Abstract
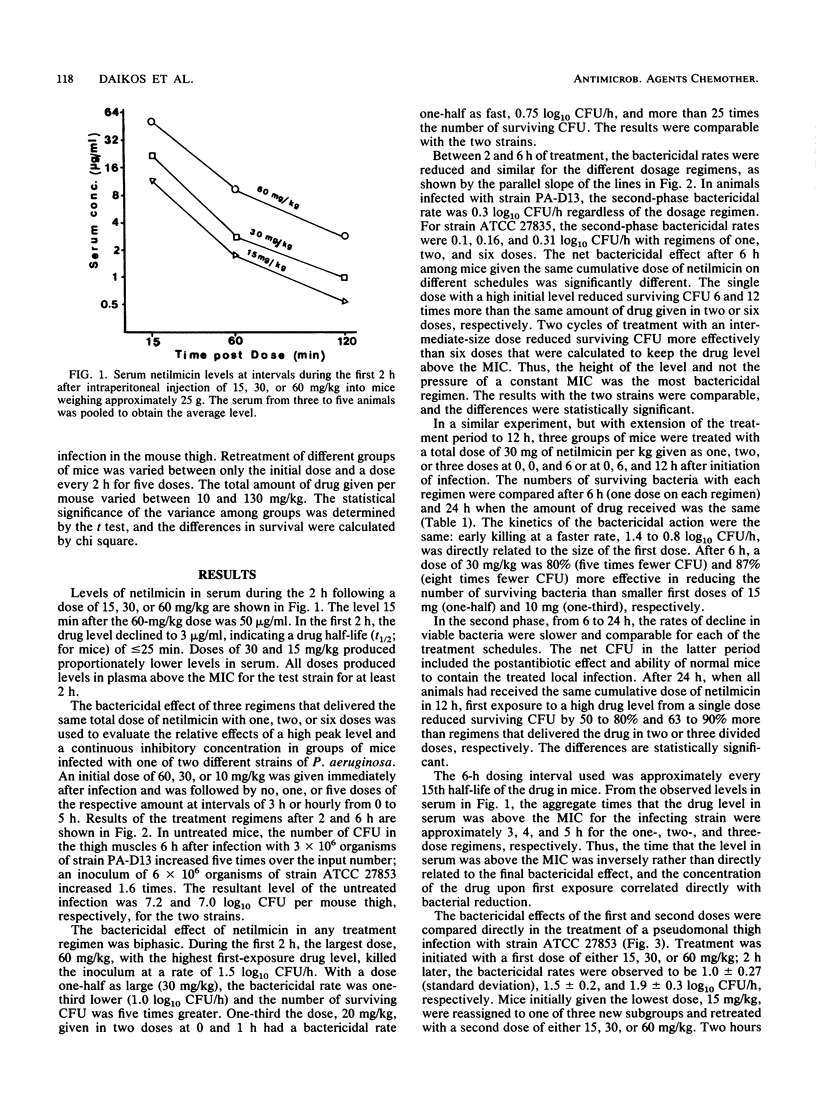
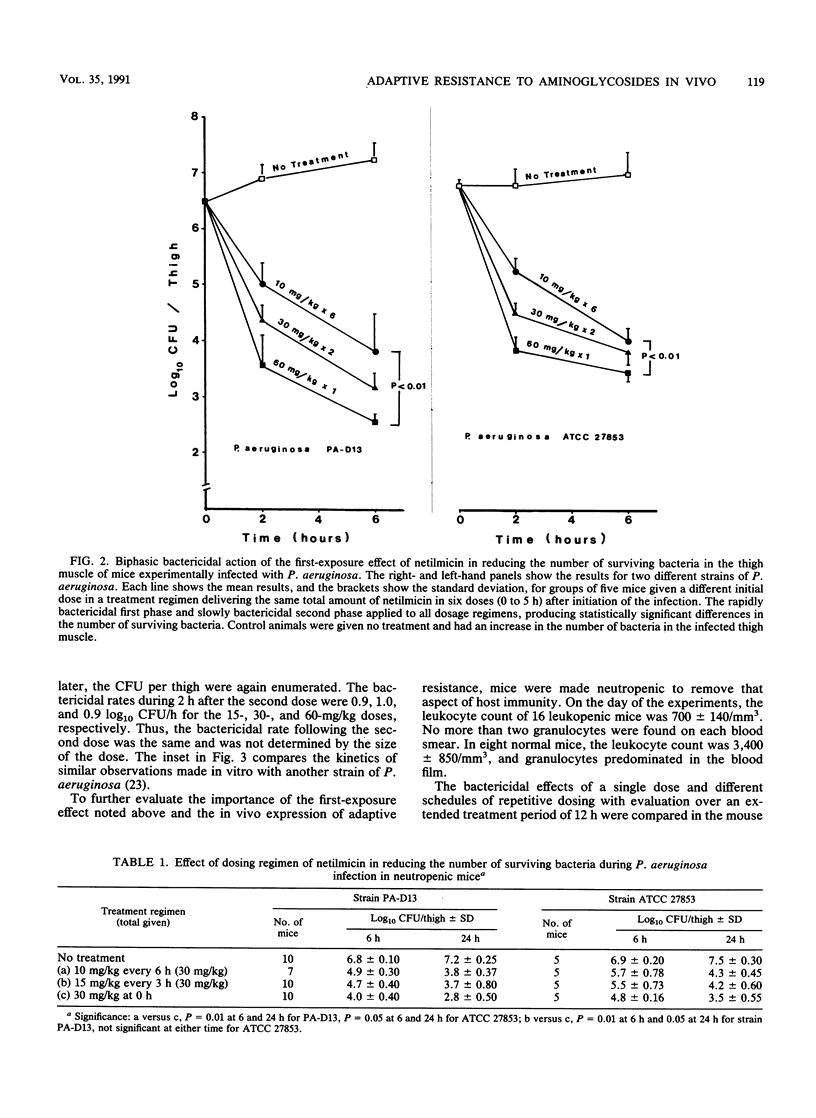
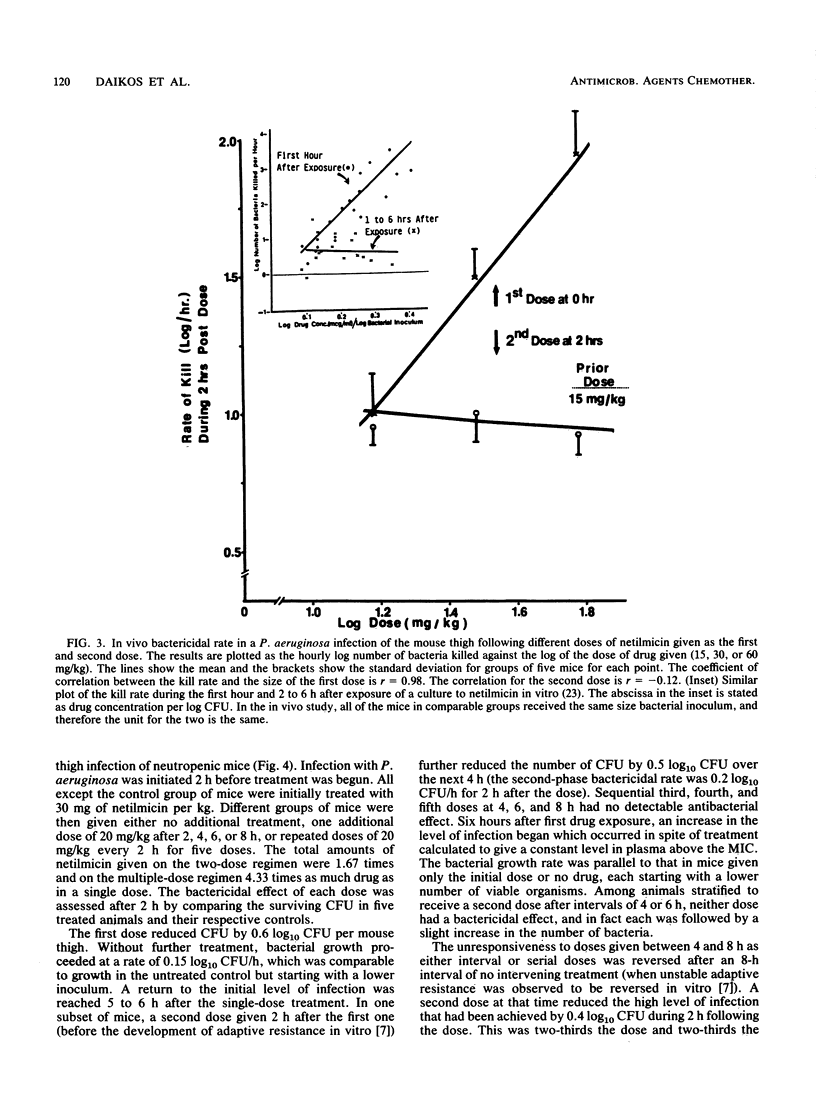
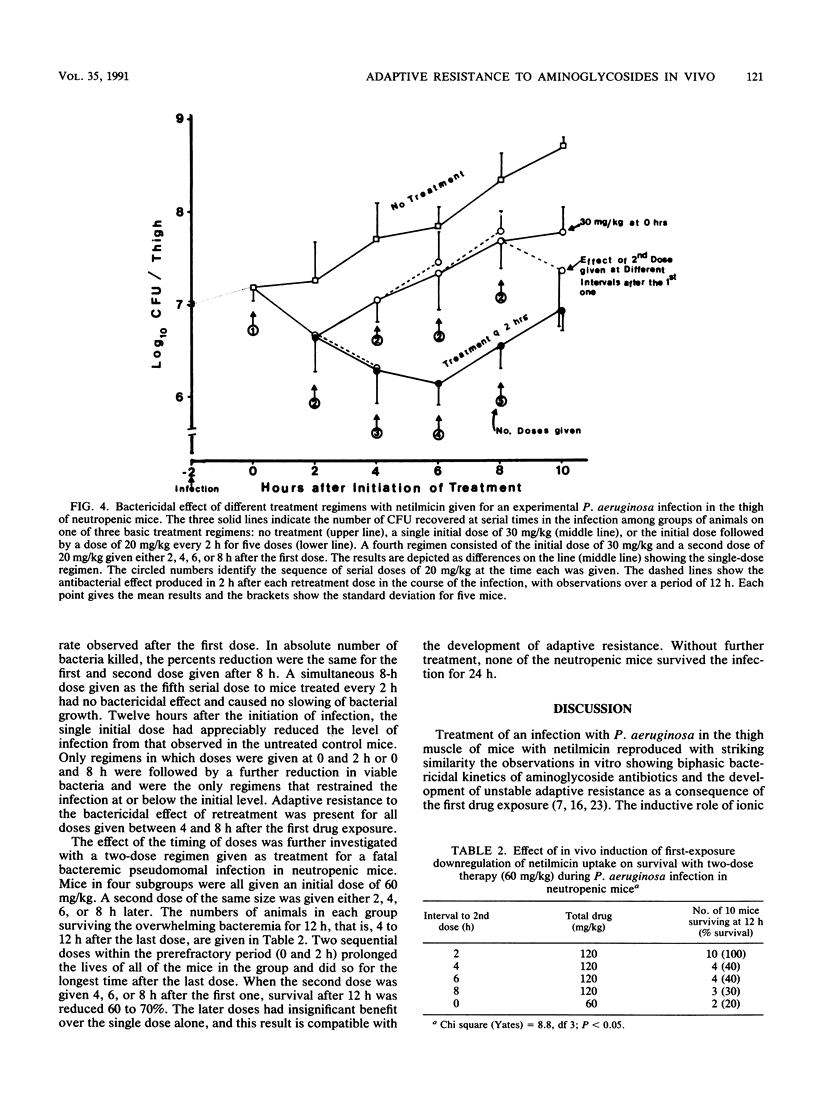
The first exposure of gram-negative bacilli to an aminoglycoside antibiotic in vitro induces a biphasic bactericidal response and adaptive drug resistance (G. L. Daikos, G. G. Jackson, V. T. Lolans, and D. M. Livermore, J. Infect. Dis. 162:414-420, 1990; G. G. Jackson, G. L. Daikos, and V. T. Lolans, J. Infect. Dis. 162:408-413, 1990). The therapeutic implications were examined in netilmicin treatment of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of normal and neutropenic mice. For 2 h after the first dose, the bactericidal rates were rapid, 0.75, 1.0, and 1.5 log10 CFU/h with doses of 10, 30, and 60 mg/kg, respectively. Each twofold increase in dosage reduced the number of surviving bacteria fivefold. Between 2 and 6 h, the second-phase bactericidal rate was slow, less than or equal to 0.3 log10 CFU/h, regardless of the dose. In a multiple-dose regimen, the same amount of netilmicin given in one dose was 70 and 90% more effective than two or three doses, respectively. Doses calculated to keep the drug level in plasma above the MIC were less effective than regimens giving first exposure to a high drug concentration. Adaptive resistance occurred when doses were given more than 2 h after the start of treatment. Temporary survival of bacteremic neutropenic mice was 60 to 70% greater with a second dose at 2 h than after a longer interval. In a thigh infection of neutropenic mice treated every 2 h, doses 4, 6, and 8 h after the first one showed no bactericidal effect. A drug-free interval of 8 h (20 times the drug half-life) renewed bacterial susceptibility to drug action. The results in vivo confirm the biphasic bactericidal action and induction of adaptive resistance that characterized first exposure of gram-negative bacilli to aminoglycoside antibiotics. The phenomena have meaning for the optimum clinical use of aminoglycosides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen N. E., Alborn W. E., Jr, Kirst H. A., Toth J. E. Comparison of aminoglycoside antibiotics with respect to uptake and lethal activity in Escherichia coli. J Med Chem. 1987 Feb;30(2):333–340. doi: 10.1021/jm00385a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. T., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Simultaneous antibiotic levels in "breakthrough" gram-negative rod bacteremia. Am J Med. 1976 Oct;61(4):493–497. