Abstract
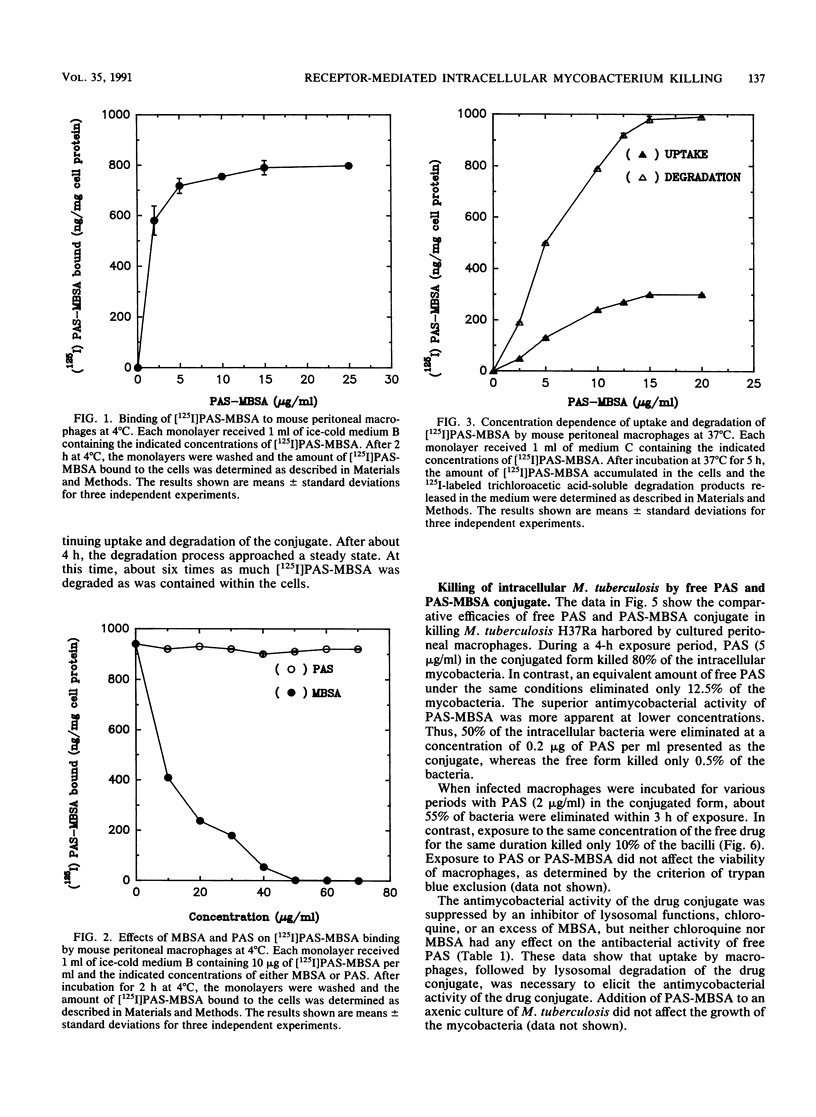
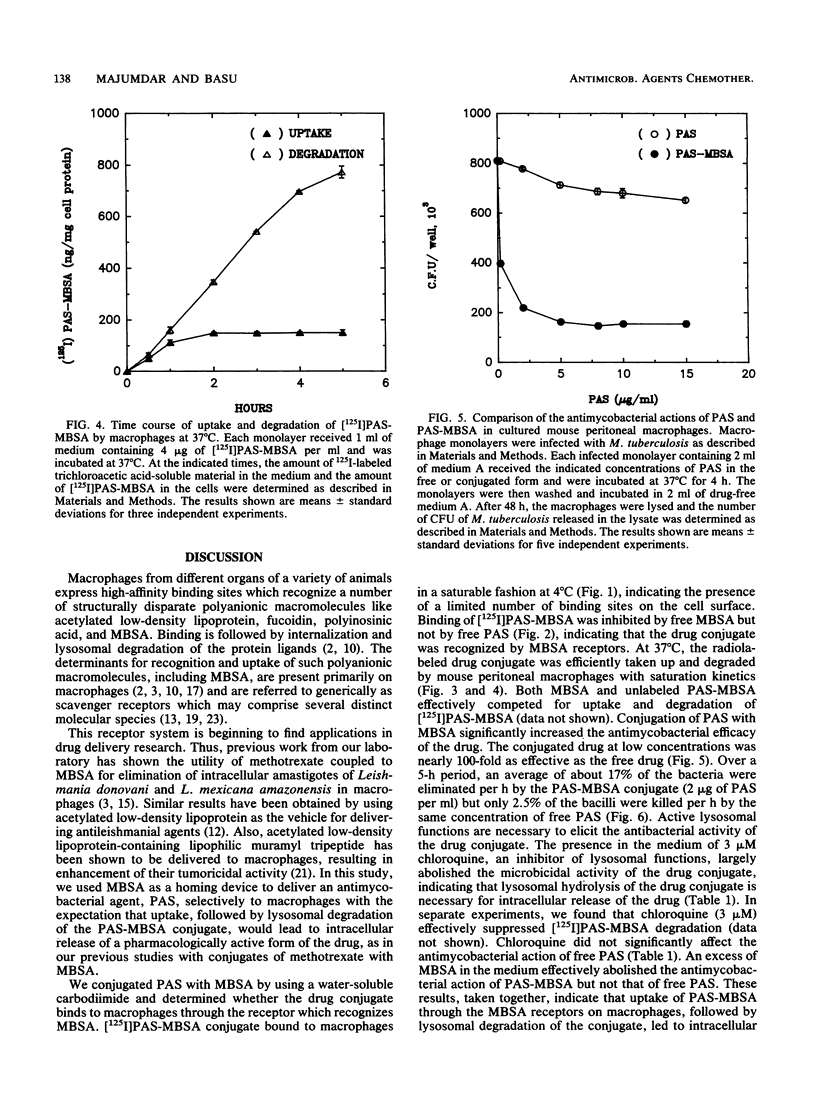
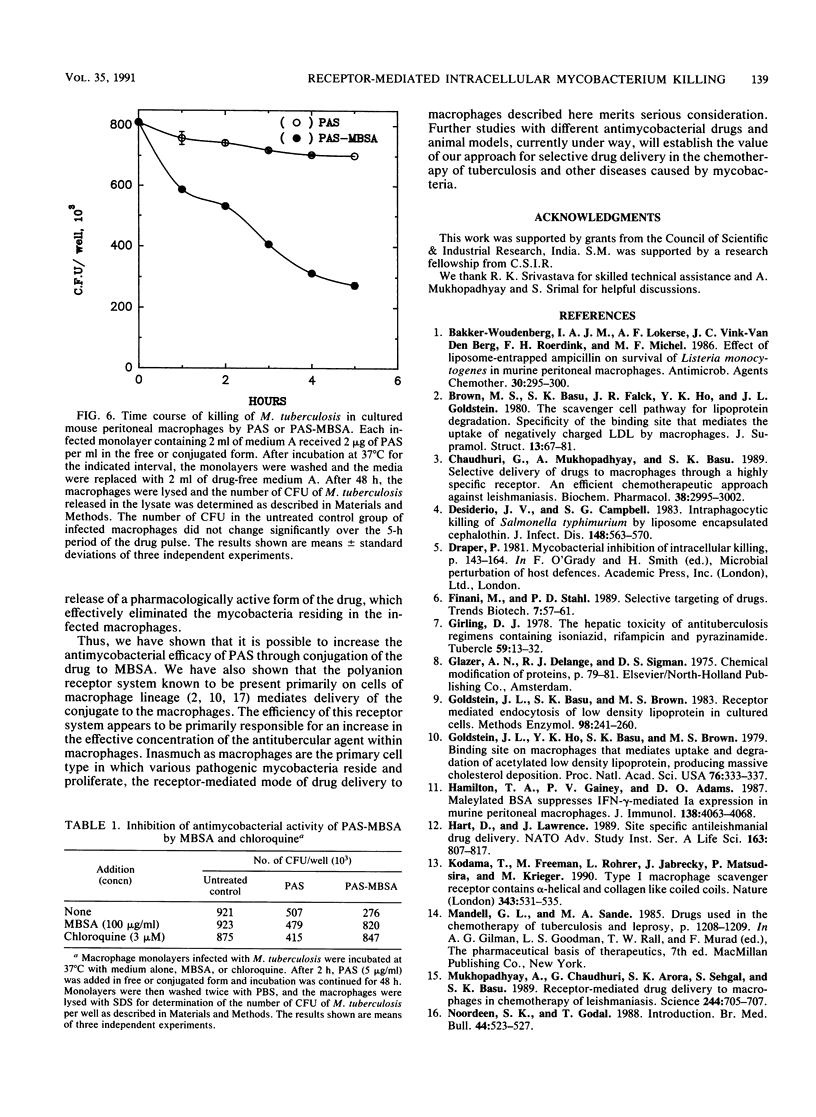
p-Aminosalicylic acid (PAS) conjugated to maleylated bovine serum albumin (MBSA) was taken up efficiently through high-affinity MBSA-binding sites on macrophages. Binding of the radiolabeled conjugate to cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages at 4 degrees C was competed for by MBSA but not by PAS. At 37 degrees C, the radiolabeled conjugate was rapidly degraded by the macrophages, leading to release of acid-soluble degradation products in the medium. The drug conjugate was nearly 100 times as effective as free PAS in killing the intracellular mycobacteria in mouse peritoneal macrophages infected in culture with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The killing of intracellular mycobacteria mediated by the drug conjugate was effectively prevented by simultaneous addition of excess MBSA (100 micrograms/ml) or chloroquine (3 microM) to the medium, whereas these agents did not affect the microbicidal action of free PAS. These results suggest that (i) uptake of the PAS-MBSA conjugate was mediated by cell surface receptors on macrophages which recognize MBSA and (ii) lysosomal hydrolysis of the internalized conjugate resulted in intracellular release of a pharmacologically active form of the drug, which led to selective killing of the M. tuberculosis harbored by mouse macrophages infected in culture. This receptor-mediated modality of delivering drugs to macrophages could contribute to greater therapeutic efficacy and minimization of toxic side effects in the management of tuberculosis and other intracellular mycobacterial infections.