochemical properties of bacilysin-resistant mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):46–54. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury W. D., Boehm J. C., Mehta R. J., Grappel S. F., Gilvarg C. A novel peptide delivery system involving peptidase activated prodrugs as antimicrobial agents. Synthesis and biological activity of peptidyl derivatives of 5-fluorouracil. J Med Chem. 1984 Nov;27(11):1447–1451. doi: 10.1021/jm00377a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury W. D., Boehm J. C., Mehta R. J., Grappel S. F. Transport of antimicrobial agents using peptide carrier systems: anticandidal activity of m-fluorophenylalanine--peptide conjugates. J Med Chem. 1983 Dec;26(12):1725–1729. doi: 10.1021/jm00366a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichliter W. D., Naider F., Becker J. M. Basis for the design of anticandidal agents from studies of peptide utilization in Canadida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):483–490. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy P. J., Newman D. J., Nisbet L. J., Kingsbury W. D. Relative rates of transport of peptidyl drugs by Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):494–499. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Glauner W., Bernard E., Armstrong D., Merrifield B. The antifungal activity of carrier peptides, L-arginyl-X-L-phenylalanine, containing amino acid antagonists or atypical non-biogenic D-amino acids in the central position. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1982 Jun;252(2):274–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewski S., Chmara H., Andruszkiewicz R., Borowski E. Synthetic derivatives of N3-fumaroyl-L-2,3-diaminopropanoic acid inactivate glucosamine synthetase from Candida albicans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 29;828(3):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewski S., Chmara H., Andruszkiewicz R., Borowski E., Zaremba M., Borowski J. Antifungal peptides with novel specific inhibitors of glucosamine 6-phosphate synthase. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1988;14(7):461–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy B. B., Lively D. H., Gale R. M., Gorman M., Boeck L. D. A new dipeptide antibiotic from Streptomyces collinus, Lindenbein. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Feb;25(2):137–140. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. W. Drug delivery systems: optimising the structure of peptide carriers for synthetic antimicrobial drugs. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1986;12(6-7):585–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., Gancedo C. Purification and properties of three intracellular proteinases from Candida albicans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 11;881(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthou P., Gonneau M., Le Goffic F. Photoaffinity inhibition of peptide transport in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 10;110(3):884–889. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa O., Nakayama H. Isolation of a Candida albicans mutant with reduced content of cell wall mannan and deficient mannan phosphorylation. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(4):315–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ti J. S., Steinfeld A. S., Naider F., Gulumoglu A., Lewis S. V., Becker J. M. Anticandidal activity of pyrimidine-peptide conjugates. J Med Chem. 1980 Aug;23(8):913–918. doi: 10.1021/jm00182a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Poulain D., Herbaut J., Biguet J. Localization of chitin in the cell wall of Candida albicans by means of wheat germ agglutinin. Fluorescence and ultrastructural studies. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Hiratani T., Iwata K., Yamamoto Y. Studies on the mechanism of antifungal action of aculeacin A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Feb;35(2):210–219. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]