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Gilbert D. N., Parker R. A., Porter G. A. The influence of dosage regimen on experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity: dissociation of peak serum levels from renal failure. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):576–580. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser J., Stone B. B., Groner M. C., Zinner S. H. Comparative study with enoxacin and netilmicin in a pharmacodynamic model to determine importance of ratio of antibiotic peak concentration to MIC for bactericidal activity and emergence of resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1054–1060. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodey G. P., Middleman E., Umsawasdi T., Rodriguez V. Intravenous gentamicin therapy for infections in patients with cancer. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S174–S179. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kwan S. Roles of ribosomal binding, membrane potential, and electron transport in bacterial uptake of streptomycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):835–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikos G. L., Jackson G. G., Lolans V. T., Livermore D. M. Adaptive resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics from first-exposure down-regulation. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):414–420. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame P. T., Phair J. P., Watanakunakorn C., Bannister T. W. Pharmacologic factors associated with gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):952–956. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Brugger H. P., Feller C., Stritzko T., Stalder B. Antibiotic therapy of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in normal and granulocytopenic mice: comparison of murine and human pharmacokinetics. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):90–97. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Craig W. A., Brugger H. P., Feller C., Vastola A. P., Brandel J. Impact of dosing intervals on activity of gentamicin and ticarcillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in granulocytopenic mice. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):910–917. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Vastola A. P., Brandel J., Craig W. A. Selection of aminoglycoside-resistant variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an in vivo model. J Infect Dis. 1982 Nov;146(5):691–697. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.5.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Wiprächtiger P., Stettler-Spichiger U., Lebek G. Constant infusions vs. intermittent doses of gentamicin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):554–560. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilleland H. E., Jr Adaptive alterations in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria during human infection. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):499–502. doi: 10.1139/m88-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Raffle V. J., Nicas T. I. Involvement of the outer membrane in gentamicin and streptomycin uptake and killing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):777–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. W., Pien F. D., Kominami N. Massive amikacin "overdose". Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):227–228. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. G., Lolans V. T., Daikos G. L. The inductive role of ionic binding in the bactericidal and postexposure effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics with implications for dosing. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):408–413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. G., Riff L. J. Pseudomonas bacteremia: pharmacologic and other bases for failure of treatment with gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S185–S191. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapusnik J. E., Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F., Carpenter T., Sande M. A. Single, large, daily dosing versus intermittent dosing of tobramycin for treating experimental pseudomonas pneumonia. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):7–12. