Abstract
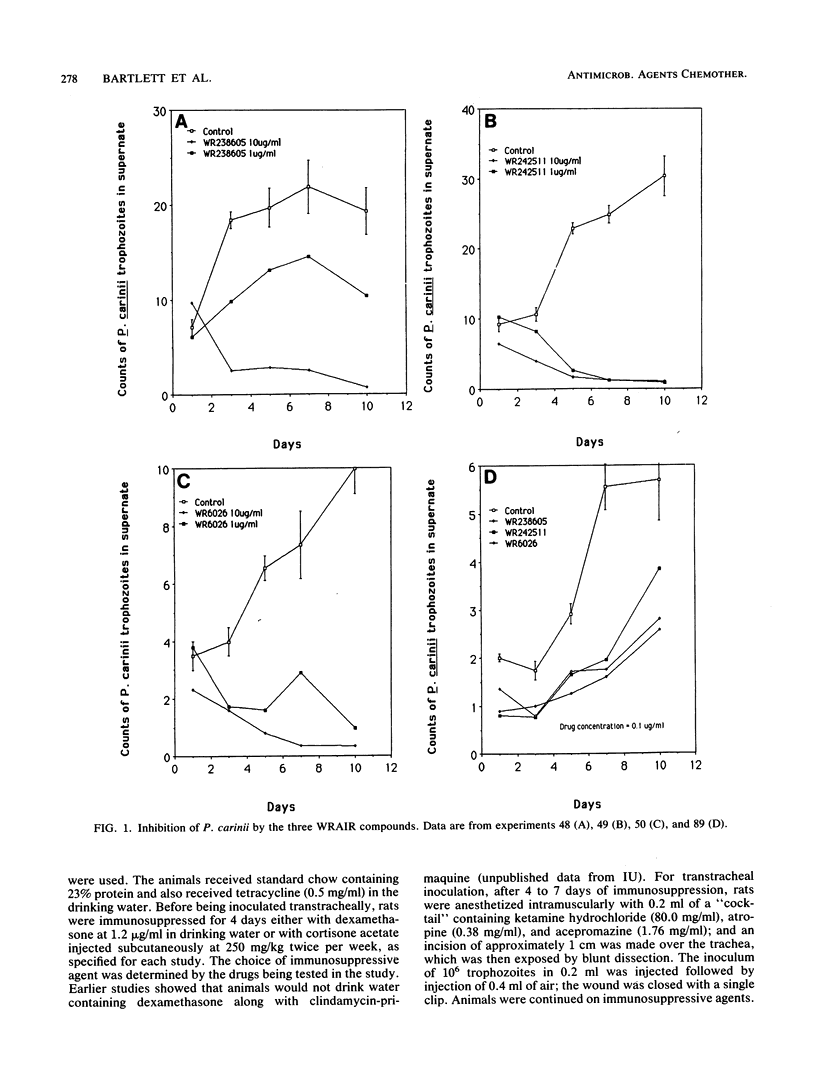
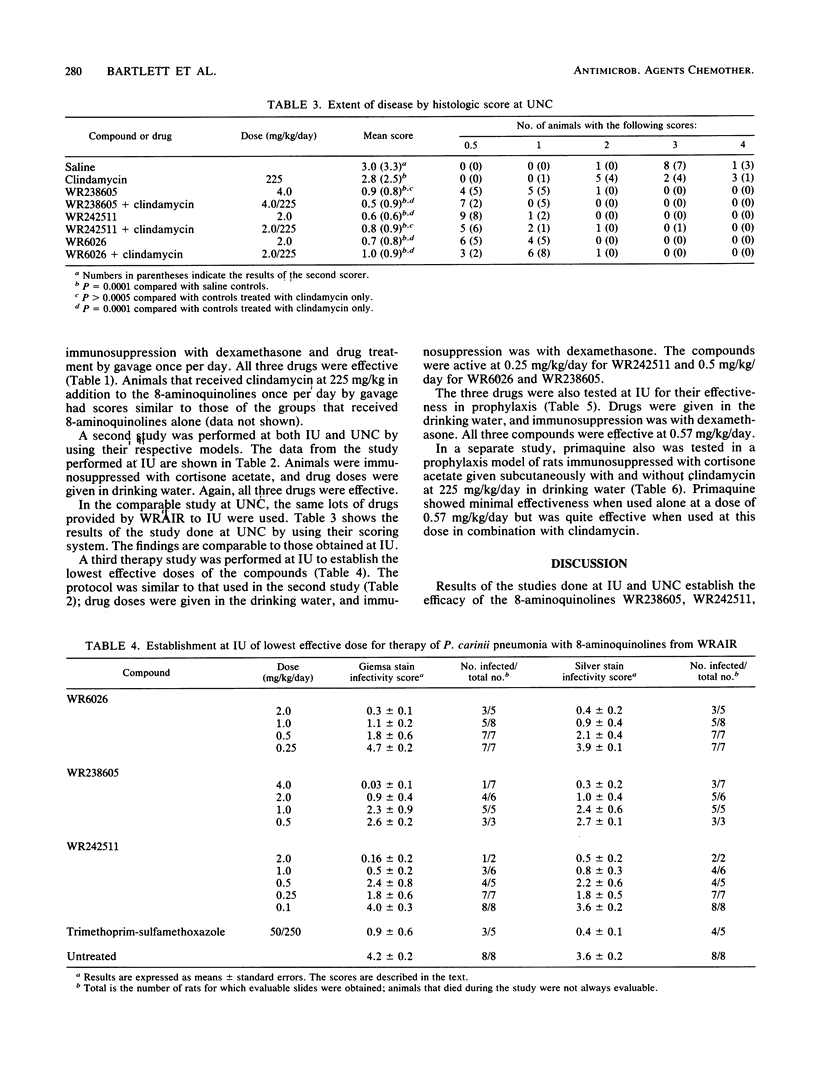
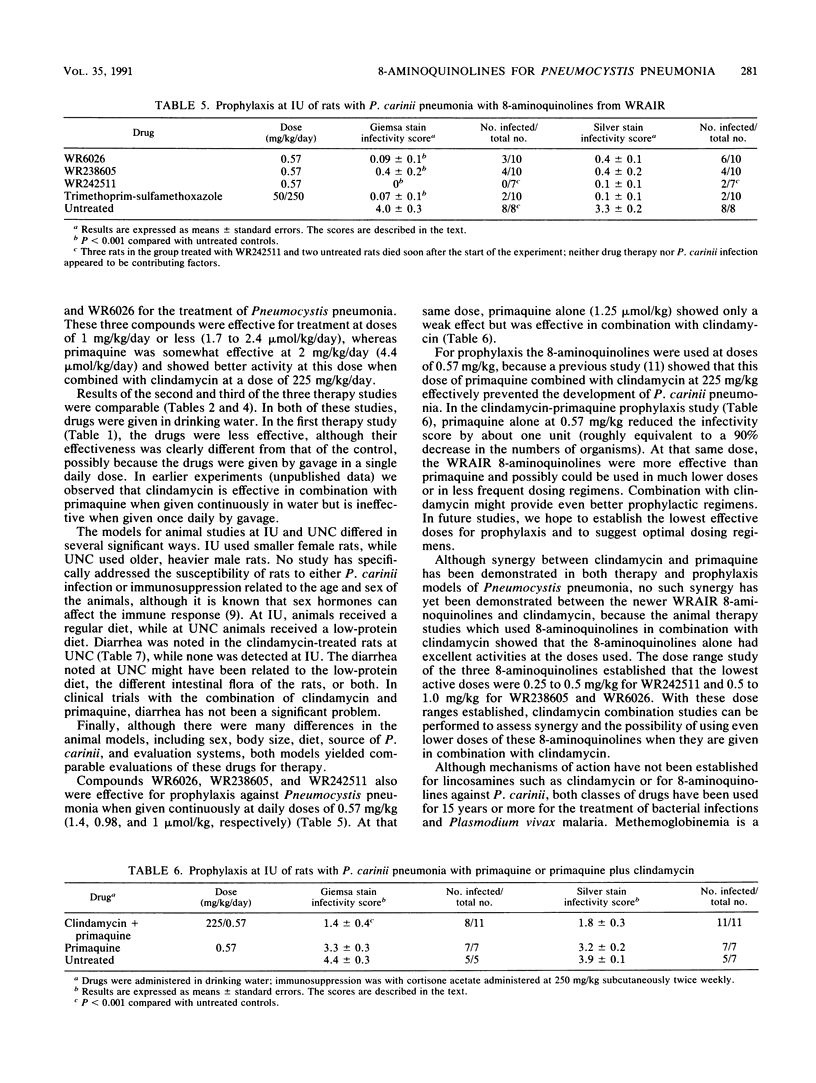
Three 8-aminoquinolines from the Walter Reed Army Institute for Research (WRAIR), WR6026, WR238605, and WR242511, strongly inhibited Pneumocystis carinii growth in vitro at 1 microgram/ml. This activity was similar to that of primaquine. In rat therapy models, the WRAIR compounds affected Pneumocystis pneumonia at doses as low as 0.25 mg/kg (WR242511) or 0.5 mg/kg (WR6026 and WR238605). At these doses, primaquine alone was ineffective as therapy. In a rat prophylaxis model, all three WRAIR 8-aminoquinolines were extremely effective at daily doses of 0.57 mg/kg, showing activity greater than that of primaquine at this dosage and comparable to that of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole at 50/250 mg/kg.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett M. S., Fishman J. A., Durkin M. M., Queener S. F., Smith J. W. Pneumocystis carinii: improved models to study efficacy of drugs for treatment or prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in the rat (Rattus spp.). Exp Parasitol. 1990 Jan;70(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90089-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Verbanac P. A., Smith J. W. Cultivation of Pneumocystis carinii with WI-38 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):796–799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.796-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. E. Sporontocidal activity of the antimalarial WR-238605 against Plasmodium berghei ANKA in Anopheles stephensi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Mar;42(3):196–205. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. R., Pappas M. G., Hansen B. D. Fluorogenic substrate detection of viable intracellular and extracellular pathogenic protozoa. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):435–438. doi: 10.1126/science.2578226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R., DuBois R. E. Clindamycin/primaquine therapy and secondary prophylaxis against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with AIDS. South Med J. 1990 Apr;83(4):403–404. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199004000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Allegra C. J., Kennedy S., Swan J. C., Drake J., Parrillo J. E., Chabner B., Masur H. Efficacy of trimetrexate, a potent lipid-soluble antifolate, in the treatment of rodent Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Nov;39(5):491–496. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. J., Butler L. D., Petersen B. H. Estradiol-induced alteration in the immune system. II. Suppression of cellular immunity in the rat is not the result of direct estrogenic action. Immunopharmacology. 1986 Feb;11(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(86)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Bartlett M. S., Jay M. A., Durkin M. M., Smith J. W. Activity of lipid-soluble inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase against Pneumocystis carinii in culture and in a rat model of infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1323–1327. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Bartlett M. S., Richardson J. D., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. Activity of clindamycin with primaquine against Pneumocystis carinii in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf B., Pohle H. D. Clindamycin/primaquine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):626–627. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90755-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma E., Fournier S., Poisson M., Morisset R., Phaneuf D., Vega C. Clindamycin with primaquine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1989 May 13;1(8646):1046–1048. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