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., Lokerse A. F., Vink-van den Berg J. C., Roerdink F. H., Michel M. F. Effect of liposome-entrapped ampicillin on survival of Listeria monocytogenes in murine peritoneal macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):295–300. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Falck J. R., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The scavenger cell pathway for lipoprotein degradation: specificity of the binding site that mediates the uptake of negatively-charged LDL by macrophages. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):67–81. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri G., Mukhopadhyay A., Basu S. K. Selective delivery of drugs to macrophages through a highly specific receptor. An efficient chemotherapeutic approach against leishmaniasis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 15;38(18):2995–3002. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio J. V., Campbell S. G. Intraphagocytic killing of Salmonella typhimurium by liposome-encapsulated cephalothin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):563–570. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling D. J. The hepatic toxicity of antituberculosis regimens containing isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide. Tubercle. 1978 Mar;59(1):13–32. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(77)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Gainey P. V., Adams D. O. Maleylated-BSA suppresses IFN-gamma-mediated Ia expression in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4063–4068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Freeman M., Rohrer L., Zabrecky J., Matsudaira P., Krieger M. Type I macrophage scavenger receptor contains alpha-helical and collagen-like coiled coils. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):531–535. doi: 10.1038/343531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay A., Chaudhuri G., Arora S. K., Sehgal S., Basu S. K. Receptor-mediated drug delivery to macrophages in chemotherapy of leishmaniasis. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.2717947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Boyles J., Mahley R. W., Bissell D. M. Uptake of chemically modified low density lipoproteins in vivo is mediated by specific endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):103–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer L., Freeman M., Kodama T., Penman M., Krieger M. Coiled-coil fibrous domains mediate ligand binding by macrophage scavenger receptor type II. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):570–572. doi: 10.1038/343570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Tomioka H. Therapeutic efficacy of liposome-entrapped rifampin against Mycobacterium avium complex infection induced in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):429–433. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. M., Futch W. S., Jr, Schook L. B. Induction of macrophage antitumor activity by acetylated low density lipoprotein containing lipophilic muramyl tripeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata K., Horiuchi S., Morino Y. Scavenger receptor-mediated recognition of maleylated albumin and its relation to subsequent endocytic degradation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 18;984(3):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuberculosis and leprosy. Br Med Bull. 1988 Jul;44(3):523–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierski M., Bek E. Side-effects of drug regimens used in short-course chemotherapy for pulmonary tuberculosis. A controlled clinical study. Tubercle. 1980 Mar;61(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(80)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