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly N. M., Rawling E. G., Hancock R. E. Determinants of the efficacy of tobramycin therapy against isogenic nonmucoid and mucoid derivatives of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 growing in peritoneal chambers in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1207–1211. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labovitz E., Levison M. E., Kaye D. Single-dose daily gentamicin therapy in urinary tract infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):465–470. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledergerber B., Blaser J., Lüthy R. Computer-controlled in-vitro simulation of multiple dosing regimens. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):169–173. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett J. E., Fantin B., Ebert S., Totsuka K., Vogelman B., Calame W., Mattie H., Craig W. A. Comparative antibiotic dose-effect relations at several dosing intervals in murine pneumonitis and thigh-infection models. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):281–292. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur R. D., Lolans V., Zar F. A., Jackson G. G. Biphasic, concentration-dependent and rate-limited, concentration-independent bacterial killing by an aminoglycoside antibiotic. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):778–779. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. A., Bates N. C., Hancock R. E. Interaction of polycationic antibiotics with Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide and lipid A studied by using dansyl-polymyxin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):496–500. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Lietman P. S., Smith C. R. Clinical response to aminoglycoside therapy: importance of the ratio of peak concentration to minimal inhibitory concentration. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):93–99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Smith C. R., Lietman P. S. Association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with therapeutic outcome in gram-negative pneumonia. Am J Med. 1984 Oct;77(4):657–662. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90358-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Smith C. R., Lietman P. S. The association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with mortality in patients with gram-negative bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):443–448. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noone P., Parsons T. M., Pattison J. R., Slack R. C., Garfield-Davies D., Hughes K. Experience in monitoring gentamicin therapy during treatment of serious gram-negative sepsis. Br Med J. 1974 Mar 16;1(5906):477–481. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5906.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. A., Hancock R. E., McGroarty E. J. Binding of polycationic antibiotics and polyamines to lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1256-1261.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. H., Thompson W. L., Luthe M. A., Stern R. C., Grossniklaus D. A., Bloxham D. D., Groden D. L., Jacobs M. R., DiScenna A. O., Cash H. A. Once-daily vs. continuous aminoglycoside dosing: efficacy and toxicity in animal and clinical studies of gentamicin, netilmicin, and tobramycin. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):918–932. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Bloxham D. D., Thompson W. L. Nephrotoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin given once daily or continuously in dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4 (Suppl A):85–101. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_a.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm A. W. Netilmicin in the treatment of gram-negative bacteremia: single daily versus multiple daily dosage. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):931–937. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Leggett J., Turnidge J., Ebert S., Craig W. A. Correlation of antimicrobial pharmacokinetic parameters with therapeutic efficacy in an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):831–847. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. A., Norton D. R., Kohlhepp S. J., Kohnen P. W., Porter G. A., Houghton D. C., Brummett R. E., Bennett W. M., Gilbert D. N. The influence of tobramycin dosage regimens on nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and antibacterial efficacy in a rat model of subcutaneous abscess. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):13–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


